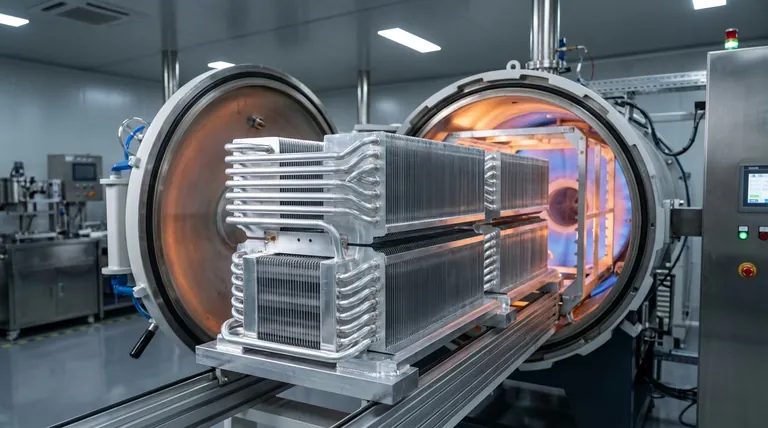
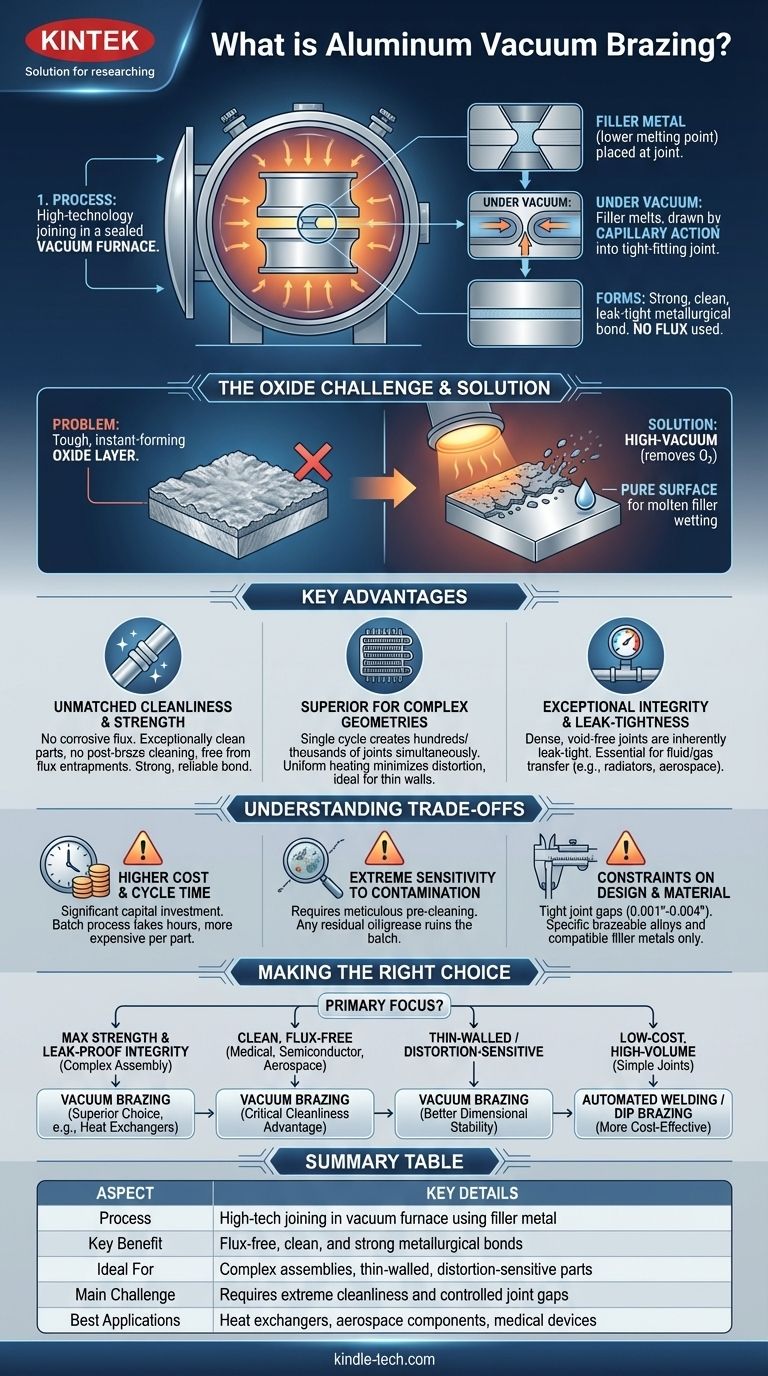
At its core, aluminum vacuum brazing is a high-technology joining process used to create a strong, permanent bond between aluminum parts inside a vacuum furnace. The process involves heating the components with a filler metal that has a lower melting point than the aluminum itself. Under vacuum, this filler melts and is drawn into the tight-fitting joints by capillary action, forming an exceptionally clean, leak-tight, and metallurgically sound connection without the use of chemical flux.
Joining aluminum presents a significant challenge due to its tough, instant-forming oxide layer. Aluminum vacuum brazing overcomes this not with corrosive chemicals, but by using a high-vacuum environment to remove oxygen, enabling a pristine metallurgical bond for complex, high-performance assemblies.
How Does Vacuum Brazing Overcome the Aluminum Challenge?
To understand the value of this process, you must first understand the fundamental problem it solves. The principles are straightforward but have profound implications for component quality and design freedom.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
The entire process takes place in a sealed chamber where pressure is reduced to a near-perfect vacuum (typically 10⁻⁵ Torr or lower). This environment is not just a container; it is an active part of the process.
By removing virtually all oxygen, the vacuum prevents the aluminum parts from oxidizing as they are heated. This is the key to why the process is "fluxless."
Breaking Down the Oxide Layer
Even with a vacuum, aluminum parts enter the furnace with a pre-existing, tenacious layer of aluminum oxide. The combination of high heat and the vacuum environment, often assisted by small amounts of magnesium in the filler alloy acting as an oxygen "getter," causes this oxide layer to break down and dissipate.
This reveals a pure, pristine aluminum surface, allowing the molten filler metal to properly "wet" the base metal and create a strong bond.
The Filler Metal and Capillary Action
A specialized aluminum-silicon filler alloy, often in the form of a thin foil or paste, is placed at the edge of the joint before heating. As the furnace reaches the precise brazing temperature—just below the melting point of the parent aluminum—the filler melts.
Because the surfaces are perfectly clean, the molten filler is naturally pulled into the microscopic gaps between the parts through a physical phenomenon called capillary action, completely filling the joint.
Key Advantages Over Traditional Joining
Vacuum brazing is not a replacement for all welding or conventional brazing, but it offers distinct advantages for specific, demanding applications.
Unmatched Cleanliness and Strength
Because no corrosive flux is used, the finished parts are exceptionally clean and bright, requiring no post-braze cleaning. The resulting joint is free from flux entrapments that can cause voids, weak spots, or future corrosion, leading to a stronger and more reliable bond.
Superior for Complex and Delicate Geometries
A single cycle in a vacuum furnace can create hundreds or even thousands of joints simultaneously on a complex assembly, such as a heat exchanger. This is impossible with welding, which requires sequential, point-by-point joining. The uniform heating also minimizes distortion, making it ideal for thin-walled components.
Exceptional Joint Integrity and Leak-Tightness
The process produces dense, void-free joints that are inherently leak-tight. This is non-negotiable for applications involving the transfer of fluids or gases, such as radiators, cooling plates for electronics, and aerospace fuel lines.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect for every situation. Objectivity requires acknowledging the limitations of aluminum vacuum brazing.
Higher Process Cost and Cycle Time
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment, and the process itself—involving pump-down, heating, brazing, and controlled cooling—is a batch process that takes several hours. This makes it more expensive per part than most high-volume welding operations.
Extreme Sensitivity to Contamination
The success of a fluxless braze depends entirely on the cleanliness of the components. Any residual oils, greases, or other surface contaminants can outgas in the vacuum, ruining the entire batch. This necessitates a meticulous pre-cleaning process.
Constraints on Design and Material
Joints must be designed with tight, controlled gaps (typically 0.001" - 0.004") to facilitate proper capillary action. Furthermore, only specific "brazeable" grades of aluminum alloys can be used, and the filler metal must be compatible with the parent material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right joining method requires aligning the process capabilities with your primary design and performance goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and leak-proof integrity for a complex assembly: Aluminum vacuum brazing is the superior choice, especially for parts like multi-channel heat exchangers.
- If your primary focus is producing clean, flux-free components for medical, semiconductor, or aerospace use: The inherent cleanliness of vacuum brazing is a critical advantage that avoids potential contamination.
- If your primary focus is joining thin-walled or distortion-sensitive parts: The uniform, controlled heating of vacuum brazing offers far better dimensional stability than localized welding.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, high-volume production of simple joints: Automated welding or dip brazing may be a more cost-effective solution.
By understanding its principles and trade-offs, you can leverage aluminum vacuum brazing to achieve a level of quality and design complexity unattainable with conventional methods.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Process | High-tech joining in vacuum furnace using filler metal |
| Key Benefit | Flux-free, clean, and strong metallurgical bonds |
| Ideal For | Complex assemblies, thin-walled, distortion-sensitive parts |
| Main Challenge | Requires extreme cleanliness and controlled joint gaps |
| Best Applications | Heat exchangers, aerospace components, medical devices |
Ready to enhance your aluminum component quality with precision vacuum brazing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables that support high-performance joining processes like aluminum vacuum brazing. Our expertise helps manufacturers in aerospace, medical, and electronics industries achieve superior joint integrity and cleanliness without flux contamination.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your brazing process and deliver the strong, leak-tight assemblies your applications demand.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Control, Cleanliness, and Quality
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Hot Zone Materials and Processed Metals



















