At its core, a crucible furnace is a high-temperature oven used to melt materials without direct contact from the heat source. Its primary function is to heat a separate container—the crucible—which holds the material to be melted, most commonly non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, bronze, gold, and silver.
A crucible furnace is best understood as a versatile tool for small-batch melting where material purity and flexibility are the highest priorities. It excels in applications ranging from artisan metal casting to precise laboratory analysis, but it is not designed for large-scale industrial production.
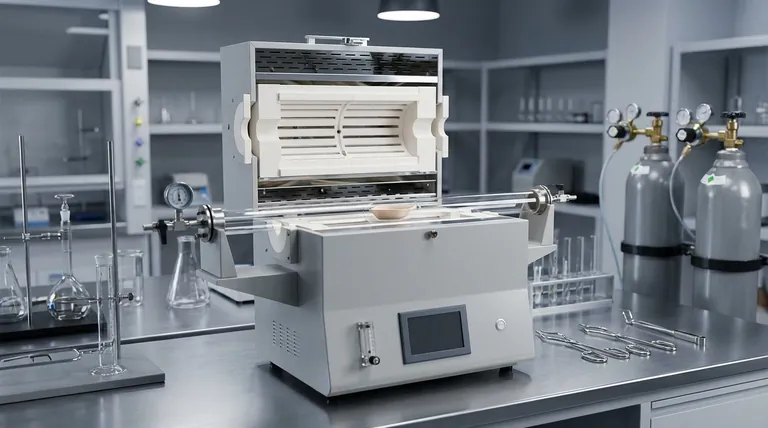

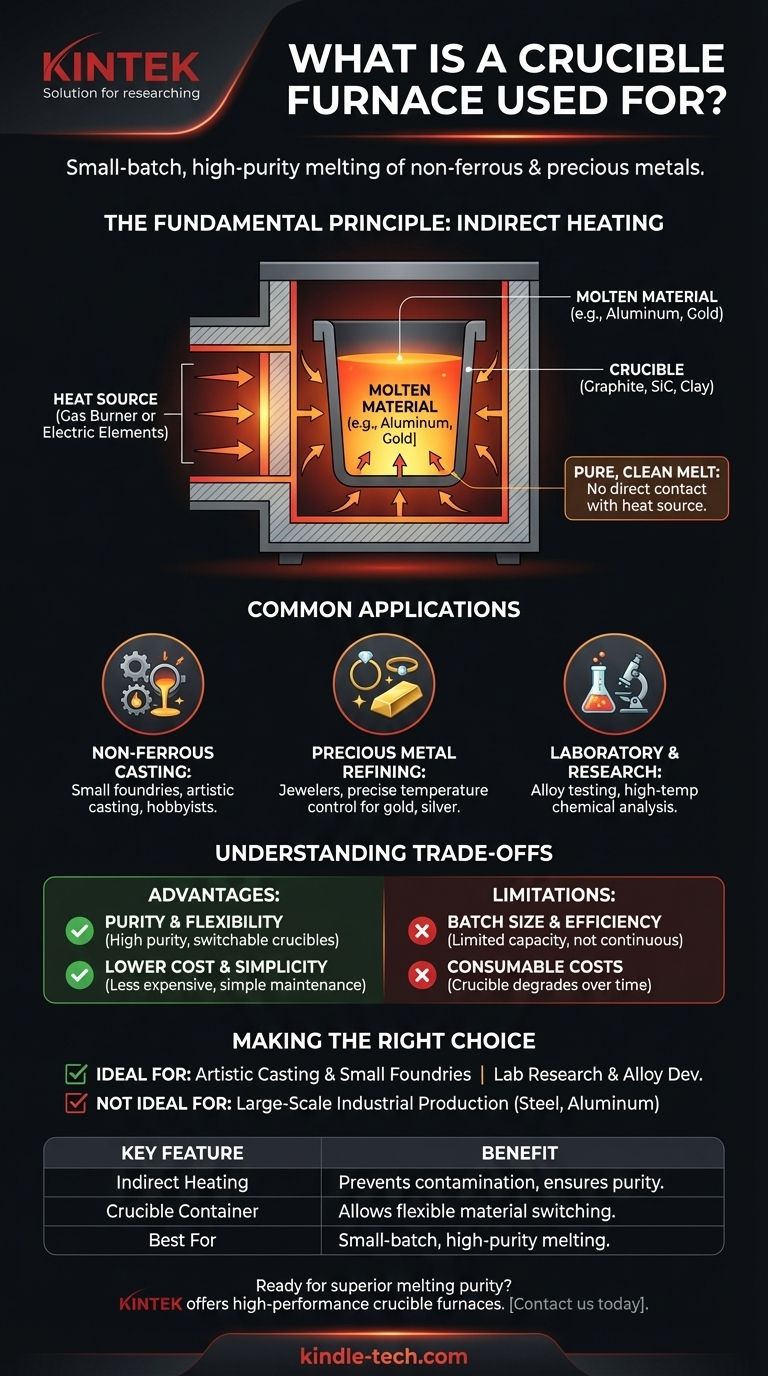
The Fundamental Principle: Indirect Heating
The defining characteristic of this furnace is its method of heating. Unlike other furnaces that might apply a flame or electric arc directly to the material, a crucible furnace heats the container, which then transfers that heat to its contents.
What is a Crucible?
The crucible is simply a high-temperature-resistant pot. It is typically made from materials like graphite, silicon carbide, or ceramic clay that can withstand extreme thermal shock without breaking or reacting with the molten metal inside.
The Role of the Furnace
The furnace itself is an insulated chamber designed to generate and contain intense heat. It acts like a high-performance oven for the crucible. The heat source can be a powerful gas burner (propane or natural gas), electric resistance elements, or even solid fuel like coke in more traditional designs.
Why Indirect Heating Matters
This separation between the heat source and the material is critical. It prevents contamination from the products of combustion (in a gas furnace) or the heating elements themselves. This ensures the chemical purity of the final molten material, which is essential for creating specific alloys or high-quality castings.
Common Applications and Materials
The versatility and simplicity of the crucible furnace make it a staple in many fields, from small workshops to advanced research labs.
Non-Ferrous Metal Casting
This is the most common application. Small foundries, artists creating bronze sculptures, and hobbyists casting aluminum parts all rely on crucible furnaces. Their ability to melt relatively small, clean batches of metal is perfect for these tasks.
Precious Metal Refining
Jewelers and precious metal refiners use smaller, often electric, crucible furnaces to melt gold, silver, and platinum. The precise temperature control and purity offered by this method are non-negotiable when working with such valuable materials.
Laboratory and Research
In materials science, crucible furnaces are used to create and test new alloys, melt glass formulations, or perform high-temperature chemical analyses. The ability to switch out crucibles allows researchers to work with many different materials without cross-contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single tool is perfect for every job. The crucible furnace's strengths in one area create limitations in another. Understanding these trade-offs is key to knowing when to use one.
Advantage: Purity and Flexibility
Because the material only touches the inert crucible, you achieve a very pure melt. Furthermore, if you want to switch from melting aluminum to bronze, you simply switch crucibles. This flexibility is unmatched by larger, single-purpose furnaces.
Advantage: Lower Cost and Simplicity
Compared to industrial-scale induction or arc furnaces, crucible furnaces are significantly less expensive to purchase and operate. Their design is mechanically simple, making them easier to maintain, especially in smaller workshops.
Limitation: Batch Size and Efficiency
Crucible furnaces are inherently batch-process tools. Their capacity is limited by the size of the crucible, which typically ranges from a few kilograms to a few hundred kilograms at most. They are not efficient for the continuous, high-volume production required for industries like steel manufacturing.
Limitation: Consumable Costs
The crucible itself is a consumable item. Repeated heating and cooling cycles cause thermal stress, and chemical interaction with molten metal eventually causes it to degrade. Crucibles must be inspected regularly and replaced, which represents a recurring operational cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your specific objective, scale, and material requirements.
- If your primary focus is artistic casting, hobbyist metalworking, or running a small foundry: A crucible furnace is almost certainly your best choice for its versatility and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is laboratory research or developing new alloys: The precise control and prevention of contamination make a crucible furnace an indispensable tool.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial production of metals like steel or aluminum: A crucible furnace is inappropriate; you require a much larger induction, reverberatory, or electric arc furnace.
Understanding the purpose and limitations of a crucible furnace is the first step toward mastering any high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Indirect Heating | Prevents contamination, ensuring material purity. |
| Crucible Container | Allows flexible switching between different materials. |
| Common Applications | Jewelry making, lab research, small-scale metal casting. |
| Best For | Small-batch, high-purity melting processes. |
Ready to achieve superior melting purity and flexibility in your lab or workshop?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including crucible furnaces designed for precise, small-batch melting of non-ferrous metals and precious materials. Our solutions ensure the material purity and operational simplicity your work demands.
Contact us today to find the perfect crucible furnace for your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis



















