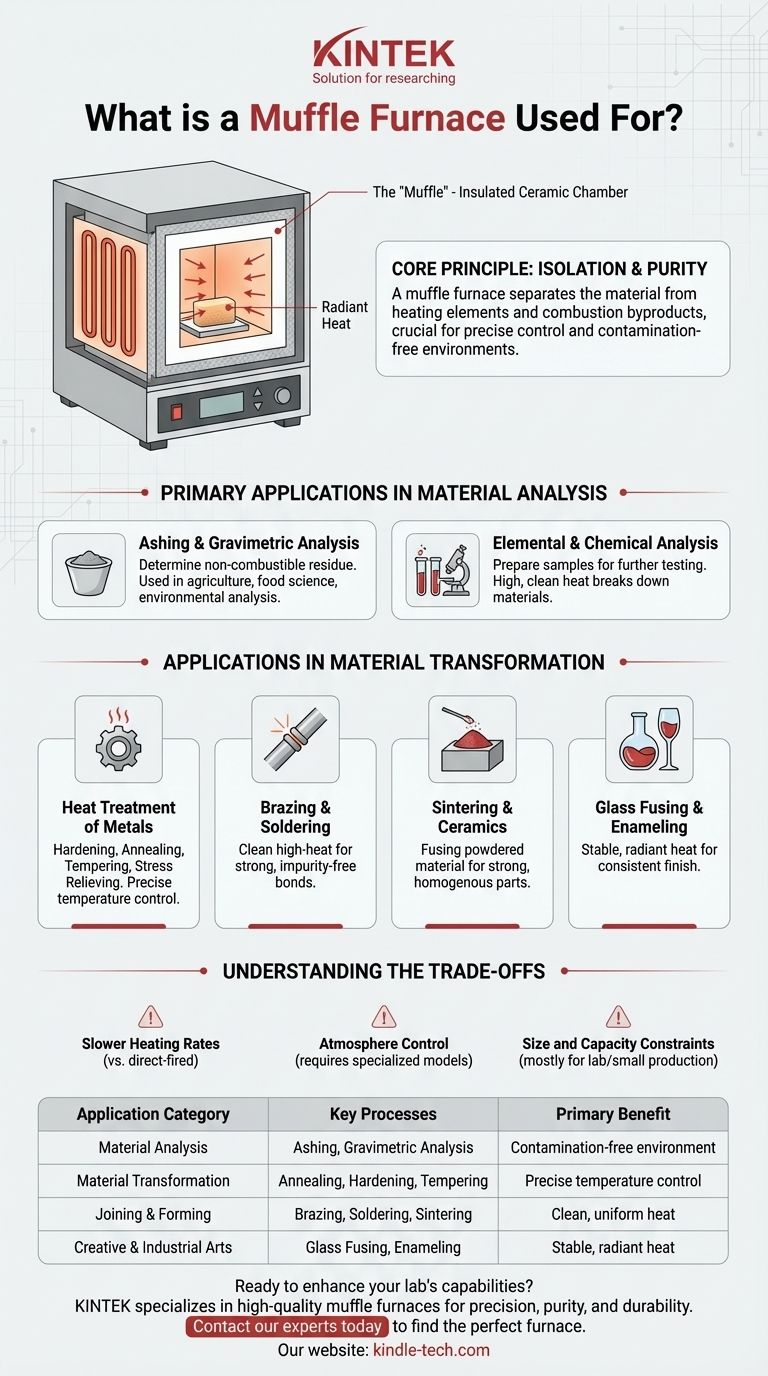
In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature, front-loading box oven used for a wide range of laboratory and industrial processes. Its defining feature is an insulated inner chamber—the "muffle"—that separates the material being heated from the actual heating elements and any combustion byproducts. This isolation is crucial for applications that demand precise temperature control and an environment free from contamination.
A muffle furnace is not just about achieving high temperatures; it is about providing a chemically pure and thermally uniform environment. Its core value lies in isolating a sample from the heating source, which is critical for accurate material analysis and high-purity material transformation.

The Core Principle: Isolation and Purity
The unique capabilities of a muffle furnace stem directly from its design. Understanding this principle is key to knowing when to use one over a standard oven or kiln.
What is the "Muffle"?
The muffle is a dedicated chamber, typically made of high-temperature ceramic, that contains the sample. The furnace's heating elements heat the outside of this chamber, and the heat radiates inward to the sample.
Preventing Contamination
By separating the sample from the heating elements (which can be electric coils or gas flames), the muffle prevents any contaminants from the heat source from affecting the sample. This is essential for sensitive chemical analyses where purity is paramount.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
Because the entire muffle chamber is heated, it radiates heat evenly from all sides. This creates a highly uniform temperature zone, which is critical for consistent results in processes like annealing or tempering metals.
Primary Applications in Material Analysis
A major use for muffle furnaces is to analyze the fundamental composition of a sample by subjecting it to extreme heat.
Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
Muffle furnaces are ideal for ashing, a process where a sample is burned completely to determine the amount of non-combustible residue (ash) it contains. This is a common technique in agriculture, environmental analysis, and food science.
Elemental and Chemical Analysis
In laboratories and research units, these furnaces are used to prepare samples for further elemental or chemical analysis. The high, clean heat can break down complex organic materials or prepare inorganic samples for testing.
Materials Research and Testing
Engineers use muffle furnaces for a variety of tests, such as determining the properties of cement, soils, and aggregates after high-temperature exposure.
Applications in Material Transformation
Beyond analysis, muffle furnaces are used to fundamentally change the physical properties of materials.
Heat Treatment of Metals
The precise temperature control makes these furnaces perfect for heat-treating metals. This includes processes like hardening, annealing (softening), tempering (increasing toughness), and stress relieving.
Brazing and Soldering
The clean, high-heat environment is used for joining metals through brazing and soldering. The furnace ensures the filler metal flows cleanly into the joint without introducing impurities that could weaken the bond.
Sintering and Ceramics
In technical ceramics and powder metallurgy, sintering involves heating powdered material to just below its melting point, causing the particles to fuse together. The uniform heat of a muffle furnace is essential for creating strong, homogenous ceramic parts.
Glass Fusing and Enameling
Muffle furnaces are widely used by artisans and manufacturers for fusing glass and creating durable enamel coatings on metal. The stable, radiant heat prevents thermal shock and ensures a smooth, consistent finish.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, muffle furnaces are not the right tool for every job. It's important to understand their limitations.
Slower Heating Rates
Because heat must first saturate the muffle chamber before reaching the sample, the heating and cooling cycles can be slower compared to a direct-fired kiln. This can impact throughput in high-volume production.
Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace operates with a normal air atmosphere. While some processes can be performed in a controlled atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation), this often requires specialized models with sealed chambers and gas inlets, which increases complexity and cost.
Size and Capacity Constraints
Muffle furnaces are most often found as benchtop laboratory or small production units. They are generally not suited for processing very large parts or massive batches, which are better handled by industrial-scale furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right high-temperature process, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is determining the composition of a sample: A muffle furnace is the correct tool, as its ability to prevent contamination is essential for accurate ashing and analysis.
- If your primary focus is modifying the physical properties of a material: The uniform and precisely controlled heat of a muffle furnace is ideal for heat treatments like annealing, hardening, and creating ceramics.
- If your primary focus is high-purity joining of metals: A muffle furnace provides the clean, stable environment needed for reliable brazing and soldering operations.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the tool of choice whenever high temperatures must be paired with high purity and precise process control.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Material Analysis | Ashing, Gravimetric Analysis | Contamination-free environment for accurate results |
| Material Transformation | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering | Precise temperature control for property modification |
| Joining & Forming | Brazing, Soldering, Sintering | Clean, uniform heat for strong, reliable bonds |
| Creative & Industrial Arts | Glass Fusing, Enameling | Stable, radiant heat prevents thermal shock |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a muffle furnace?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including muffle furnaces designed for precision, purity, and durability. Whether your work involves sensitive material analysis, metal heat treatment, or high-purity brazing, our solutions are engineered to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your application and discover how KINTEK can support your research and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do you keep a sample in a muffle furnace? A Guide to Safe and Accurate Placement
- How is a muffle furnace used for sample digestion? A Guide to Dry Ashing for Accurate Analysis
- Which type of material is used for overheating protection in muffle furnace? A Dual-Layer Safety System Explained
- What controls melting point? The Hierarchy of Forces from Ionic Bonds to Intermolecular Attractions
- What is a natural sintering? Uncover the Geological Process That Forms Ore Deposits



















