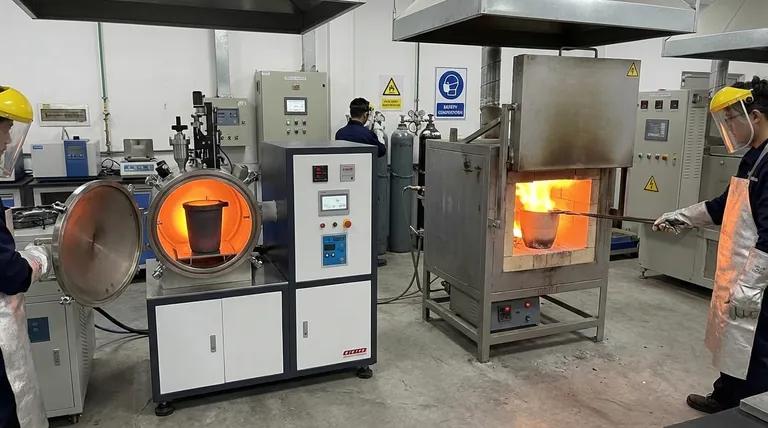
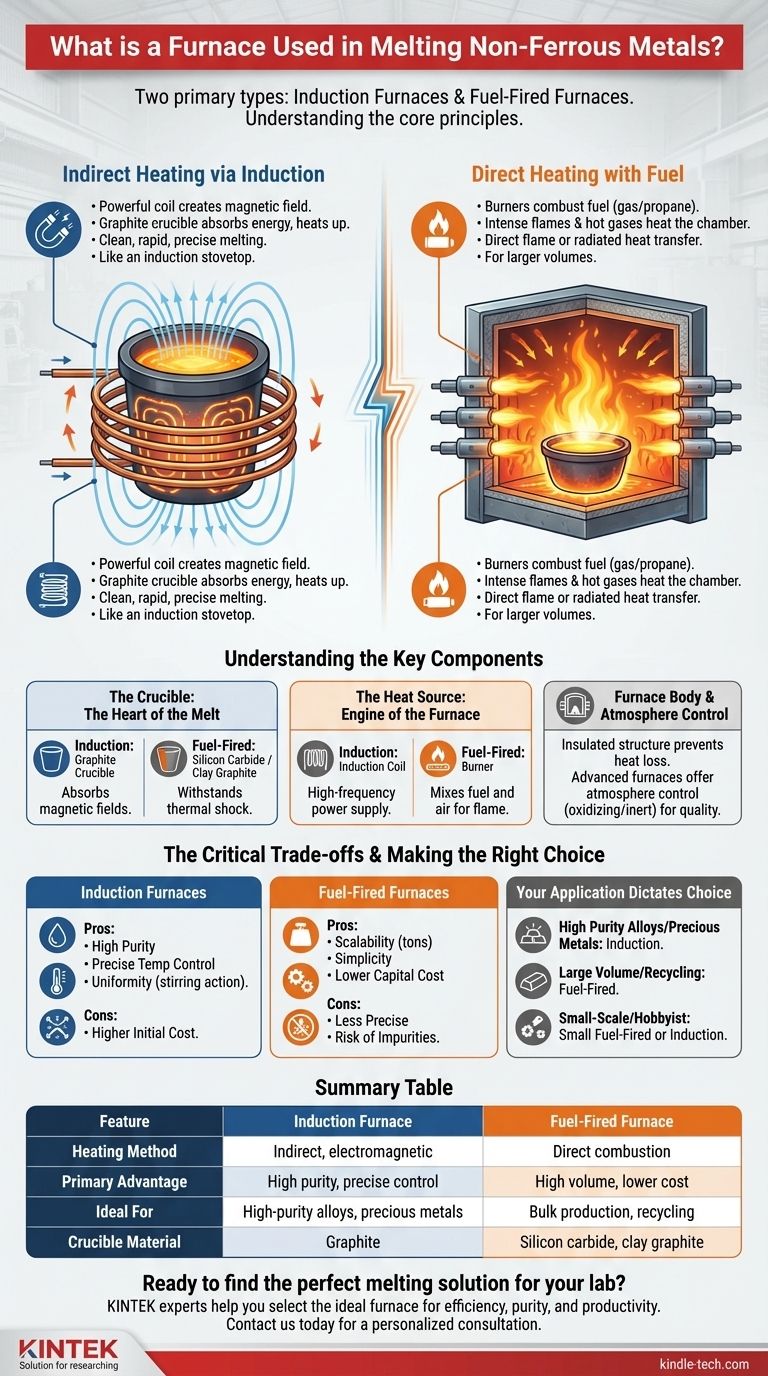
For melting non-ferrous metals, two primary types of furnaces are commonly used: induction furnaces and fuel-fired furnaces. An induction furnace uses a powerful, high-frequency magnetic field to heat a graphite crucible, which in turn melts the metal inside without any direct flame. A fuel-fired furnace works more like a conventional oven, using burners to combust fuel and generate intense heat within a chamber to melt the metal directly.
The fundamental difference lies in how heat is generated and transferred. Induction furnaces use clean, indirect electromagnetic heating for precision, while fuel-fired furnaces use direct combustion for handling larger volumes, with each method offering distinct advantages for different applications.

How Furnaces Melt Metal: Two Core Principles
To understand which furnace is right for a given task, you must first understand the two distinct methods they use to generate extreme heat. The choice between them impacts everything from purity to operational cost.
Indirect Heating via Induction
An induction furnace does not heat the metal directly. Instead, it uses a powerful coil to create a rapidly changing magnetic field.
This magnetic field is absorbed by a graphite crucible, which is a perfect "susceptor" for this energy. This absorption causes the crucible itself to become extremely hot through a process called eddy current heating.
The metal placed inside this superheated crucible then melts quickly and cleanly, much like water boiling in a pot on an induction stovetop.
Direct Heating with Fuel
Fuel-fired furnaces, often called reverberatory or crucible furnaces, take a more straightforward approach. They are essentially superheated ovens.
These furnaces use burners to combust a fuel source, such as natural gas or propane. The intense flame and hot gases produced by this combustion heat the chamber.
The heat is then transferred to the metal charge either directly (by the flame) or indirectly (by radiating off the hot furnace walls), raising its temperature past its melting point.
Understanding the Key Components
While designs vary, all melting furnaces share a few critical components that define their function.
The Crucible: The Heart of the Melt
The crucible is the container that holds the liquid metal. Its material is critical to the success of the melt.
In induction furnaces, the crucible is typically made of graphite because of its unique ability to absorb magnetic fields and convert them into heat.
In fuel-fired furnaces, crucibles are often made from materials like silicon carbide or clay graphite, chosen for their ability to withstand extreme thermal shock from the direct flame.
The Heat Source: Induction Coil vs. Burner
The heat source is the engine of the furnace. An induction coil, powered by a high-frequency power supply, generates the magnetic field required for induction heating.
A burner, on the other hand, is a mechanical device that mixes fuel and air (or oxygen) to create a controlled, high-temperature flame for direct heating.
The Furnace Body & Atmosphere Control
The furnace body is the insulated structure that contains the heat and the crucible. Its primary job is to prevent heat loss and ensure energy is focused on the metal.
Advanced furnaces also allow for atmosphere control. By injecting specific gases, operators can create an environment that is either oxidizing (to burn off impurities) or inert (to prevent the metal from reacting with air), protecting the quality of the final product.
The Critical Trade-offs
Neither furnace type is universally superior. The choice involves a clear set of trade-offs between precision, cost, scale, and cleanliness.
Induction Furnaces: Precision and Purity
The primary advantage of induction is cleanliness. Since there is no combustion, byproducts from a flame cannot contaminate the metal. This results in a higher-purity final product.
Temperature control is also exceptionally precise, and the magnetic field often creates a gentle stirring action in the molten metal, which promotes a more uniform and consistent alloy. However, the initial investment in the power supply and coils is typically higher.
Fuel-Fired Furnaces: Scale and Simplicity
Fuel-fired furnaces are often simpler in design and have a lower initial capital cost.
Their main advantage is scalability. They can be built to enormous sizes capable of melting tons of metal at once, making them the workhorse of many large foundries and recycling operations. The trade-off is less precise temperature control and a higher risk of impurities entering the melt from the fuel combustion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal should dictate your choice of technology. Focus on the desired outcome, and the correct furnace type becomes clear.
- If your primary focus is high-purity alloys or precious metals: An induction furnace is the definitive choice for its clean, controllable heating.
- If your primary focus is large-volume melting for casting or recycling: A fuel-fired furnace provides the scale and economic efficiency required for bulk production.
- If your primary focus is small-scale hobbyist work or prototyping: A small propane-fired furnace offers a low-cost entry point, while smaller induction units provide superior quality for those with a larger budget.
Ultimately, understanding the core principle of how heat is delivered to the metal is the key to selecting the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Furnace | Fuel-Fired Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect, electromagnetic | Direct combustion |
| Primary Advantage | High purity, precise control | High volume, lower cost |
| Ideal For | High-purity alloys, precious metals | Bulk production, recycling |
| Crucible Material | Graphite | Silicon carbide, clay graphite |
Ready to find the perfect melting solution for your lab?
Whether you need the precision of an induction furnace for high-purity alloys or the robust capacity of a fuel-fired furnace for larger volumes, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's specific needs. Our specialists can help you select the ideal furnace to enhance efficiency, purity, and productivity.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment can power your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision



















