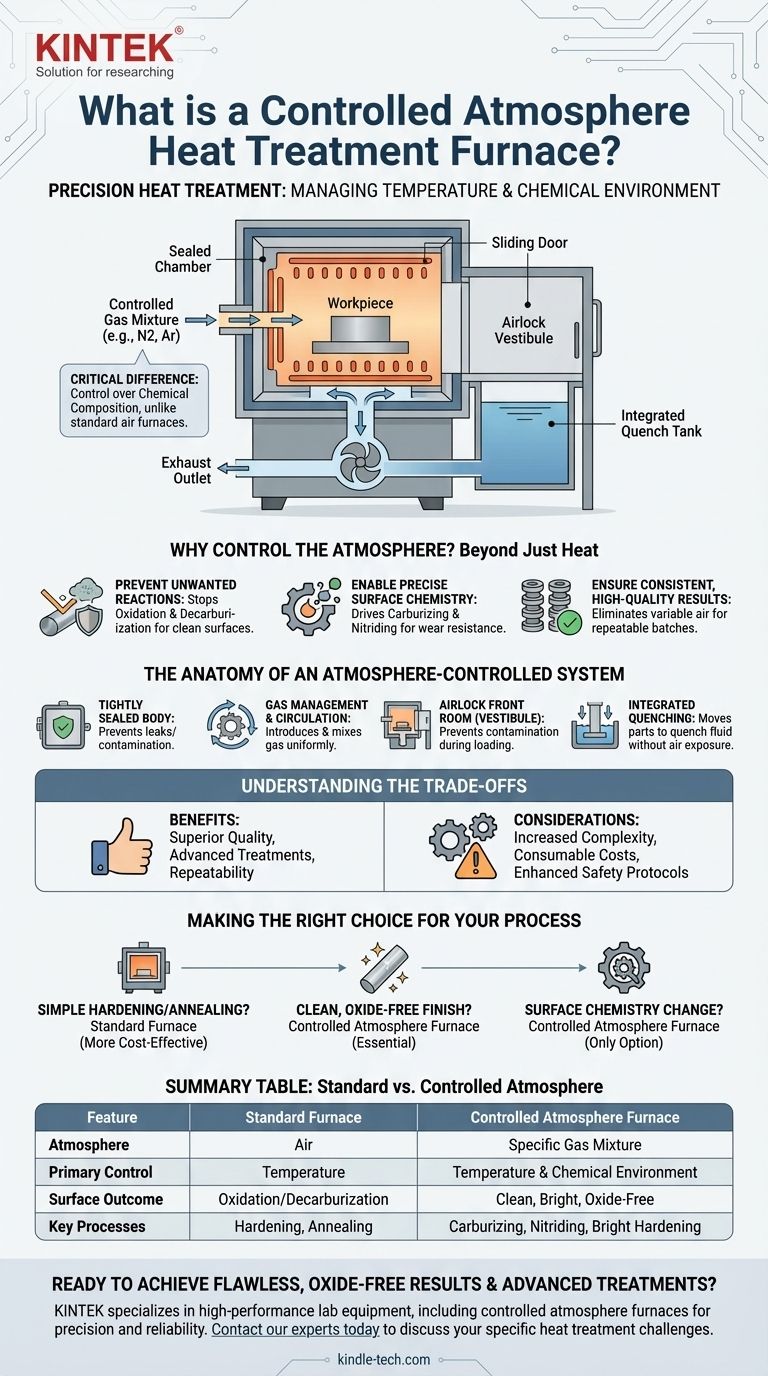
At its core, a controlled atmosphere heat treatment furnace is a system that precisely manages the chemical composition of the gas surrounding a material during heating and cooling. Unlike a standard furnace that only controls temperature, this specialized equipment also regulates the internal atmosphere to prevent unwanted reactions like oxidation and to intentionally alter the surface properties of the workpiece.
The critical difference is control over the chemical environment. A standard furnace operates in air, which can damage a material's surface at high temperatures. A controlled atmosphere furnace replaces the air with a specific gas mixture, protecting the material and enabling advanced surface modification treatments.
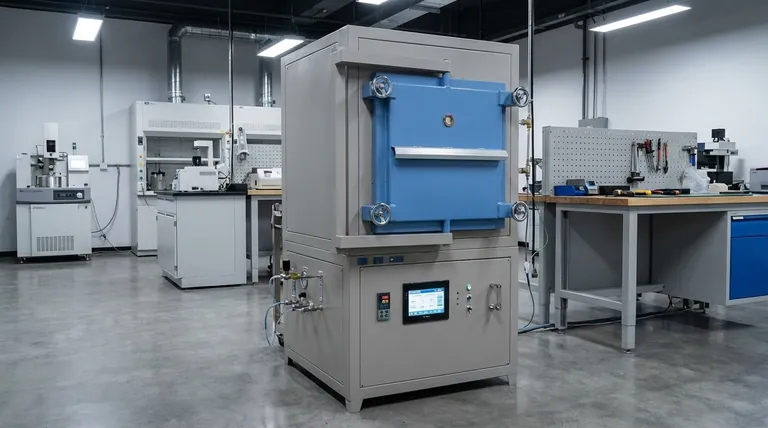

Why Control the Atmosphere? Beyond Just Heat
Controlling the furnace environment is fundamental to achieving specific metallurgical outcomes that are impossible in open-air heating. This control moves beyond simple temperature regulation to actively manage surface chemistry.
Preventing Unwanted Reactions
At high temperatures, metals readily react with oxygen in the air, forming a layer of scale or oxide. This is often undesirable as it can ruin the surface finish and dimensional accuracy of a part.
Similarly, the carbon content in steel can be depleted from the surface in a reaction known as decarburization, which softens the material. A controlled atmosphere prevents both oxidation and decarburization.
Enabling Precise Surface Chemistry
Beyond just preventing reactions, these furnaces can introduce specific elements into a material's surface.
By creating an atmosphere rich in a specific chemical, you can drive reactions like carburizing (adding carbon) or nitriding (adding nitrogen). These processes are used to create a hard, wear-resistant surface layer on a component while maintaining a tougher core.
Ensuring Consistent, High-Quality Results
By eliminating the variable of ambient air, a controlled atmosphere ensures that every part processed sees the exact same thermal and chemical conditions. This leads to significantly improved product quality, higher qualification rates, and repeatable results batch after batch.
The Anatomy of an Atmosphere-Controlled System
The design of a controlled atmosphere furnace is similar to a standard furnace but includes several critical components dedicated to managing the internal environment.
A Tightly Sealed Furnace Body
The foundation of atmospheric control is an exceptionally well-sealed furnace chamber. This prevents the controlled gas from leaking out and, more importantly, prevents air from leaking in and contaminating the process.
Gas Management and Circulation
A dedicated system introduces the desired gas mixture (e.g., nitrogen, argon, endothermic gas) and purges the initial air. A sealed, water-cooled fan circulates this gas to ensure uniform temperature and chemical composition throughout the furnace.
The "Airlock" Front Room
A key feature is a front room, or vestibule, that acts as an airlock. Workpieces enter this chamber first, which is then purged of air and filled with the protective atmosphere before the inner door to the main heating chamber opens. This prevents contamination of the entire furnace when loading or unloading parts.
Integrated Quenching and Handling
Many systems include integrated, sealed quenching tanks. This allows a part to be moved from the heating chamber directly into the quenching fluid (like oil) without ever being exposed to outside air, ensuring a clean, oxide-free finish.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are significant, adopting this technology involves important considerations that differ from standard furnace operations.
Increased System Complexity
The addition of gas control panels, seals, safety interlocks, and circulation systems makes these furnaces mechanically more complex than their open-air counterparts. This requires more sophisticated operational knowledge and maintenance.
Consumable and Operational Costs
The protective gases used in the furnace are a continuous operational cost. Furthermore, maintaining the integrity of all seals and safety systems is critical and adds to the maintenance budget.
Enhanced Safety Protocols
Many process gases can be flammable or present other hazards. Therefore, these furnaces require mandatory safety and explosion-proof devices, along with strict operational protocols to ensure a safe working environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use a controlled atmosphere furnace depends entirely on the required properties of the finished product.
- If your primary focus is simple hardening or annealing where surface oxidation is acceptable or can be removed later: A standard, non-controlled furnace is often sufficient and more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is a clean, bright finish with no surface oxidation or decarburization: A controlled atmosphere furnace is absolutely essential to protect the material's integrity.
- If your primary focus is to intentionally change the surface chemistry of a part (e.g., case hardening via carburizing): A controlled atmosphere furnace is the only technology capable of performing this task.
Ultimately, choosing a controlled atmosphere furnace is a decision to invest in precise process control to achieve superior material quality and consistency.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Furnace | Controlled Atmosphere Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Air | Specific Gas Mixture (e.g., Nitrogen, Argon) |
| Primary Control | Temperature | Temperature & Chemical Environment |
| Surface Outcome | Oxidation/Decarburization | Clean, Bright, Oxide-Free |
| Key Processes | Hardening, Annealing | Carburizing, Nitriding, Bright Hardening |
Ready to achieve flawless, oxide-free results and advanced surface treatments?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including controlled atmosphere heat treatment furnaces designed for precision and reliability. Our systems are engineered to protect your materials and enable advanced processes like carburizing and nitriding, ensuring consistent, high-quality outcomes for your laboratory.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK furnace can solve your specific heat treatment challenges and enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using an atmosphere-controlled heating furnace for Cu reduction? Achieve Active Catalytic States
- How does an atmosphere furnace facilitate the post-treatment of nickel-plated carbon fibers? Ensure Peak Bonding
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes



















