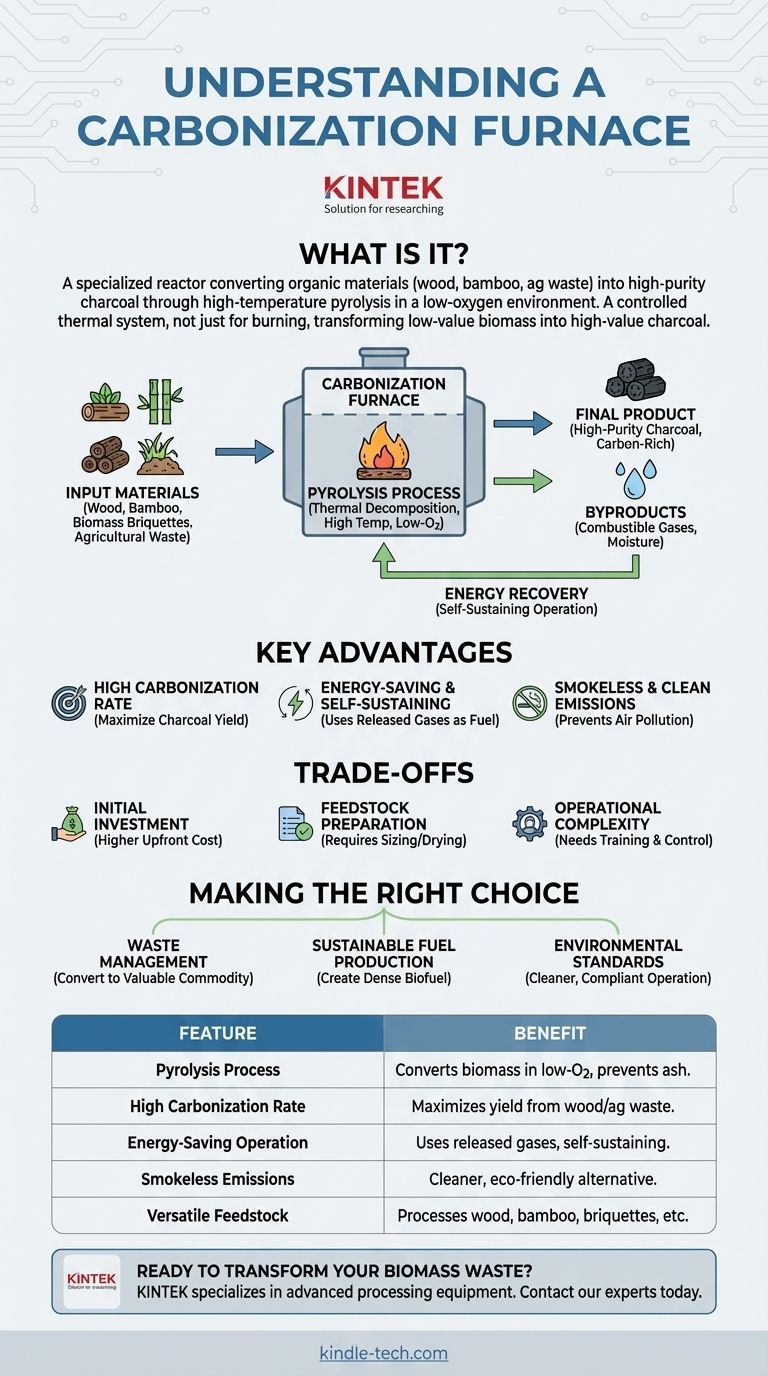
In essence, a carbonization furnace is a specialized reactor designed to convert organic materials like wood, bamboo, and agricultural waste into high-purity charcoal. It accomplishes this through a high-temperature process in a low-oxygen environment, ensuring the material doesn't simply burn into ash. The primary goal is to drive off water and volatile compounds, leaving behind a stable, carbon-rich product.
A carbonization furnace isn't simply for burning material; it's a controlled thermal system that transforms low-value biomass into high-value charcoal, offering an energy-efficient and environmentally cleaner conversion process.

How a Carbonization Furnace Works
The Core Principle: Pyrolysis
A carbonization furnace operates on the principle of pyrolysis. This is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an inert or low-oxygen atmosphere.
Unlike combustion (burning), which requires ample oxygen and produces mostly ash and heat, pyrolysis breaks down the material's chemical structure, releasing combustible gases and leaving behind a solid residue called charcoal.
Common Input Materials
The furnace is versatile and designed to process a wide range of biomass. This feedstock is the raw organic material that will be converted.
Common inputs include wood and forestry residues like pine or willow branches, as well as manufactured biomass briquettes. These briquettes are often made from compressed agricultural waste such as sawdust, crop straws, rice husks, or bamboo shavings.
The Final Product
The process systematically removes moisture and volatile organic compounds (like methane and wood gas) from the feedstock.
The result is charcoal, a lightweight, black, porous material consisting of almost pure carbon. This final product is significantly more energy-dense and burns cleaner than the original raw biomass.
Key Operational Advantages
High Carbonization Rate
Modern furnaces are engineered for efficiency. A high carbonization rate means that a large percentage of the input biomass is successfully converted into charcoal, minimizing waste and maximizing yield.
Energy-Saving and Self-Sustaining Operation
Many designs are highly energy-efficient. The combustible gases released during pyrolysis are often captured and redirected back to the furnace's combustion chamber to serve as fuel.
This self-sustaining loop dramatically reduces or even eliminates the need for external energy sources once the process reaches its operational temperature.
Smokeless and Cleaner Emissions
Traditional charcoal production is notoriously smoky and polluting. A carbonization furnace contains the process, preventing the release of smoke.
The captured gases that would have become smoke are either used as fuel or passed through a purification system, leading to a much cleaner, often smokeless, operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Initial Investment
This is specialized industrial equipment. The upfront cost for a modern, efficient carbonization furnace is significantly higher than for traditional, rudimentary methods like earth-mound kilns.
Feedstock Preparation
For optimal performance, raw materials often require preparation. This can include chopping wood to a uniform size or drying the biomass to a specific moisture content, adding a step to the production workflow.
Operational Complexity
While modern systems are designed for ease of use, they are still industrial machines. Achieving consistent, high-quality output requires proper training and a clear understanding of process parameters like temperature and airflow.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the value of a carbonization furnace depends on your objective.
- If your primary focus is waste management: This technology provides an excellent method for converting agricultural or forestry waste streams into a valuable and storable commodity.
- If your primary focus is sustainable fuel production: The furnace creates a dense, stable biofuel (charcoal) from renewable biomass sources, serving as a superior alternative to raw wood.
- If your primary focus is environmental standards: The controlled, smokeless operation of a furnace is an essential upgrade over polluting traditional methods, ensuring compliance and reducing local air pollution.
A carbonization furnace provides a controlled and efficient pathway to unlock the energy and value hidden within organic materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Pyrolysis Process | Converts biomass to charcoal in a low-oxygen environment, preventing ash formation. |
| High Carbonization Rate | Maximizes charcoal yield from input materials like wood and agricultural waste. |
| Energy-Saving Operation | Uses released combustible gases as fuel, creating a self-sustaining system. |
| Smokeless Emissions | Provides a cleaner, environmentally friendly alternative to traditional methods. |
| Versatile Feedstock | Processes wood, bamboo, rice husks, and other biomass briquettes. |
Ready to transform your biomass waste into a valuable resource?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory and processing equipment, including carbonization furnaces designed for efficiency and environmental compliance. Whether your goal is sustainable fuel production, waste management, or cleaner operations, our solutions are tailored to meet your specific laboratory and production needs.
Contact our experts today to discover how a KINTEK carbonization furnace can enhance your process and deliver a strong return on investment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions



















