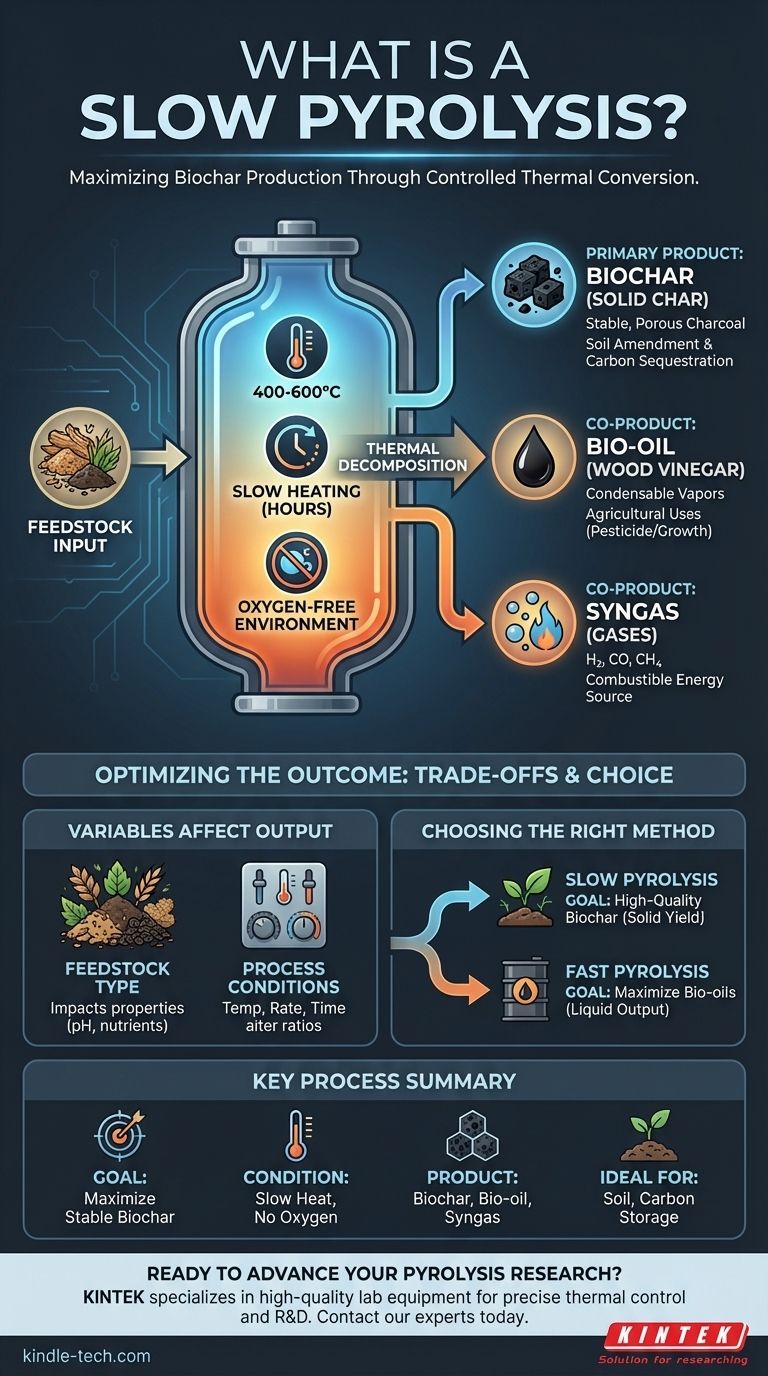
In essence, slow pyrolysis is a thermal conversion process that heats organic material, such as wood or agricultural waste, to high temperatures in an environment with very little or no oxygen. Unlike rapid heating methods, this process is done gradually over several hours. The primary goal is to maximize the production of a stable, solid, carbon-rich product known as biochar.
The critical distinction of slow pyrolysis is its deliberate pace. By heating biomass slowly, the process is optimized to convert the material primarily into solid biochar, whereas faster methods are designed to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oils.

How Slow Pyrolysis Works: The Core Principles
Slow pyrolysis is defined by a specific set of controlled conditions designed to favor the creation of solid char over liquids and gases.
Low Temperature and Slow Heating
The process typically operates at lower temperatures (around 400-600°C) compared to other thermal methods. The feedstock is heated very slowly over several hours, allowing organic compounds to fully decompose and carbonize.
This gradual heating minimizes the production of volatile gases and allows more carbon to remain in the solid structure.
An Oxygen-Free Environment
Like all pyrolysis, the process must occur in an anaerobic (oxygen-free) or anoxic (low-oxygen) chamber. The absence of oxygen is critical because it prevents the biomass from combusting or simply burning away into ash.
Instead of burning, the heat breaks down the chemical bonds within the material, a process known as thermal decomposition.
The Goal: Maximizing Solid Yield
The slow reaction time promotes the formation of high-quality biochar. It allows complex vapors to "crack" and re-condense on the surface of the solid material, increasing the final char yield and its stability.
The Primary Products of Slow Pyrolysis
While optimized for one output, the process creates a valuable mix of solid, liquid, and gas products.
Biochar (Solid Char)
This is the main product, often accounting for a significant portion of the initial biomass weight. Biochar is a highly porous and stable form of charcoal.
Its primary uses are in agriculture as a soil amendment to improve water retention and nutrient availability, and for carbon sequestration to lock carbon away for centuries.
Bio-oil (Wood Vinegar)
The condensable vapors from the process are cooled to form a dark, aqueous liquid. When derived from wood, this is often called wood vinegar.
This liquid can have applications in agriculture as a natural pesticide or plant growth promoter, although its composition varies widely.
Syngas (Non-Condensable Gases)
The process also produces non-condensable gases like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane. This mixture, known as syngas, is combustible.
In many systems, the syngas is captured and looped back to provide the heat required for the pyrolysis process itself, making the operation more energy-efficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variables
The output of slow pyrolysis is not a fixed commodity. The results are highly sensitive to the inputs and operating conditions, which presents both challenges and opportunities.
Feedstock Is a Critical Factor
The type of biomass used has a direct impact on the final products. Wood chips will produce a different biochar than corn stover or manure.
The properties of the biochar, such as its pH and nutrient content, are highly dependent on the feedstock.
Process Conditions Dictate Output
Slight adjustments to the peak temperature, heating rate, and residence time can significantly alter the ratio of biochar, bio-oil, and syngas produced. This allows for process optimization but requires precise control.
Market and Economic Uncertainty
Because the product properties vary so much with feedstock and conditions, it can be difficult to define a clear market value. The price for biochar or wood vinegar is not standardized and depends on its specific qualities and intended application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use slow pyrolysis hinges on your primary objective. It is not a one-size-fits-all solution for biomass conversion.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality biochar for soil amendment or carbon sequestration: Slow pyrolysis is the ideal method due to its high, stable solid yield.
- If your primary focus is generating liquid bio-oils for fuel or chemical production: You should consider fast pyrolysis, which uses rapid heating to maximize liquid output.
Understanding this fundamental trade-off allows you to select the precise thermal process that aligns with your material and economic goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Goal | Maximize production of stable, solid biochar |
| Key Condition | Slow heating rate (several hours) at 400-600°C in an oxygen-free environment |
| Primary Product | Biochar (solid, carbon-rich) |
| Co-Products | Bio-oil (wood vinegar) and syngas |
| Ideal For | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration, agricultural applications |
Ready to turn your biomass into valuable biochar? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you are optimizing process conditions or scaling up production, our solutions help you achieve precise thermal control and maximize your output. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in biomass conversion and sustainable technology.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process



















