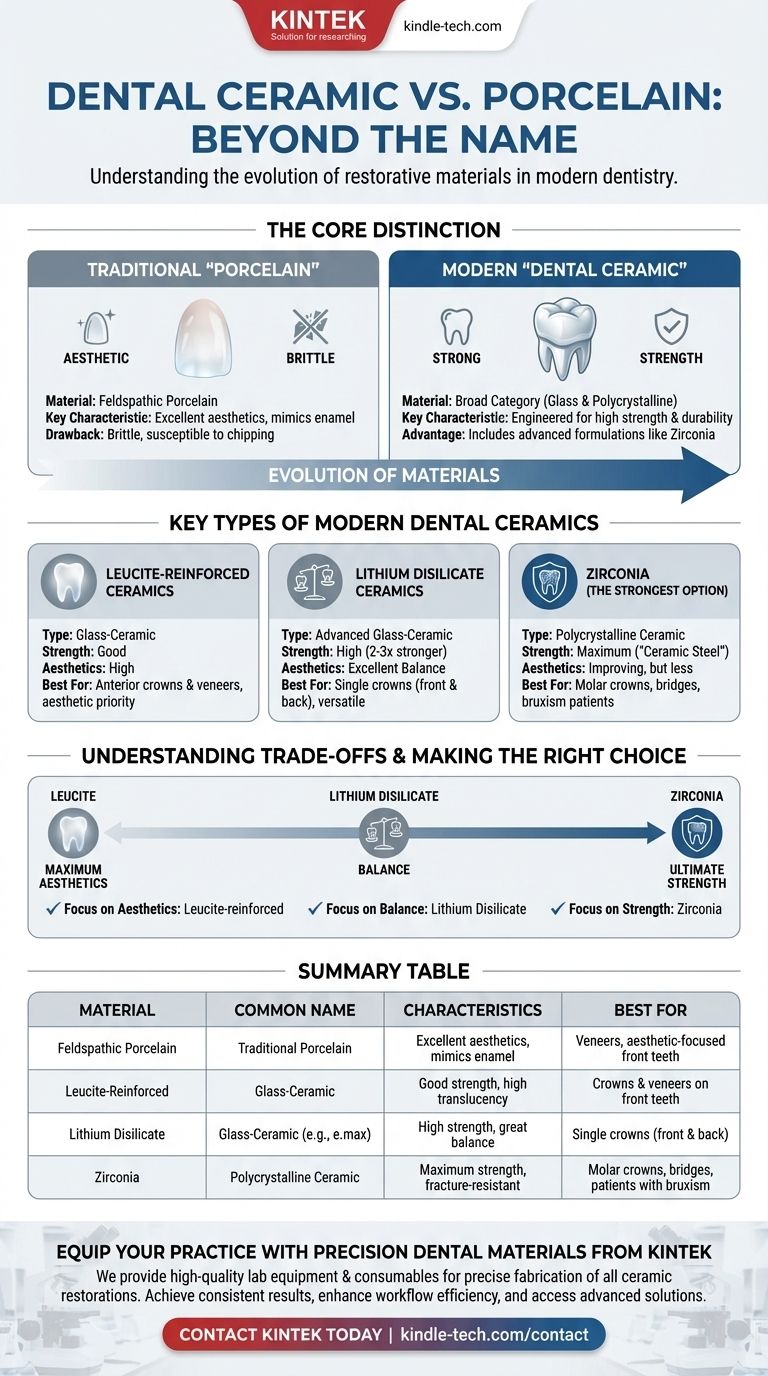
In the world of dentistry, the most common alternative name for dental ceramic is porcelain. While patients and even some professionals use these terms interchangeably, "ceramic" is the more technically accurate term that encompasses a wide range of modern, high-strength restorative materials, including but not limited to traditional porcelain.
The key takeaway is that while "porcelain" is the familiar term, "dental ceramic" refers to a diverse and evolving class of materials. The specific type of ceramic chosen—from aesthetic leucite-based options to high-strength lithium disilicate or zirconia—is a critical decision based on balancing strength, appearance, and the location of the tooth.
From Simple Porcelain to Advanced Ceramics
Understanding the difference between the classic term "porcelain" and the modern term "ceramic" is key to appreciating the advances in restorative dentistry. The terms tell a story of material evolution.
The Traditional "Porcelain"
Historically, dental restorations were made from feldspathic porcelain. This is the material most people imagine—it excels at mimicking the translucency and color of natural tooth enamel.
However, traditional porcelain can be brittle, making it more susceptible to chipping or fracture under heavy biting forces, particularly on back teeth.
The Modern Definition of "Ceramic"
Today, dental ceramic is a broad category of inorganic, non-metallic materials that are hardened by heat. This includes traditional porcelain but has expanded to include far more advanced formulations.
These newer materials are often glass-ceramics or polycrystalline ceramics, which are engineered with added crystals or different structures to dramatically increase their strength and fracture resistance.
Why the Distinction Matters
Using the term "ceramic" acknowledges that your dentist is not limited to one material. They have a toolkit of options, each with a unique profile of strength, translucency, and durability. This allows for a much more customized and resilient restoration than was possible in the past.
Key Types of Modern Dental Ceramics
The choice of ceramic depends entirely on the clinical requirements of your specific case. A front-tooth veneer has very different needs than a molar crown.
Leucite-Reinforced Ceramics
As mentioned in the references, leucite-based materials are a type of glass-ceramic. They are significantly stronger than traditional porcelain while maintaining excellent aesthetics.
These are often a top choice for single crowns and veneers, especially on front teeth where a natural, life-like appearance is the highest priority.
Lithium Disilicate Ceramics
Lithium disilicate is another advanced glass-ceramic known for its exceptional strength and durability, often two to three times stronger than leucite-reinforced materials.
This strength makes it a highly versatile material, suitable for single crowns on both front and back teeth. It provides a fantastic balance of robust performance and high-end aesthetics.
Zirconia: The Strongest Option
Zirconia is a polycrystalline ceramic, meaning it has no glass component. It is the strongest of all dental ceramics, sometimes called "ceramic steel" for its incredible resistance to fracture.
Because of its supreme durability, zirconia is the go-to material for crowns on molars that sustain heavy chewing forces, for multi-tooth bridges, and for patients who grind their teeth (bruxism).
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single material is perfect for every situation. Your dentist weighs several factors to select the optimal ceramic for your restoration.
Aesthetics vs. Strength
The primary trade-off is often between translucency and strength. The most life-like materials (like feldspathic porcelain or leucite ceramics) tend to be less strong than the powerhouse materials.
While newer formulations of zirconia are improving in appearance, they typically cannot match the nuanced translucency of a glass-ceramic.
Preparation and Bonding
The type of ceramic can influence how it is bonded to the tooth and how much of the natural tooth structure needs to be removed. Some materials can be bonded directly to enamel, while others require different cementing protocols.
The Dentist's Expertise
Ultimately, the success of a ceramic restoration depends on the dentist's diagnosis, skill in preparing the tooth, and collaboration with the dental laboratory. The material is just one piece of the puzzle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Restoration
Discussing these options with your dentist is crucial. Understanding the goals for your specific tooth will help you understand their recommendation.
- If your primary focus is maximum aesthetics (e.g., a front tooth veneer): A leucite-reinforced or other highly translucent glass-ceramic is often the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is a balance of strength and beauty (e.g., a front or back crown): Lithium disilicate provides a reliable, durable, and highly aesthetic solution.
- If your primary focus is ultimate strength (e.g., a molar or a dental bridge): Zirconia is the most durable material available and can withstand the most extreme biting forces.
Understanding these material differences empowers you to have a more informed conversation with your dental professional about the long-term health and beauty of your smile.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Name(s) | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feldspathic Porcelain | Traditional Porcelain | Excellent aesthetics, mimics enamel | Veneers, aesthetic-focused front teeth |
| Leucite-Reinforced | Glass-Ceramic | Good strength, high translucency | Crowns & veneers on front teeth |
| Lithium Disilicate | Glass-Ceramic (e.g., e.max) | High strength, great balance of aesthetics & durability | Single crowns (front & back) |
| Zirconia | Polycrystalline Ceramic | Maximum strength, fracture-resistant | Molar crowns, bridges, patients with bruxism |
Equip Your Practice with Precision Dental Materials from KINTEK
Choosing the right dental ceramic is crucial for lasting, beautiful restorations. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables that support the precise fabrication of everything from traditional porcelain to advanced zirconia restorations.
We help dental labs and clinics like yours:
- Achieve Consistent Results: Reliable materials and equipment for predictable aesthetics and strength.
- Enhance Workflow Efficiency: Streamline the production of crowns, veneers, and bridges.
- Access Advanced Solutions: Stay at the forefront of dental ceramic technology.
Ready to elevate the quality of your ceramic restorations? Let's discuss how our products can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact KINTEK today to speak with an expert about your requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Head Tweezers with Pointed Elbow Zirconia Ceramic Tip
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Precision Machined Yttria Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Yttrium Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Rod for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of zirconia ceramics? Unlock High-Performance Solutions for Extreme Environments
- Why is the ball milling process utilized in the preparation of Al2O3-SiC pre-mixed powders? Boost Sintering Performance
- What is the strongest type of zirconia? A Guide to Choosing the Right Dental Zirconia
- What is the main disadvantage of zirconia? Balancing Strength, Aesthetics, and Tooth Wear
- What is the strongest zirconia phase? Tetragonal Zirconia Offers Unmatched Toughness















