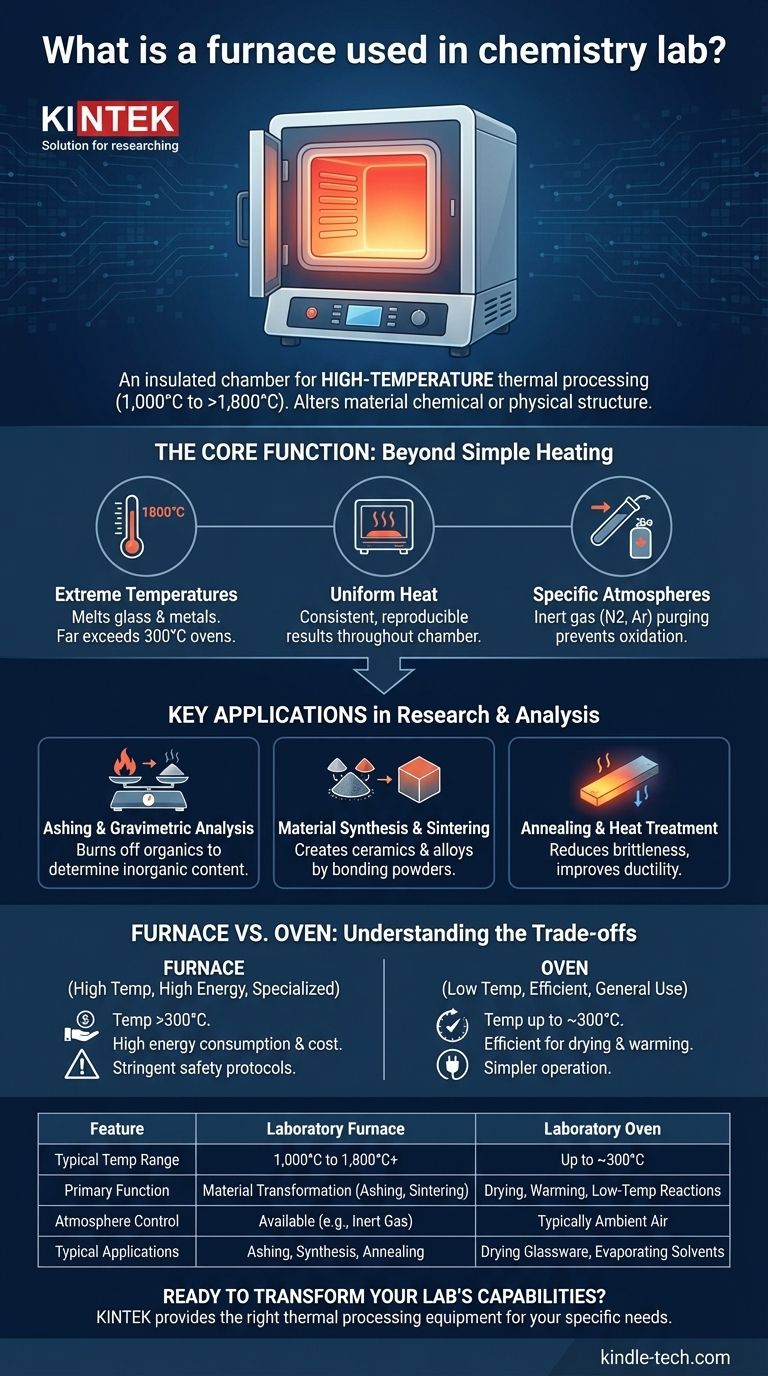
In a chemistry laboratory, a furnace is an insulated chamber designed for high-temperature thermal processing. Unlike a standard lab oven, which typically operates up to 300°C, a furnace can reach temperatures from 1,000°C to over 1,800°C. This capability allows for processes that fundamentally alter a material's chemical or physical structure, such as ashing, heat treatment, or synthesis.
A laboratory furnace should not be seen as just a more powerful oven. It is a precision instrument for controlled, extreme heat treatment, essential for tasks where the goal is to induce a fundamental change in the material itself, not just to dry or warm it.
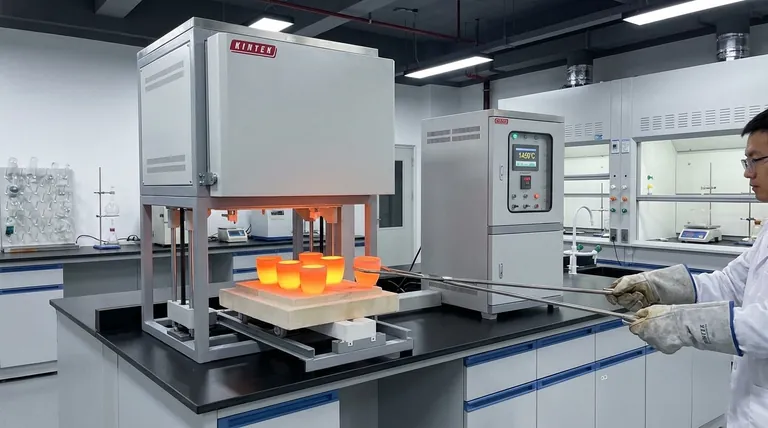

The Core Function: Beyond Simple Heating
The primary role of a laboratory furnace is to provide a tightly controlled, high-temperature environment. This capability is critical for applications that are impossible to perform in standard ovens or with open-flame burners.
Reaching Extreme Temperatures
The defining feature of a furnace is its temperature range. Most lab ovens are limited to around 300°C (approx. 570°F), which is sufficient for drying glassware or removing moisture from samples.
Furnaces, by contrast, start where ovens leave off. They routinely operate at temperatures that can melt glass and metals, enabling a different class of chemical and physical transformations.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
A high-quality furnace provides uniform heat throughout its chamber. This ensures that an entire sample or batch of samples is exposed to the exact same thermal conditions, leading to consistent, reproducible results.
Creating Specific Atmospheres
Many chemical processes at high temperatures are sensitive to oxygen. Advanced furnaces, particularly tube furnaces, allow for the internal atmosphere to be purged and replaced with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, preventing oxidation and unwanted side reactions.
Key Applications in Research and Analysis
Furnaces are not used for everyday tasks but are reserved for specific, high-impact procedures.
Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
One of the most common uses is ashing. A sample is heated to a high temperature (e.g., 500-900°C) to completely burn off all organic matter. The remaining inorganic residue, or ash, can then be weighed to determine the inorganic content of the original sample.
Material Synthesis and Sintering
Furnaces are central to materials science. They are used to create ceramics, alloys, and other advanced materials by heating precursor powders to the point where they bond together, a process known as sintering.
Annealing and Heat Treatment
In metallurgy and glassworking, annealing involves heating a material to a specific temperature and then carefully cooling it. This process can reduce brittleness, remove internal stresses, and improve a material's ductility and toughness.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Furnace vs. Oven
Choosing between a furnace and an oven depends entirely on the required temperature and the nature of the process. Understanding their differences is key to proper lab procedure.
Temperature is the Deciding Factor
The single biggest differentiator is the operating temperature range. If your process requires temperatures above 300°C, a furnace is your only option. For simple drying or low-temperature heating, a furnace is inefficient and unnecessary.
Energy Consumption and Cost
Furnaces require immense amounts of energy to reach and maintain their target temperatures. They are significantly more expensive to purchase and operate than laboratory ovens due to their specialized heating elements and heavy-duty insulation.
Safety and Operational Complexity
Operating a furnace requires more stringent safety protocols. The extreme temperatures pose a significant burn and fire risk. Modern furnaces incorporate sophisticated safety interlocks and self-diagnostic features—such as overheat prevention, sensor error detection, and heater disconnection—to mitigate these dangers and ensure mechanical stability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal processing tool is fundamental to achieving valid scientific results safely and efficiently. Use the specific requirements of your procedure as your guide.
- If your primary focus is drying samples or low-temperature reactions below 300°C: A standard laboratory oven is the more efficient, cost-effective, and appropriate tool.
- If your primary focus is determining inorganic content (ashing) or heat-treating metals: A muffle furnace, which can reliably reach 900-1200°C, is the required instrument.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials or running reactions in an oxygen-free environment: You need a specialized tube furnace that allows for precise atmospheric control.
Ultimately, your choice depends on whether you need to simply heat a sample or fundamentally transform it.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Laboratory Furnace | Laboratory Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Temperature Range | 1,000°C to 1,800°C+ | Up to ~300°C |
| Primary Function | Fundamental material transformation (e.g., ashing, sintering) | Drying, warming, low-temperature reactions |
| Atmosphere Control | Available (e.g., inert gas in tube furnaces) | Typically ambient air |
| Typical Applications | Ashing, gravimetric analysis, material synthesis, annealing | Drying glassware, evaporating solvents, incubation |
Ready to transform your lab's capabilities?
Whether your research requires precise ashing, high-temperature material synthesis, or controlled atmosphere heat treatment, KINTEK's range of laboratory furnaces is engineered for accuracy, safety, and reproducibility.
We specialize in providing the right thermal processing equipment for your specific laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the requisites of refractories? The Four Pillars for High-Temperature Success
- What are the materials used in a muffle furnace? A Guide to Durable Construction & Optimal Performance
- How is heat transferred in a furnace? Master Radiation, Convection & Conduction
- At what temperature is it safe to open a muffle furnace? A Guide to Preventing Injury and Equipment Damage
- What construction features contribute to the practicality and reliability of a muffle furnace? Key Design Elements for Lab Success



















