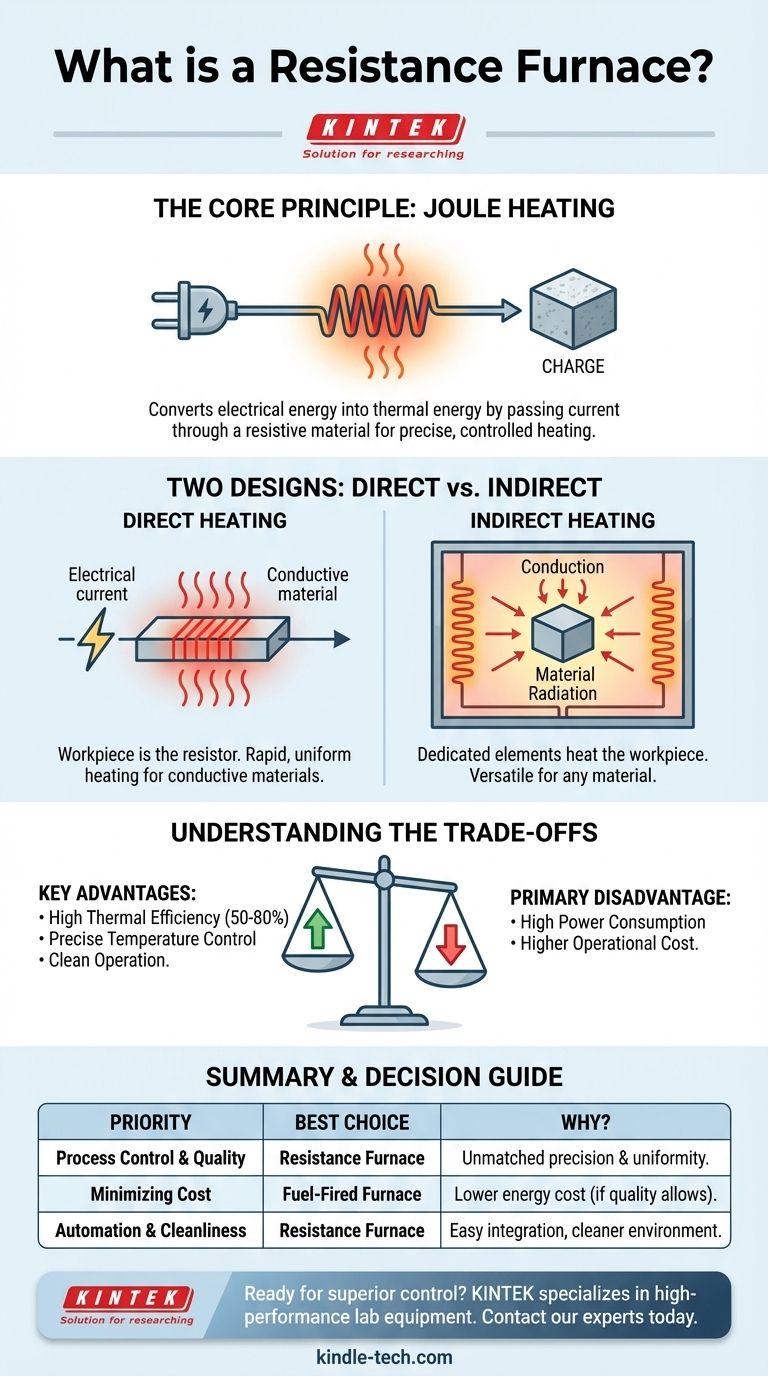
In essence, a resistance furnace is a type of industrial furnace that generates heat by passing an electric current through a resistive material. It operates on the fundamental principle of Joule heating, converting electrical energy directly into thermal energy. This method allows for highly controlled and efficient heating, making it a cornerstone of modern material processing.
A resistance furnace leverages the predictable heat generated by electrical resistance to offer precise temperature control. The core decision in using one comes down to a trade-off: accepting its high power consumption in exchange for superior heating quality and automation potential.

How Resistance Furnaces Generate Heat
A resistance furnace functions by exploiting a simple physical principle. Understanding this mechanism is key to appreciating its applications and limitations.
The Principle of Joule Heating
At its heart, the furnace operates on Joule's first law. This law states that when an electric current passes through a conductor, it generates heat. The amount of heat is directly proportional to the material's electrical resistance and the square of the current.
By controlling the voltage and current, the furnace can produce a precise and predictable amount of thermal energy. This is the same principle that powers common appliances like electric stoves and toasters, but applied on an industrial scale.
From Electrical to Thermal Energy
The furnace is powered by electricity, typically using the existing voltage available at an industrial plant. This electrical energy is channeled into a resistive material. As the electricity struggles to pass through this resistance, it dissipates its energy as heat, which is then transferred to the material or "charge" inside the furnace.
The Two Core Designs: Direct vs. Indirect Heating
Resistance furnaces are broadly categorized into two types based on how the heat is applied to the workpiece. This design choice has significant implications for the furnace's application.
Direct Heating: The Material is the Resistor
In a direct heating design, the material being heated (known as the furnace charge) also serves as the heating element. An electric current is passed directly through the workpiece itself.
This method is less common and is only suitable for materials that are sufficiently conductive. The heat is generated internally within the workpiece, which can lead to very rapid and uniform heating.
Indirect Heating: Using Dedicated Heating Elements
This is the more prevalent design. In an indirect furnace, specialized electric heating elements made of high-resistance alloys are installed inside the furnace, often lining the walls.
Current passes through these elements, causing them to glow hot. The heat is then transferred to the workpiece via a combination of conduction, convection, and radiation. This method is more versatile as it can heat any type of material, regardless of its electrical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is a universal solution. The value of a resistance furnace is defined by its specific advantages and its primary, unavoidable drawback.
Key Advantages: High Efficiency and Control
Resistance furnaces are known for their high thermal efficiency, often ranging from 50% to 80%. Because the heat is generated inside the furnace, less energy is lost to the surrounding environment compared to fuel-fired alternatives.
Their greatest strength is the ease of controlling the thermal system. Electrical input can be adjusted with extreme precision, allowing for stable temperatures and complex heating profiles. This makes them ideal for heating demanding workpieces that require strict quality control.
The Primary Disadvantage: High Power Consumption
The main drawback is cost. Converting electricity to heat on an industrial scale consumes a significant amount of power. While they are efficient in using heat, their reliance on electricity can make them expensive to operate, especially in regions with high electricity costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a heating technology depends entirely on your project's priorities.
- If your primary focus is process control and final product quality: A resistance furnace is an excellent choice due to its unmatched temperature precision and uniformity.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational expenditure: The high power consumption is a critical factor, and a fuel-fired furnace might be a more economical alternative, provided it can meet your quality standards.
- If your primary focus is automation and clean operation: The simple, electrically-driven system of a resistance furnace integrates easily into automated production lines and provides a cleaner working environment.
Understanding this balance between precision and power consumption is the key to leveraging resistance furnace technology effectively.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Direct Heating | Indirect Heating |
|---|---|---|
| How it Works | Current passes through the workpiece itself | Current passes through dedicated heating elements |
| Best For | Electrically conductive materials | Any material type |
| Heating Speed | Very rapid and uniform | Slower, transferred via radiation/convection |
| Primary Advantage | High efficiency for specific materials | Versatility |
Ready to achieve superior process control and product quality?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including resistance furnaces designed for precise temperature control and uniform heating. Whether your priority is R&D, quality assurance, or automated production, our solutions deliver the reliability and efficiency your laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect heating solution for your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation



















