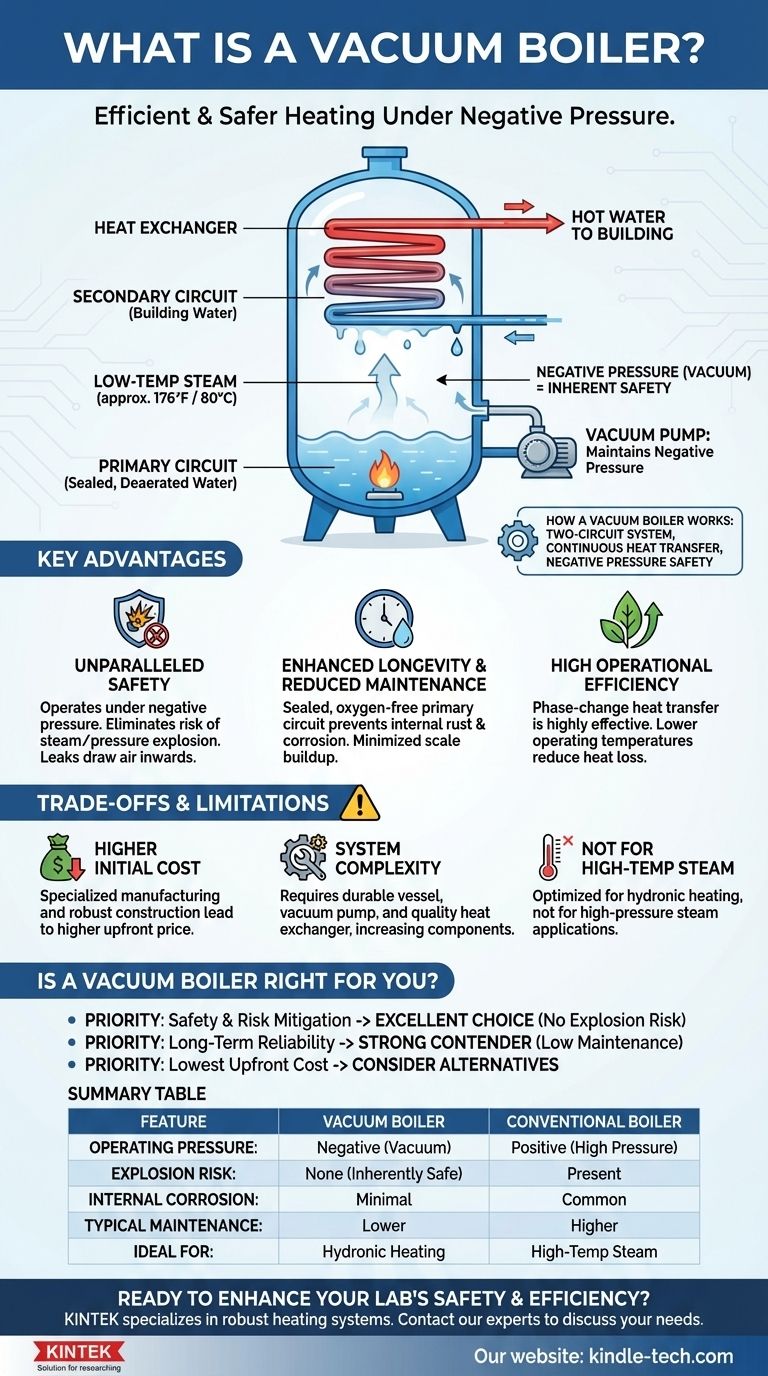
At its core, a vacuum boiler is a steel pressure vessel that heats water under negative pressure, or a vacuum. Because water boils at a much lower temperature in a vacuum (around 176°F / 80°C), this design allows for the efficient and incredibly safe transfer of heat. The low-temperature steam created inside the boiler heats a separate water circuit for your building, without the two sources of water ever mixing.
A vacuum boiler is not just a different type of boiler; it's a fundamentally safer heating system. By leveraging the physics of low-pressure boiling, it eliminates the risk of explosion and minimizes the internal corrosion common in conventional pressurized boilers.
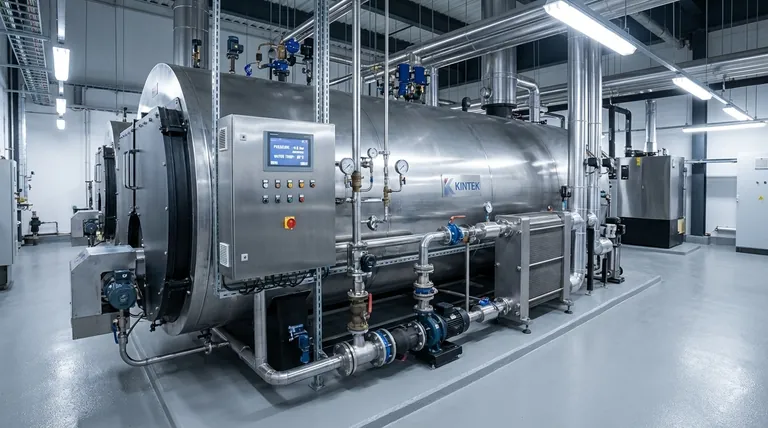

How a Vacuum Boiler Works: The Core Principle
A vacuum boiler operates on a simple, powerful principle from physics: the lower the pressure on a liquid, the lower its boiling point. The system harnesses this to create a safe and efficient heat transfer cycle.
The Two-Circuit System
The design is built around two independent water circuits. The primary circuit is a small amount of purified, deaerated water permanently sealed inside the boiler's pressure vessel. The secondary circuit is the water that circulates through your building's radiators, fan coils, or other hydronic systems. A heat exchanger is the only thing connecting them.
The Heat Transfer Process
The process is a continuous loop. A burner heats the primary water inside the vacuum vessel, causing it to boil and turn into low-temperature steam. This steam rises and condenses on the surface of the heat exchanger, transferring its latent heat to the secondary circuit water flowing through it. The now-condensed primary water simply drips back down to be reheated, repeating the cycle.
Why Negative Pressure is Key
The entire primary vessel is held under a strong vacuum by a pump. This negative pressure is the "secret sauce." If a leak were ever to develop in the vessel, high-pressure steam wouldn't explode outwards. Instead, air would be drawn inwards, causing the system to shut down safely.
The Key Advantages of Operating Under Vacuum
The unique design of a vacuum boiler provides distinct benefits that directly address the common pain points of traditional pressurized systems.
Unparalleled Safety
This is the most significant advantage. Because they operate under negative pressure, vacuum boilers are physically incapable of having a steam or pressure explosion. This inherent safety often exempts them from the strict regulations and mandatory operator licensing required for high-pressure boilers.
Enhanced Longevity and Reduced Maintenance
The primary water is deaerated and sealed for life. With virtually no oxygen inside the vessel, internal rust and corrosion are almost completely eliminated. This prevents the buildup of scale and sludge on heat transfer surfaces, maintaining high efficiency over decades and drastically reducing maintenance requirements.
High Operational Efficiency
The phase-change heat transfer (liquid to steam and back to liquid) is a highly effective way to move energy. Furthermore, the lower operating temperatures can reduce standby heat losses and improve the overall efficiency of the system, especially in condensing models which can capture even more waste heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, vacuum boilers are not the perfect solution for every scenario. Understanding their limitations is critical for making an informed decision.
Higher Initial Cost
Specialized manufacturing and robust construction mean vacuum boilers typically have a higher upfront purchase price than a conventional non-condensing boiler of a similar capacity. The investment is in safety and long-term reliability rather than initial savings.
System Complexity
While the operating principle is straightforward, the equipment itself includes more components than a basic atmospheric boiler. A durable vacuum vessel, a high-quality heat exchanger, and a vacuum pump are all essential parts that contribute to the cost and complexity.
Not Ideal for High-Temperature Steam
Vacuum boilers are optimized for hydronic heating applications (hot water). They are not designed to produce the high-temperature, high-pressure steam required for certain industrial processes or power generation.
Is a Vacuum Boiler Right for Your Application?
Choosing the right boiler technology depends entirely on balancing your priorities for safety, cost, and long-term performance.
- If your primary focus is safety and risk mitigation: A vacuum boiler is an exceptional choice, as its fundamental design eliminates the risk of a pressure explosion.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and low maintenance: The sealed, oxygen-free design that prevents internal corrosion makes it a strong contender for reducing lifecycle costs.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible upfront cost: A conventional atmospheric or pressurized boiler will likely be a more budget-friendly initial investment, though it comes with a different risk and maintenance profile.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum boiler is an investment in inherent safety and long-term operational stability for your heating system.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Boiler | Conventional Pressurized Boiler |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Pressure | Negative (Vacuum) | Positive (High Pressure) |
| Explosion Risk | None (Inherently Safe) | Present |
| Internal Corrosion | Minimal (Sealed, Oxygen-Free System) | Common |
| Typical Maintenance | Lower | Higher |
| Ideal For | Hydronic Heating Systems | High-Temperature Steam Applications |
Ready to enhance your lab's safety and efficiency?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust laboratory equipment, including heating systems designed for reliability and safety. If you're considering a vacuum boiler for your facility's hydronic heating needs, our experts can help you determine if it's the right investment for your long-term operational stability.
Contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements and discover the KINTEK difference in performance and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- 30T 40T Split Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What does hot-pressing do? Transform Materials with High-Temperature, High-Pressure Densification
- Why is a heated laboratory hydraulic press necessary for composite laminates? Achieve Void-Free Structural Integrity
- How can porosity be reduced? Achieve Maximum Material Strength and Density
- What are hot presses used for? Transforming Materials with Heat and Pressure
- What is a vacuum heat press machine? The Ultimate Tool for 3D Product Decoration



















