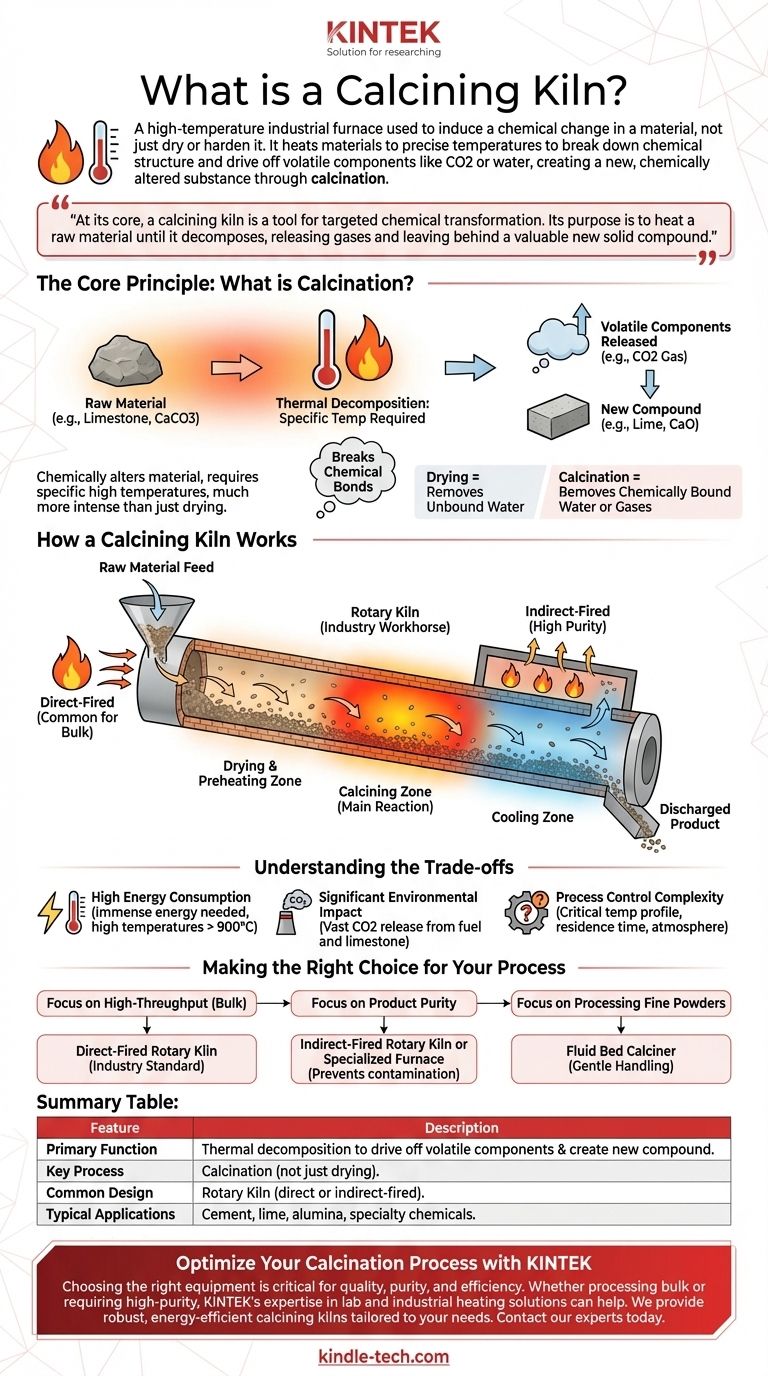
In simple terms, a calcining kiln is a high-temperature industrial furnace used to induce a chemical change in a material, not just to dry or harden it. Unlike a simple pottery kiln that fires clay into a ceramic, a calcining kiln heats materials to a precise temperature to break down their chemical structure and drive off volatile components like carbon dioxide or water. This process, known as calcination, creates a new, chemically altered substance.
At its core, a calcining kiln is a tool for targeted chemical transformation. Its purpose is to heat a raw material until it decomposes, releasing gases and leaving behind a valuable new solid compound like lime or alumina.

The Core Principle: What is Calcination?
Calcination is a specific type of thermal decomposition, a process where heat is used to break the chemical bonds within a compound. It is a fundamental process in many heavy industries.
From Raw Material to New Compound
The goal of calcination is to change the chemical makeup of the input material. For example, limestone (calcium carbonate) is heated to produce lime (calcium oxide). The original material is fundamentally altered.
The Critical Role of Temperature
Calcination isn't just about getting something hot; it's about reaching and maintaining a specific decomposition temperature. Below this temperature, the reaction won't occur. Above it, you risk wasting energy or causing unwanted side reactions or melting.
It's Not Just Drying
Drying is the removal of unbound water from a material. Calcination is a much more intense process that removes chemically bound water (water of hydration) or gases like carbon dioxide (CO2) that are part of the material's molecular structure.
How a Calcining Kiln Works
While many designs exist, the vast majority of industrial calcination happens in a specific type of furnace designed for continuous processing and high throughput.
The Rotary Kiln: An Industry Workhorse
The most common design is the rotary kiln. This is a massive, slowly rotating steel cylinder lined with refractory brick. The cylinder is mounted at a slight incline.
Raw material is fed into the higher end, and as the kiln rotates, the material tumbles and flows down toward the lower end. This tumbling action ensures the material is heated evenly.
Direct vs. Indirect Firing
There are two primary ways to heat the material:
- Direct-fired kilns pass hot combustion gases directly over and through the material. This is efficient and common for bulk materials like limestone.
- Indirect-fired kilns heat the material through the wall of a sealed chamber. The material never touches the flame or exhaust gas, which is critical for high-purity applications where contamination is a concern.
Key Zones Inside the Kiln
A large rotary kiln operates with distinct temperature zones. Material moving through the kiln first passes through a drying and preheating zone, then enters the central calcining zone where the main reaction occurs, and finally a cooling zone before being discharged.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Calcining kilns are powerful tools, but they come with significant operational challenges that define their use and impact.
High Energy Consumption
Heating tons of material to temperatures often exceeding 900°C (1650°F) requires an immense amount of energy. This makes energy costs a primary operational expense and a major focus for efficiency improvements.
Significant Environmental Impact
The calcination of carbonates, especially in cement production, releases vast quantities of CO2. This comes from both the fuel burned to heat the kiln and the CO2 released from the limestone itself, making it a major source of industrial greenhouse gas emissions.
Process Control Complexity
Maintaining the correct temperature profile, material residence time, and kiln atmosphere is critical for product quality. Any deviation can lead to incomplete calcination or over-burnt material, resulting in waste and lost revenue.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The design and operation of a calcining kiln are dictated entirely by the material being processed and the desired final product.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production of bulk materials like cement or lime: A large, direct-fired rotary kiln is the industry standard for its efficiency and scale.
- If your primary focus is product purity for catalysts or specialty chemicals: An indirectly fired rotary kiln or a more specialized furnace is necessary to prevent contamination from combustion gases.
- If your primary focus is processing fine powders or materials that require gentle handling: A fluid bed calciner, which suspends the material in a flow of hot gas, may be a more suitable choice than a rotary kiln.
Ultimately, a calcining kiln is a precise instrument for converting raw minerals and chemicals into the foundational products that build our modern world.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Thermal decomposition to drive off volatile components (e.g., CO2) and create a new chemical compound. |
| Key Process | Calcination (not just drying). |
| Common Design | Rotary Kiln (direct or indirect-fired). |
| Typical Applications | Cement, lime, alumina, and specialty chemicals production. |
Optimize Your Calcination Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right calcining equipment is critical for your product's quality, purity, and operational efficiency. Whether you are processing bulk materials like limestone or require high-purity conditions for specialty chemicals, KINTEK's expertise in lab and industrial heating solutions can help.
We provide robust, energy-efficient calcining kilns tailored to your specific material and throughput needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your thermal processing challenges and help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to regenerate activated carbon? Master the 3-Stage Thermal Process for Cost Savings
- What temperature is needed for porcelain? A Guide to Cone 6 and Cone 10 Firing
- What is the temperature of a carbon regeneration kiln? Mastering the 750-800°C Reactivation Process
- How do you carbonize charcoal? Master the 3-Step Pyrolysis Process for High-Purity Carbon
- Can you restore activated carbon? Understanding the Industrial Reactivation Process



















