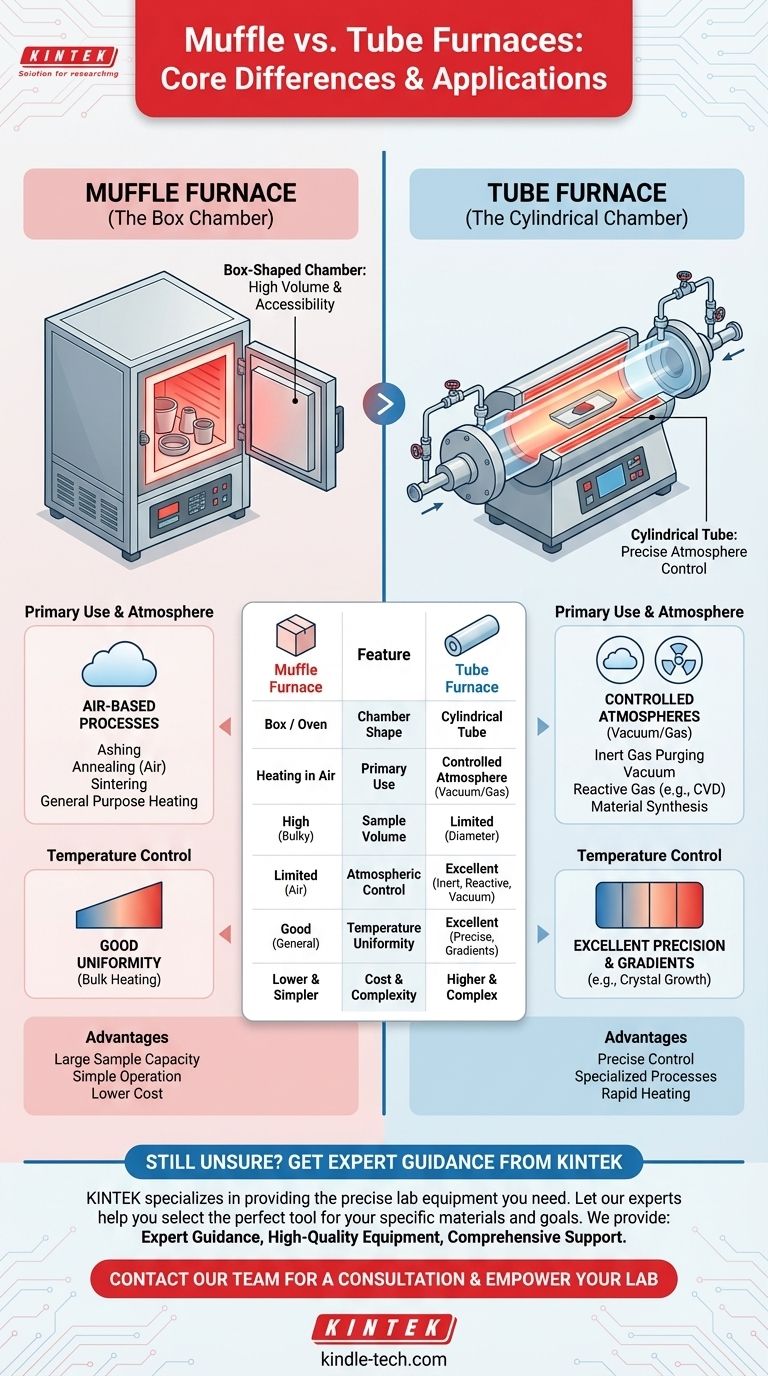
At its core, the difference between a muffle furnace and a tube furnace lies in the shape of their heating chamber and, consequently, their intended application. A muffle furnace is essentially a high-temperature oven with a box-shaped chamber, ideal for heating samples in air. A tube furnace uses a long, cylindrical tube as its chamber, a design that makes it exceptionally well-suited for processes requiring precise control over the gas atmosphere.
The choice is not about which furnace is superior, but which geometry best serves your purpose. Muffle furnaces are for general-purpose, large-volume heating in air, while tube furnaces are specialized tools for processes demanding a tightly controlled vacuum or gaseous environment.

The Core Difference: Chamber Geometry
The most fundamental distinction between these two furnaces is their physical design, which dictates how samples are placed and heated.
Muffle Furnace: The Box Chamber
A muffle furnace contains a large, box-like chamber, typically accessed by a front-facing door. This design is analogous to a conventional oven, but one that can reach temperatures of 1200°C or higher.
Its primary advantage is accessibility and volume. The open, rectangular space makes it easy to place large or awkwardly shaped items, or multiple smaller samples at once.
Tube Furnace: The Cylindrical Chamber
A tube furnace features a cylindrical heating cavity into which a long, narrow process tube (often made of quartz, alumina, or mullite) is inserted. The sample is then placed inside this tube.
This geometry is the key to its specialized capabilities. The confined, linear space is easier to seal, purge, and maintain with a specific atmosphere.
The Critical Divide: Atmospheric Control
How you control the environment around your sample is the most significant factor when choosing between these two furnaces.
Muffle Furnaces are for Air-Based Processes
A standard muffle furnace is designed for heating samples directly in air. It is the go-to instrument for applications like ashing, annealing, or sintering where an air atmosphere is acceptable or required.
While some muffle furnaces can be modified for use with inert gas, their boxy design and simple door make it difficult to create a truly sealed, oxygen-free environment.
Tube Furnaces Excel at Controlled Atmospheres
This is the primary advantage of a tube furnace. The ends of the process tube can be sealed with flanges that incorporate ports for gas lines and vacuum pumps.
This allows you to perform processes under a specific, controlled atmosphere, such as:
- Inert Gas: Purging the tube with argon or nitrogen to prevent oxidation.
- Vacuum: Removing air entirely for vacuum-sensitive materials.
- Reactive Gas: Introducing specific gases for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Temperature Control and Uniformity
Both furnaces achieve high temperatures, but their geometry affects the precision of that heat.
Muffle Furnace: General Purpose Heating
Due to their larger chamber volume, muffle furnaces can have slight temperature variations from one point to another. They are excellent for bringing a bulk sample to a target temperature but may lack the pinpoint uniformity of a tube furnace.
Tube Furnace: Precision and Gradients
The smaller, confined volume of a tube furnace allows for very rapid and precise temperature control.
Furthermore, the linear shape is ideal for creating a temperature gradient, where the temperature changes predictably along the length of the tube. This is often achieved with multi-zone furnaces that have several independent heating elements and controllers, a critical feature for crystal growth and other advanced material synthesis methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither furnace is a universal solution. The right choice involves balancing capability against practical constraints.
Sample Size and Throughput
A muffle furnace almost always wins on volume. Its larger chamber can accommodate bigger parts or a greater quantity of material in a single batch. A tube furnace is inherently limited by the inner diameter of its process tube, restricting sample size and overall throughput.
Operational Simplicity and Cost
Muffle furnaces are generally simpler to operate and more affordable for a given heating capability. The setup involves opening a door, placing the sample, and setting the program. Tube furnaces require more complex setup with flanges, gas lines, and potential vacuum systems, which also adds to their overall cost.
Sample Placement
Placing samples in a muffle furnace is straightforward. In a tube furnace, samples must be carefully positioned within the tube, often using a long push rod to place them in the center of the heated zone, which can be a more delicate operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace is a matter of aligning the tool's core strengths with your experimental or production goals.
- If your primary focus is bulk heating, annealing, or ashing samples in air: A muffle furnace is the most straightforward and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis requiring a controlled atmosphere (inert, vacuum, or reactive gas): A tube furnace is the necessary and purpose-built tool.
- If your primary focus is creating a precise temperature gradient for processes like CVD or crystal growth: A multi-zone tube furnace is specifically designed for this task.
- If your primary focus is maximizing sample volume or throughput for a simple heating process: The larger capacity of a muffle furnace is your best choice.
By understanding the fundamental link between chamber geometry and atmospheric control, you can confidently select the precise furnace to achieve your goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Chamber Shape | Box / Oven | Cylindrical Tube |
| Primary Use | Heating in Air | Controlled Atmosphere (Vacuum/Gas) |
| Sample Volume | High (Large, bulky items) | Limited (by tube diameter) |
| Atmospheric Control | Limited (Air) | Excellent (Inert, Reactive, Vacuum) |
| Temperature Uniformity | Good (General purpose) | Excellent (Precise, with gradients) |
| Cost & Complexity | Generally lower & simpler | Generally higher & more complex |
Still Unsure Which Furnace is Right for Your Lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment you need. Whether your process requires the high-volume, air-atmosphere capability of a muffle furnace or the specialized gas and vacuum control of a tube furnace, our experts can help you select the perfect tool.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Get a personalized recommendation based on your specific materials, processes, and goals.
- High-Quality Equipment: Reliable furnaces built for precision and durability.
- Comprehensive Support: From installation to maintenance, we're here to ensure your success.
Don't let the wrong furnace hold back your research or production. Contact our team today for a consultation and let KINTEK empower your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is muffle in muffle furnace? The Key to Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is a muffle furnace and how does it work? Achieve Clean, High-Temperature Heating for Your Lab
- How do you make biochar in a muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Controlled Pyrolysis
- How hot does a muffle furnace get? Unlock the Right Temperature for Your Lab
- What does a muffle furnace do? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing



















