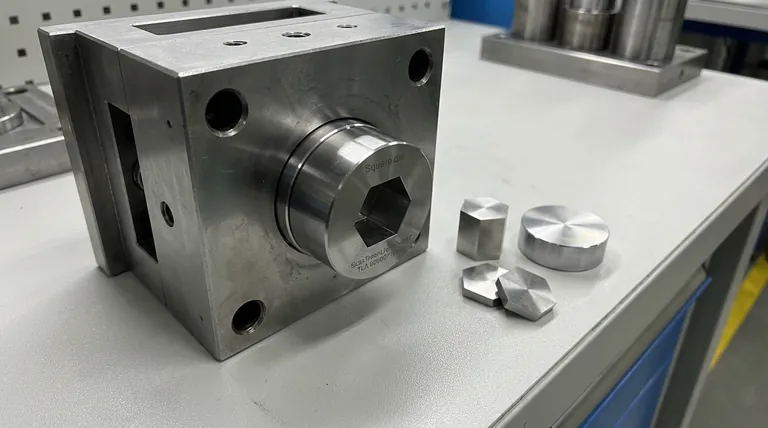
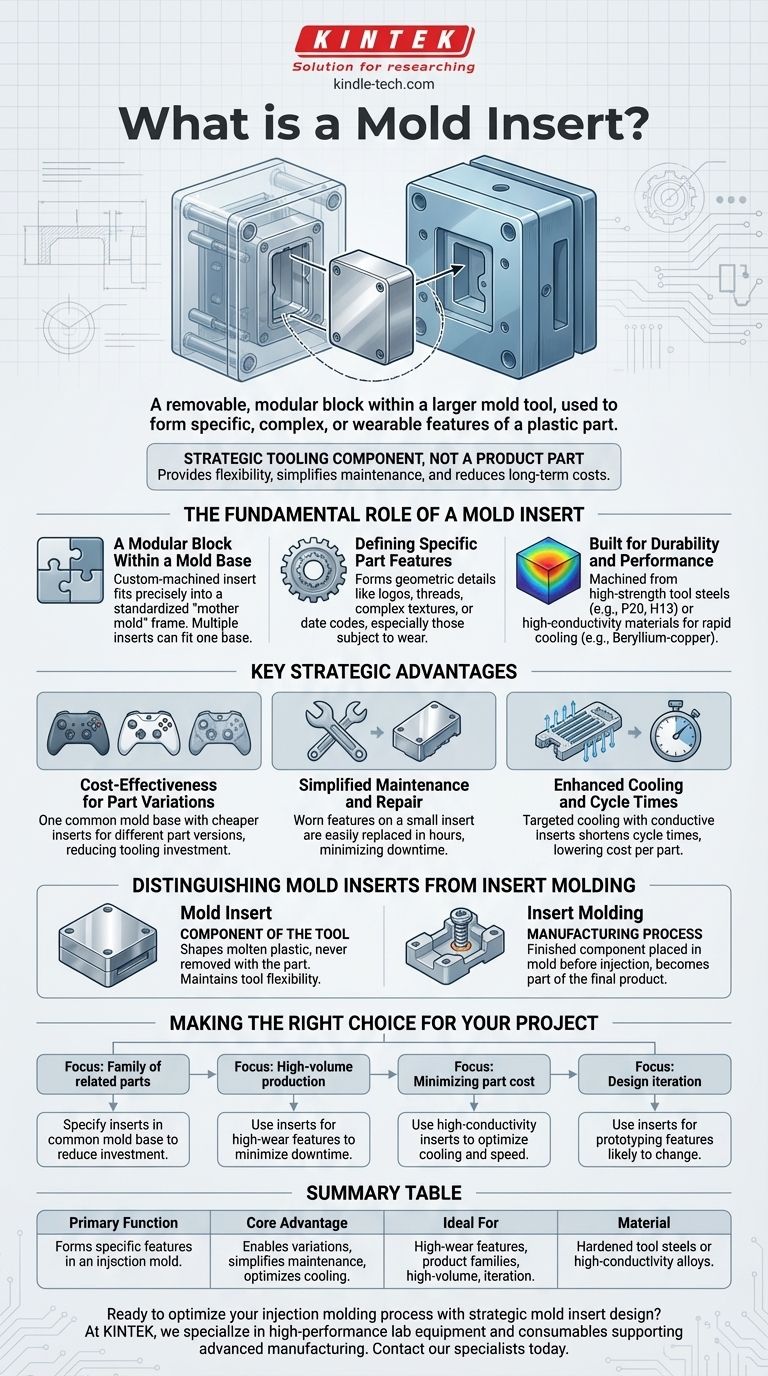
At its core, a mold insert is a removable, modular block within a larger mold tool. This insert is typically used to form a specific, often complex or wearable feature of a plastic part during the injection molding process. It is a component of the steel mold itself and should not be confused with "insert molding," a process where a separate component (like a metal screw) is placed in the mold to be encapsulated by plastic.
A mold insert is a strategic tooling component, not a part of the final product. It provides flexibility, simplifies maintenance, and reduces long-term manufacturing costs by allowing specific features of a mold to be modified or replaced without having to remake the entire tool.

The Fundamental Role of a Mold Insert
To understand the value of a mold insert, you must first see it as a piece of a larger puzzle: the injection mold.
A Modular Block Within a Mold Base
Think of the main mold as a standardized frame, often called a mold base or "mother mold." The mold insert is a custom-machined block of steel or other specialty metal that fits precisely into this base.
This modularity is the key. Multiple different inserts can be designed to fit into the same mold base, much like different cartridges fitting into a single printer.
Defining Specific Part Features
Inserts are used to form the geometric features on the final plastic part. They are especially useful for creating details that may need to be changed or are subject to high wear.
Common examples include areas that form logos, threads, complex textures, connector housings, or date codes.
Built for Durability and Performance
Mold inserts are almost always machined from high-strength, hardened tool steels (like P20, H13, or S7). In areas requiring rapid cooling to reduce cycle time, inserts may be made from materials with high thermal conductivity, such as beryllium-copper alloys.
Key Strategic Advantages of Using Mold Inserts
Using a solid mold for a simple part is effective, but inserts unlock significant strategic advantages for more complex projects.
Cost-Effectiveness for Part Variations
Imagine you need to produce five versions of a controller housing, each with a different button layout. Instead of building five separate, expensive molds, you can build one common mold base and five much cheaper sets of inserts.
This "family mold" approach dramatically reduces tooling investment and lead time for product variations.
Simplified Maintenance and Repair
The areas of a mold that form sharp corners, threads, or shut-offs are under immense pressure and wear out the fastest.
When these features are machined into a small, replaceable insert, maintenance becomes trivial. Swapping out a worn insert takes hours, whereas repairing a feature in a solid mold block can take days or weeks and may require shipping the entire heavy tool to a specialist.
Enhanced Cooling and Cycle Times
Some areas of a plastic part are thicker and take longer to cool. An insert allows a designer to target these "hot spots" with dedicated cooling channels or by making the insert from a highly conductive metal.
This targeted cooling can significantly shorten the overall molding cycle time, which directly translates to a lower cost per part in high-volume production.
Distinguishing Mold Inserts from Insert Molding
It is critical to distinguish between these two related, but distinct, manufacturing concepts. The confusion is common but can lead to significant miscommunication.
Mold Insert: A Component of the Tool
A mold insert is part of the machinery. It is a piece of the steel mold that shapes the molten plastic but is never removed with the part. Its purpose is to provide flexibility and maintainability for the tool.
Insert Molding: A Manufacturing Process
Insert molding is a process where a finished component (the "insert") is placed into the mold cavity before the plastic is injected. The plastic then flows around this component, permanently integrating it into the final part.
Examples of parts used in insert molding include metal threaded bushings, electrical contacts, shafts, or even small electronic circuits. This "insert" leaves the mold as part of the finished product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Understanding when and why to use mold inserts is a key part of designing for manufacturability (DFM).
- If your primary focus is producing a family of related parts: Specify inserts in a common mold base to reduce overall tooling investment.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Use inserts for features prone to wear (like threads or shut-offs) to minimize downtime and maintenance costs.
- If your primary focus is minimizing part cost: Use inserts made from high-conductivity materials to optimize cooling, reduce cycle times, and increase throughput.
- If your primary focus is design iteration: Use inserts for features that may change during prototyping, allowing for faster and cheaper design updates.
Ultimately, designing with mold inserts is a strategic decision that trades a small increase in upfront tool complexity for significant long-term flexibility, robustness, and cost savings.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | A removable, modular block that forms specific features in an injection mold. |
| Core Advantage | Enables part variations, simplifies maintenance, and optimizes cooling. |
| Ideal For | High-wear features, product families, high-volume production, and design iteration. |
| Material | Typically hardened tool steels (P20, H13) or high-conductivity alloys (beryllium copper). |
Ready to optimize your injection molding process with strategic mold insert design? The right tooling is critical for reducing costs and accelerating production. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including solutions that support advanced manufacturing techniques. Our expertise can help you achieve greater efficiency and flexibility. Contact our specialists today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
- Cylindrical Press Mold with Scale for Lab
People Also Ask
- What role do high-temperature pressure molds play in SiCp/Al fabrication? Enhancing Densification and Thermal Uniformity
- Is it fitting the mould or mold? A Guide to Correct Spelling by Region
- What are the primary functions of graphite molds in NiCr powder metallurgy? Optimize Your Composite Material Density
- What is the physical role of graphite molds in vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Cu-Al2O3 Composite Densification
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity



















