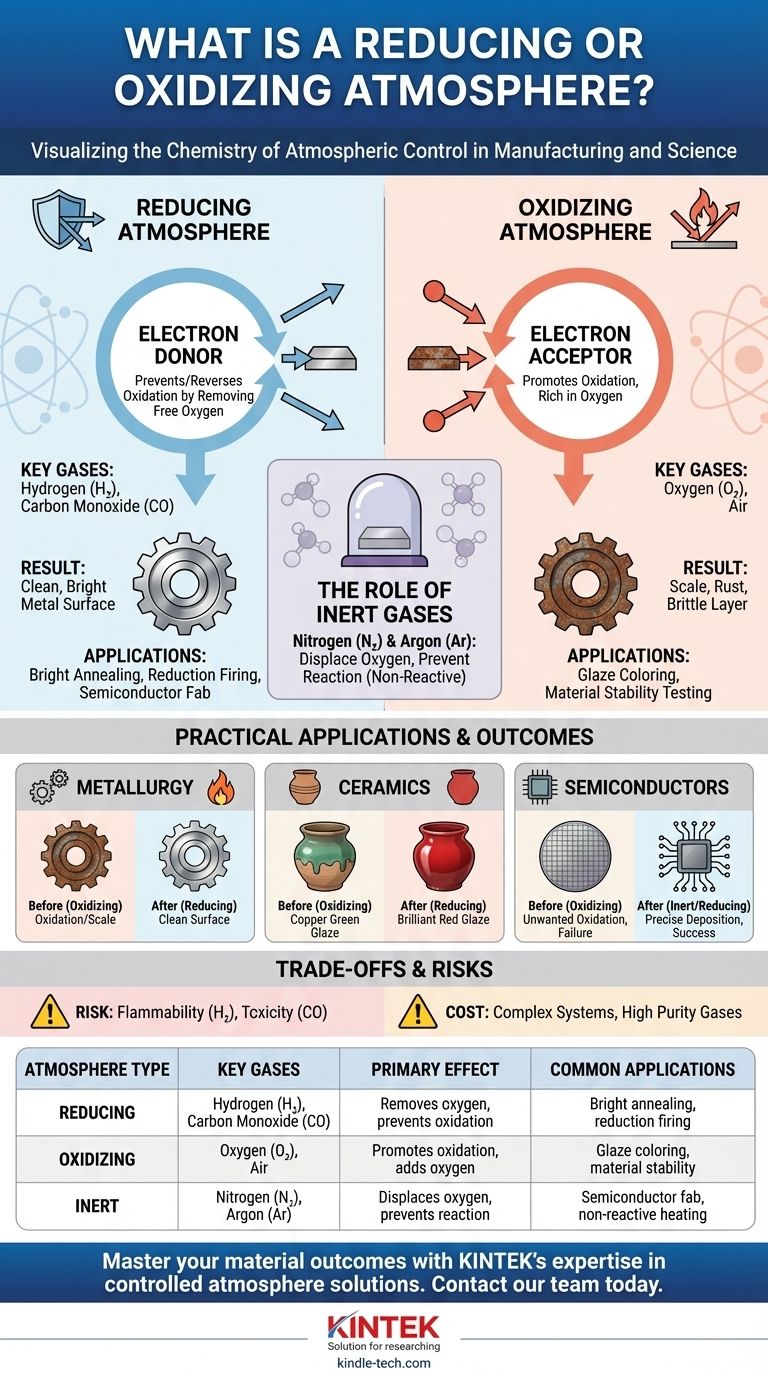
In essence, a reducing atmosphere is an environment that prevents or reverses oxidation, typically by removing free oxygen. Conversely, an oxidizing atmosphere is rich in oxygen or other oxidizing agents and actively promotes oxidation. These controlled environments are not just theoretical concepts; they are critical tools used in manufacturing and science to manipulate the chemical properties of materials.
The key distinction is not simply the amount of oxygen present, but the atmosphere's chemical potential. A reducing atmosphere is an electron donor, protecting materials from oxidation, while an oxidizing atmosphere is an electron acceptor, actively causing materials to oxidize.

The Chemistry of Atmospheric Control
To understand these atmospheres, you must first understand the fundamental chemical processes they are designed to control: oxidation and reduction. These two processes always occur together in what is known as a "redox" reaction.
Oxidation: The Tendency to Lose Electrons
Oxidation is the process where a material loses electrons. While we associate it with oxygen, other chemicals can also cause oxidation.
The most common example is rust. When iron is exposed to an oxidizing atmosphere (like the air around us), the iron atoms (Fe) lose electrons to oxygen atoms (O₂), forming iron oxide (Fe₂O₃). This creates a brittle layer of scale or rust on the material's surface.
Reduction: The Tendency to Gain Electrons
Reduction is the exact opposite of oxidation; it is the process where a material gains electrons.
A reducing atmosphere is engineered to be rich in molecules that readily donate their electrons. By flooding the environment with these "electron donors," they effectively prevent oxygen from "stealing" electrons from the material you are trying to protect.
The Role of Key Gases
The specific gas mixture determines the atmosphere's character.
- Oxidizing Gases: The primary oxidizing gas is Oxygen (O₂). Normal air is a moderately oxidizing atmosphere.
- Reducing Gases: Hydrogen (H₂) and Carbon Monoxide (CO) are powerful reducing agents. They react aggressively with any free oxygen, removing it from the environment by forming water (H₂O) or carbon dioxide (CO₂).
- Inert Gases: Nitrogen (N₂) and Argon (Ar) are neutral. They don't typically react with materials. Their main purpose is to displace oxygen, creating an inert (non-reactive) environment that prevents oxidation without actively causing reduction.
Practical Applications: Where Atmosphere is Everything
Controlling the atmosphere inside a furnace, kiln, or reactor is fundamental to achieving the desired outcome in many industrial and scientific processes.
In Metallurgy and Heat Treating
When steel is heated to high temperatures for processes like annealing or hardening, it becomes highly reactive. Exposing it to air would cause a thick, brittle layer of oxide scale to form on its surface, ruining the part's dimensions and finish.
By performing the heat treatment in a reducing atmosphere of hydrogen or nitrogen, this oxidation is completely prevented, resulting in a clean, bright metal surface.
In Ceramics and Pottery Firing
Atmosphere has a dramatic effect on the final color of ceramic glazes containing metal oxides.
In an oxidizing atmosphere, copper oxide in a glaze will turn green. However, in a reducing atmosphere, the oxygen is stripped away from the copper oxide, reducing it back to pure, colloidal copper, which results in a brilliant red color. This is the basis of "reduction firing."
In Semiconductor Manufacturing
The creation of microchips requires environments of extreme purity. Unwanted oxidation can create insulating layers where conductive paths are needed, leading to device failure.
Fabrication processes are often carried out in inert (argon) or reducing (hydrogen) atmospheres to protect the silicon wafers and ensure the precise deposition of thin films.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While powerful, creating and maintaining a specific atmosphere involves significant challenges and dangers that must be managed.
The Hazard of Reducing Gases
The most effective reducing gases are also hazardous. Hydrogen (H₂) is extremely flammable and can be explosive over a wide range of concentrations in air.
Carbon Monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and highly toxic gas that poses a serious health risk if it leaks from the furnace or kiln.
The Cost and Complexity of Control
Maintaining a specialized atmosphere is not simple. It requires a sealed furnace or kiln, a reliable supply of high-purity gases, sophisticated flow control systems, and sensors to monitor the atmospheric composition. This adds significant cost and complexity to any process.
Unintended Material Changes
Using the wrong atmosphere can be destructive. An oxidizing atmosphere can make a metal part brittle and useless. A strongly reducing atmosphere can pull oxygen out of the chemical structure of certain ceramics, changing their physical properties in undesirable ways.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice of atmosphere is dictated entirely by the chemical outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is preventing surface scale on metals: You require a reducing (hydrogen/CO) or inert (nitrogen/argon) atmosphere to eliminate oxygen contact during heat treatment.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific glaze colors in ceramics: You must actively manipulate the kiln atmosphere between oxidizing and reducing conditions to control the final state of the metal oxides.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a material's stability at high temperatures: You will likely test it in an oxidizing atmosphere (air) to simulate its real-world operating conditions.
- If your primary focus is simply heating a non-reactive material: A standard oxidizing atmosphere (air) is often sufficient and is the simplest and most cost-effective option.
Ultimately, mastering the atmospheric conditions of your process is equivalent to mastering the final chemical and physical properties of your material.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Key Gases | Primary Effect | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reducing | Hydrogen (H₂), Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Removes oxygen, prevents oxidation | Bright annealing of metals, reduction firing in ceramics |
| Oxidizing | Oxygen (O₂), Air | Promotes oxidation, adds oxygen | Glaze coloring (e.g., copper green), material stability testing |
| Inert | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar) | Displaces oxygen, prevents reaction | Semiconductor manufacturing, heating non-reactive materials |
Master your material outcomes with KINTEK's expertise in controlled atmosphere solutions. Whether you are heat-treating metals, firing ceramics, or manufacturing semiconductors, the right atmosphere is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed to create and maintain precise reducing, oxidizing, or inert environments. Let our experts help you select the perfect furnace, gas system, and controls to achieve consistent, high-quality results. Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and ensure your process is a success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- What is nitrogen atmosphere for annealing? Achieve Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment
- What are the functions of nitrogen (N2) in controlled furnace atmospheres? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment Results
- How does a high-temperature furnace with atmosphere control optimize spinel coatings? Achieve Redox Sintering Precision



















