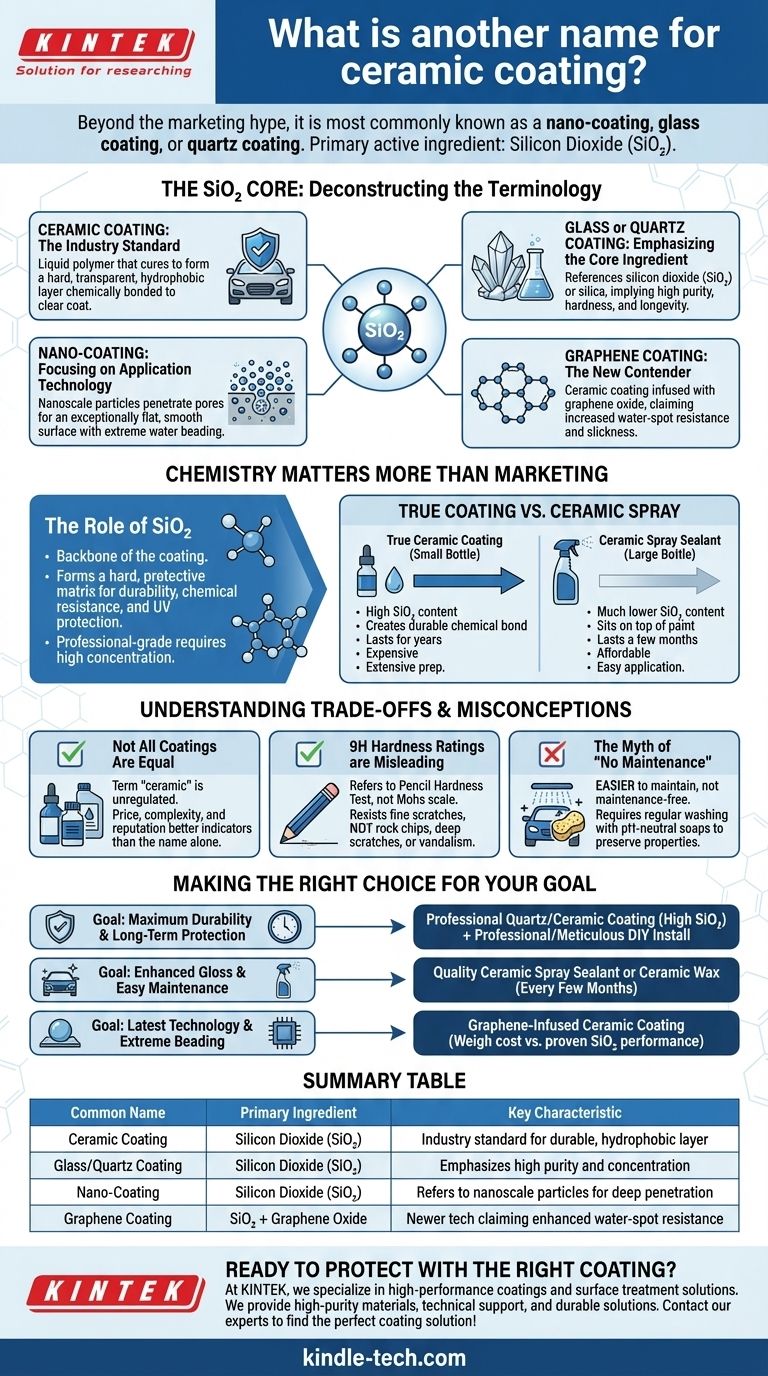
Beyond the marketing hype, a ceramic coating is most commonly known as a nano-coating, glass coating, or quartz coating. These terms are often used interchangeably to describe a liquid polymer protectant whose primary active ingredient is Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂), the same core component found in glass and quartz.
The name on the bottle—whether "ceramic," "glass," or "nano"—is less important than the underlying chemistry. True coatings are defined by a high concentration of Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) that creates a semi-permanent, chemical bond with your vehicle's paint, distinguishing them from less durable, ceramic-infused spray waxes.

Deconstructing the Terminology: What's in a Name?
Understanding the various names used in the market helps clarify what the product is designed to do and how it achieves its protective properties.
Ceramic Coating: The Industry Standard
This is the most widely recognized term. It refers to a liquid polymer that, when applied to a car's clear coat, cures to form a hard, transparent, and hydrophobic layer that chemically bonds with the surface.
Glass or Quartz Coating: Emphasizing the Core Ingredient
These names directly reference the main chemical component: silicon dioxide (SiO₂) or silica, which is the molecular basis for quartz and glass. Manufacturers often use these terms to signal a product with a high purity and concentration of SiO₂, implying greater hardness and longevity.
Nano-Coating: Focusing on the Application Technology
The term "nano" refers to the scale of the particles within the coating's formula. The silicon dioxide particles are engineered at a nanoscale, allowing them to penetrate and fill the microscopic pores and imperfections in your vehicle's clear coat. This creates an exceptionally flat and smooth surface, which is why water beads and sheets off so effectively.
Graphene Coating: The New Contender
A more recent development is the "graphene coating." These are typically ceramic coatings that have been infused with graphene oxide. Proponents claim this adds benefits like increased water-spot resistance and slickness, though the real-world advantages over high-end traditional ceramic coatings are still a subject of debate among professional detailers.
Why Chemistry Matters More Than Marketing
The performance of any coating is dictated by its chemical makeup, not its brand name. Understanding two key components is crucial.
The Role of Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂)
SiO₂ is the backbone of the coating. It forms the hard, protective matrix that delivers durability, chemical resistance, and UV protection. Professional-grade coatings typically contain a high concentration of SiO₂, which requires a careful and controlled application process.
The Spectrum of "Ceramic" Products
A major point of confusion is the difference between a true coating and a "ceramic-infused" product.
A true ceramic coating comes in a small bottle (e.g., 30-50ml), is often expensive, and requires extensive surface preparation. Its high SiO₂ content creates a durable bond that can last for years.
A ceramic spray sealant or wax comes in a larger spray bottle, is affordable, and is easy to apply. It contains a much lower concentration of SiO₂ and sits on top of the paint, offering protection that typically lasts for a few months, not years.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Misconceptions
Ceramic coatings are a significant advancement in paint protection, but it is critical to have realistic expectations.
Not All Coatings Are Created Equal
The term "ceramic" is not regulated. A product can contain a minimal amount of SiO₂ and still be marketed as ceramic. Price, application complexity, and the manufacturer's reputation are often better indicators of performance than the name alone.
Hardness Ratings (9H) Are Misleading
Many coatings advertise a 9H hardness rating. This refers to the pencil hardness test, not the Mohs scale of mineral hardness (where a diamond is 10). A 9H coating is highly resistant to fine scratches and swirl marks from improper washing, but it will not protect your paint from rock chips, deep scratches, or vandalism.
The Myth of "No Maintenance"
A coated vehicle is not maintenance-free; it is easier to maintain. It still requires regular, proper washing with pH-neutral soaps to preserve its hydrophobic properties and appearance. Using harsh detergents or abrasive automatic car washes can degrade and damage the coating over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right product, you must first define your objective, budget, and how much effort you are willing to invest.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and long-term protection: Seek a professional-grade quartz or ceramic coating with a high SiO₂ concentration and plan for professional installation or meticulous DIY prep work.
- If your primary focus is enhanced gloss and easy maintenance with moderate protection: A quality "ceramic spray sealant" or "ceramic wax" is an excellent, user-friendly choice for application every few months.
- If you are exploring the latest technology and want extreme water beading: You can investigate a graphene-infused ceramic coating, but weigh its cost against the proven performance of high-end SiO₂ alternatives.
By looking past the marketing labels and focusing on the underlying chemistry, you can confidently select the right level of protection for your vehicle.
Summary Table:
| Common Name | Primary Ingredient | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Coating | Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) | Industry standard term for a durable, hydrophobic layer |
| Glass/Quartz Coating | Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) | Emphasizes high purity and concentration of the core ingredient |
| Nano-Coating | Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) | Refers to nanoscale particles for deep surface penetration |
| Graphene Coating | SiO₂ + Graphene Oxide | Newer technology claiming enhanced water-spot resistance |
Ready to Protect Your Vehicle with the Right Coating?
Understanding the chemistry behind paint protection is just the first step. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance coatings and surface treatment solutions. Whether you're a professional detailer seeking reliable ceramic coatings or a lab developing new protective formulas, our expertise in materials science can help you achieve superior results.
We provide:
- High-purity materials for coating formulations
- Technical support for surface preparation and application
- Durable solutions for long-term protection
Let's discuss your specific needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect coating solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the thermal properties of quartz? Unlocking Extreme Temperature Stability for Your Lab
- What is high temperature quartz? A Guide to Unmatched Thermal Stability & Purity
- How does quartz differ from glass? A Guide to Material Selection for Performance
- Does quartz have a high melting point? Discover Its Superior High-Temperature Performance
- What is the temperature range of quartz glass? Master Its Thermal Limits for Demanding Applications










