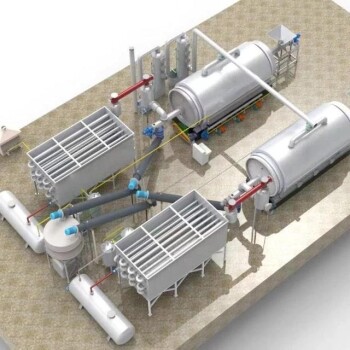
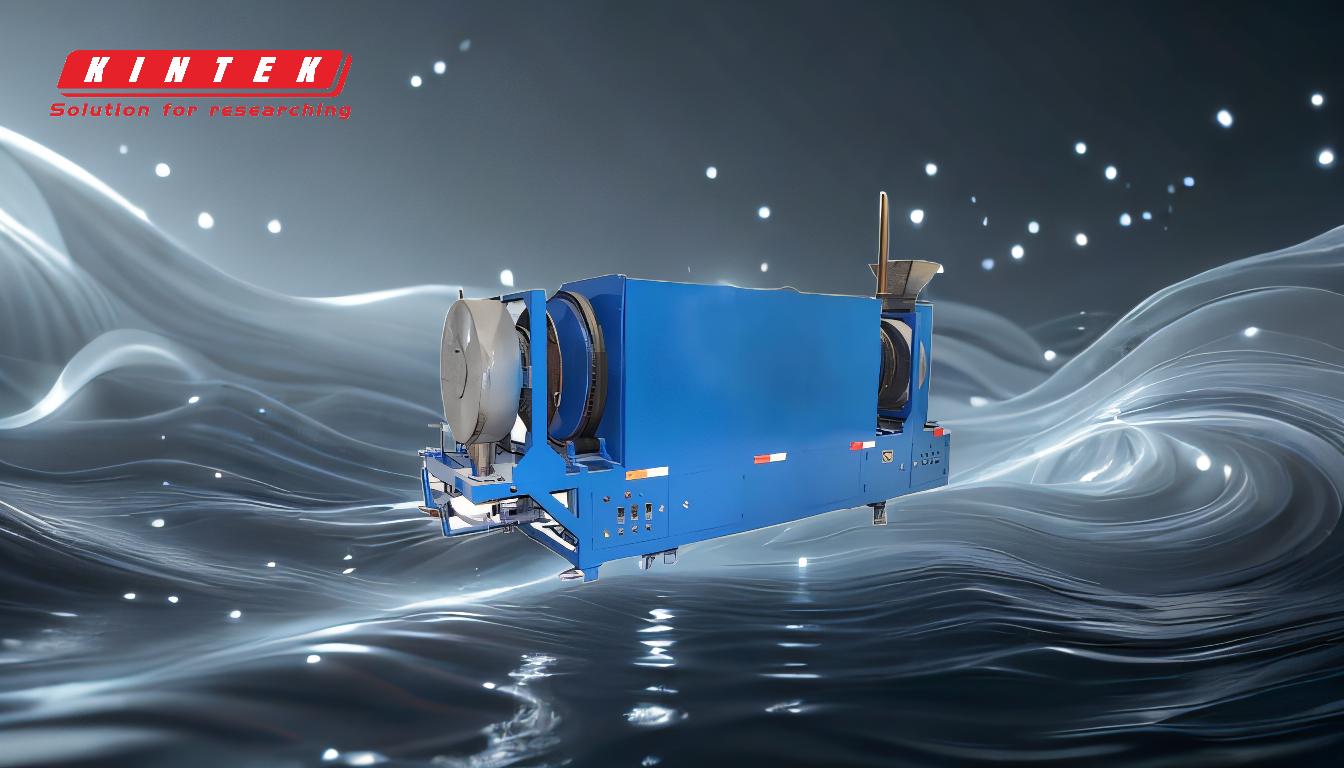
A pyrolysis furnace is a specialized device designed to carry out the pyrolysis process, which involves the thermal decomposition of organic materials at high temperatures in the absence of oxygen. This process breaks down the material into gases, liquids, and solids, which can be used for various applications such as fuel production, chemical synthesis, or the creation of activated carbon. The furnace typically consists of a chamber to hold the material, heating elements to achieve the required temperatures, and control systems to regulate the process parameters. Pyrolysis furnaces are widely used in industries such as waste management, energy production, and chemical manufacturing due to their ability to convert waste materials into valuable products efficiently.
Key Points Explained:

-
Definition and Purpose of a Pyrolysis Furnace:
- A pyrolysis furnace is a device used to perform pyrolysis, a process that decomposes organic materials at high temperatures without oxygen.
- The primary purpose is to convert organic waste into useful byproducts such as gases, liquids (bio-oil), and solids (char or activated carbon).
-
Key Components of a Pyrolysis Furnace:
- Chamber: The chamber holds the organic material during the pyrolysis process. It is designed to withstand high temperatures and maintain an oxygen-free environment.
- Heating Elements: These elements provide the necessary heat to initiate and sustain the pyrolysis reaction. They are often electric or gas-based, depending on the design and application.
- Control Systems: Temperature and process controls are critical for ensuring the efficiency and safety of the pyrolysis process. These systems regulate the heating rate, temperature, and other parameters to optimize the output.
-
How a Pyrolysis Furnace Works:
- The organic material is loaded into the chamber, and the furnace is sealed to prevent oxygen from entering.
- The heating elements raise the temperature to a range typically between 400°C and 800°C, depending on the material and desired products.
- In the absence of oxygen, the material decomposes into gases (syngas), liquids (bio-oil), and solids (char or ash).
- These byproducts are then collected and processed for further use.
-
Applications of Pyrolysis Furnaces:
- Waste Management: Pyrolysis furnaces are used to process municipal solid waste, plastic waste, and other organic materials, reducing landfill use and environmental pollution.
- Energy Production: The syngas and bio-oil produced can be used as fuels for energy generation or as feedstock for chemical production.
- Chemical Industry: Pyrolysis is used to produce chemicals such as methanol, ethanol, and other hydrocarbons.
- Activated Carbon Production: The solid char produced can be further processed to create activated carbon, which is used in water purification, air filtration, and other applications.
-
Advantages of Pyrolysis Furnaces:
- Waste Reduction: Converts waste materials into useful products, reducing the volume of waste sent to landfills.
- Resource Recovery: Recovers valuable resources such as energy, chemicals, and materials from waste.
- Environmental Benefits: Reduces greenhouse gas emissions and pollution by preventing the release of harmful substances during waste decomposition.
- Versatility: Can process a wide range of organic materials, including plastics, rubber, biomass, and municipal waste.
-
Considerations for Purchasing a Pyrolysis Furnace:
- Capacity: Choose a furnace with a capacity that matches the volume of material you need to process.
- Temperature Range: Ensure the furnace can achieve the required temperatures for your specific application.
- Control Systems: Look for advanced control systems that allow precise regulation of the pyrolysis process.
- Safety Features: Consider furnaces with safety mechanisms to prevent accidents, such as pressure relief valves and temperature monitoring.
- Maintenance and Durability: Evaluate the ease of maintenance and the durability of the furnace components to ensure long-term reliability.
By understanding these key points, a purchaser can make an informed decision when selecting a pyrolysis furnace that meets their specific needs and application requirements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Converts organic waste into gases, liquids (bio-oil), and solids (char). |
| Key Components | Chamber, heating elements, control systems. |
| Temperature Range | 400°C to 800°C, depending on material and desired products. |
| Applications | Waste management, energy production, chemical synthesis, activated carbon. |
| Advantages | Waste reduction, resource recovery, environmental benefits, versatility. |
| Purchasing Tips | Consider capacity, temperature range, control systems, safety, durability. |
Ready to transform waste into valuable resources? Contact us today to find the perfect pyrolysis furnace for your needs!