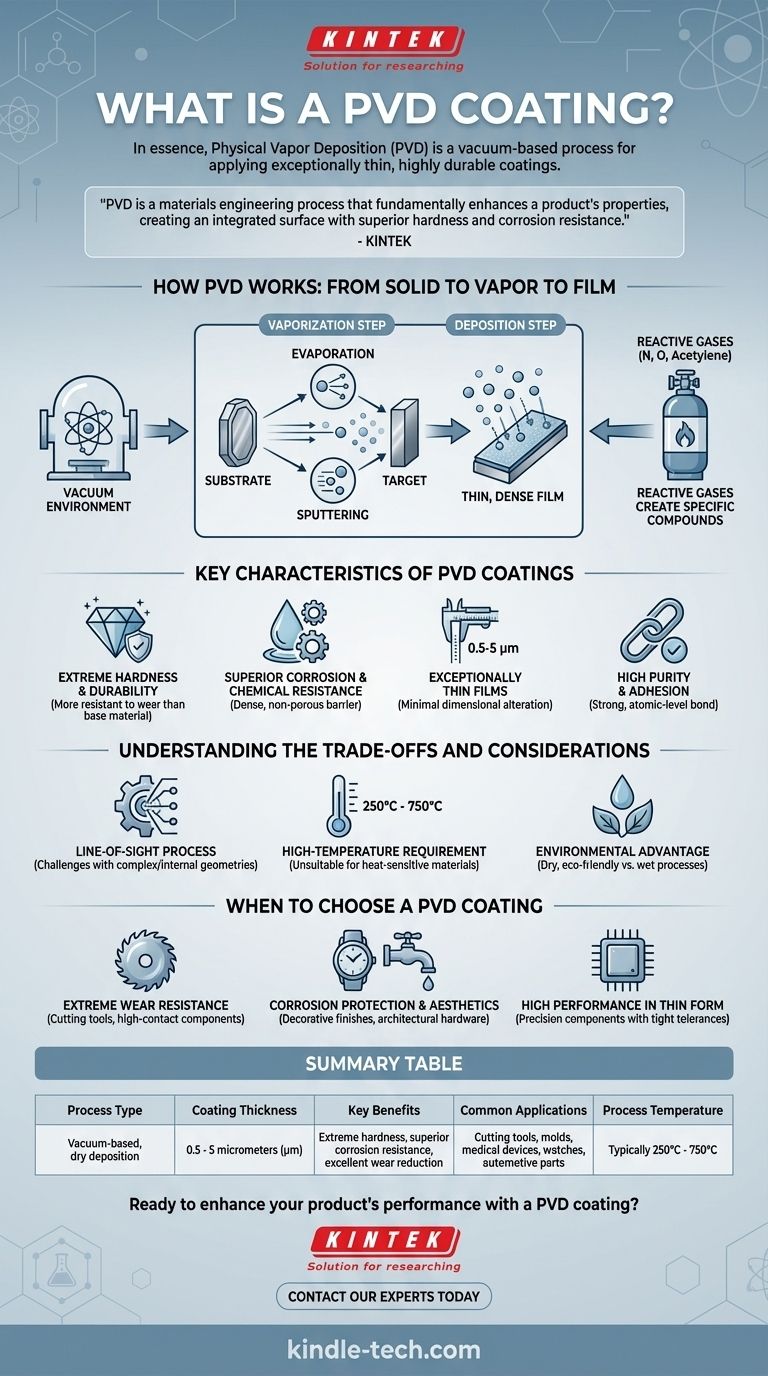
In essence, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a vacuum-based process used to apply an exceptionally thin but highly durable coating to a surface. The technique involves transforming a solid source material into a vapor, which then condenses onto the target object to form a new, high-performance surface layer. This deposition happens one atom or molecule at a time, creating a film that is remarkably pure, dense, and strongly bonded to the substrate.
PVD coating is not simply a layer applied to a surface; it is a materials engineering process that fundamentally enhances a product's properties. It creates an integrated surface with superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear reduction, all within a film that is often just a few microns thick.

How PVD Works: From Solid to Vapor to Film
The PVD process is a sophisticated technique performed inside a vacuum chamber to ensure the final coating's purity and quality. The entire method can be broken down into a few critical stages.
The Vacuum Environment
First, the object to be coated (the substrate) is placed in a vacuum chamber. Air and other gases are pumped out to create a high-vacuum environment, which is crucial for preventing contamination and allowing vaporized atoms to travel freely to the substrate.
The Vaporization Step
A solid source material, known as the target, is converted into a vapor. This is the "physical" part of PVD and is typically achieved through one of two primary methods:
- Evaporation: The target material is heated until it evaporates, often using an electron beam or a high-energy cathodic arc.
- Sputtering: The target is bombarded with energetic ions (usually of an inert gas like argon), which physically knock atoms off the target's surface.
The Deposition Step
The vaporized atoms or molecules travel through the vacuum and condense onto the substrate. This process builds a thin, uniform, and highly dense film. To ensure a strong bond, the substrate is often bombarded with ions before deposition begins, creating an atomically clean surface for the coating to adhere to.
The Role of Reactive Gases
To create specific coating compounds, reactive gases like nitrogen, oxygen, or acetylene can be introduced into the chamber. These gases react with the vaporized metal atoms to form ceramic compounds (like Titanium Nitride) on the substrate, allowing for precise control over the coating's final properties like hardness, color, and lubricity.
Key Characteristics of PVD Coatings
The atomic nature of the PVD process results in coatings with distinct and highly desirable characteristics that set them apart from traditional methods like electroplating or painting.
Extreme Hardness and Durability
PVD coatings are often significantly harder and more resistant to wear than the base material they cover. This makes them ideal for extending the life of cutting tools, molds, and other components subjected to high friction and abrasion.
Superior Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
The deposited film is extremely dense and non-porous, creating an effective barrier that protects the underlying substrate from oxidation and chemical attack. This is a major advantage for products used in harsh environments.
Exceptionally Thin Films
PVD coatings are incredibly thin, typically ranging from 0.5 to 5 micrometers (μm). This means they can enhance a part's surface properties without significantly altering its dimensions, making the process suitable for precision components with tight tolerances.
High Purity and Adhesion
Because the process occurs in a vacuum, the resulting film is of very high purity. The ion bombardment that precedes and sometimes accompanies the coating process creates an exceptionally strong, atomic-level bond between the coating and the substrate, preventing chipping or flaking.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, PVD is not a universal solution. Understanding its operational requirements is key to applying it correctly.
Line-of-Sight Process
PVD is a "line-of-sight" technique, meaning the coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. Coating complex, non-visible, or internal geometries can be challenging and may require sophisticated rotating fixtures to ensure uniform coverage.
High-Temperature Requirement
Most PVD processes operate at elevated temperatures, often between 250°C and 750°C (480°F to 1380°F). This high heat is necessary to promote good adhesion and film density, but it makes the process unsuitable for temperature-sensitive materials like some plastics or low-melting-point alloys.
The Environmental Advantage
Compared to traditional wet processes like electroplating, which involve hazardous chemicals and produce toxic waste, PVD is a dry, environmentally friendly process. This has become a significant advantage in modern manufacturing.
When to Choose a PVD Coating
The decision to use PVD should be driven by the specific performance goals for your product.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear resistance and longevity: PVD provides a surface hardness that significantly extends the life of cutting tools, dies, and high-contact components.
- If your primary focus is corrosion protection with aesthetic control: PVD offers a superior barrier against environmental attack while providing a wide range of decorative, durable finishes for watches, faucets, or architectural hardware.
- If your primary focus is high performance in a thin form factor: PVD is ideal for precision components where dimensional tolerances are critical, as the coating adds minimal thickness while maximizing surface properties.
By understanding its principles, you can leverage PVD not just as a finish, but as a strategic tool for enhancing material performance.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Vacuum-based, dry deposition |
| Coating Thickness | 0.5 - 5 micrometers (µm) |
| Key Benefits | Extreme hardness, superior corrosion resistance, excellent wear reduction |
| Common Applications | Cutting tools, molds, medical devices, watches, automotive parts |
| Process Temperature | Typically 250°C - 750°C (480°F - 1380°F) |
Ready to enhance your product's performance with a PVD coating?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for materials science and surface engineering. Our expertise can help you determine if PVD is the right solution for your application, whether you are developing high-wear tools, corrosion-resistant components, or precision consumer goods.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a PVD coating can provide the durability and performance your project demands.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
People Also Ask
- What are the effects of magnetron sputtering? Achieve High-Quality, Durable Thin Films for Your Lab
- What is deposition in environmental chemistry? Understanding How Air Pollution Harms Ecosystems
- What is a sputtering system? Achieve Unmatched Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- How many types of sputtering are there? A Guide to DC, RF, and Advanced Techniques



















