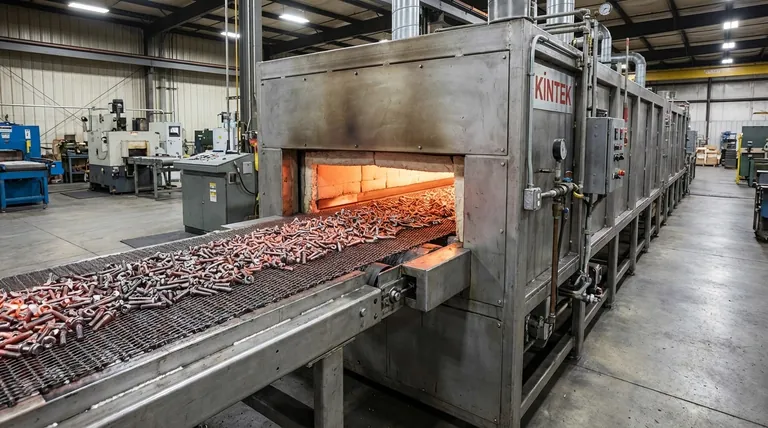
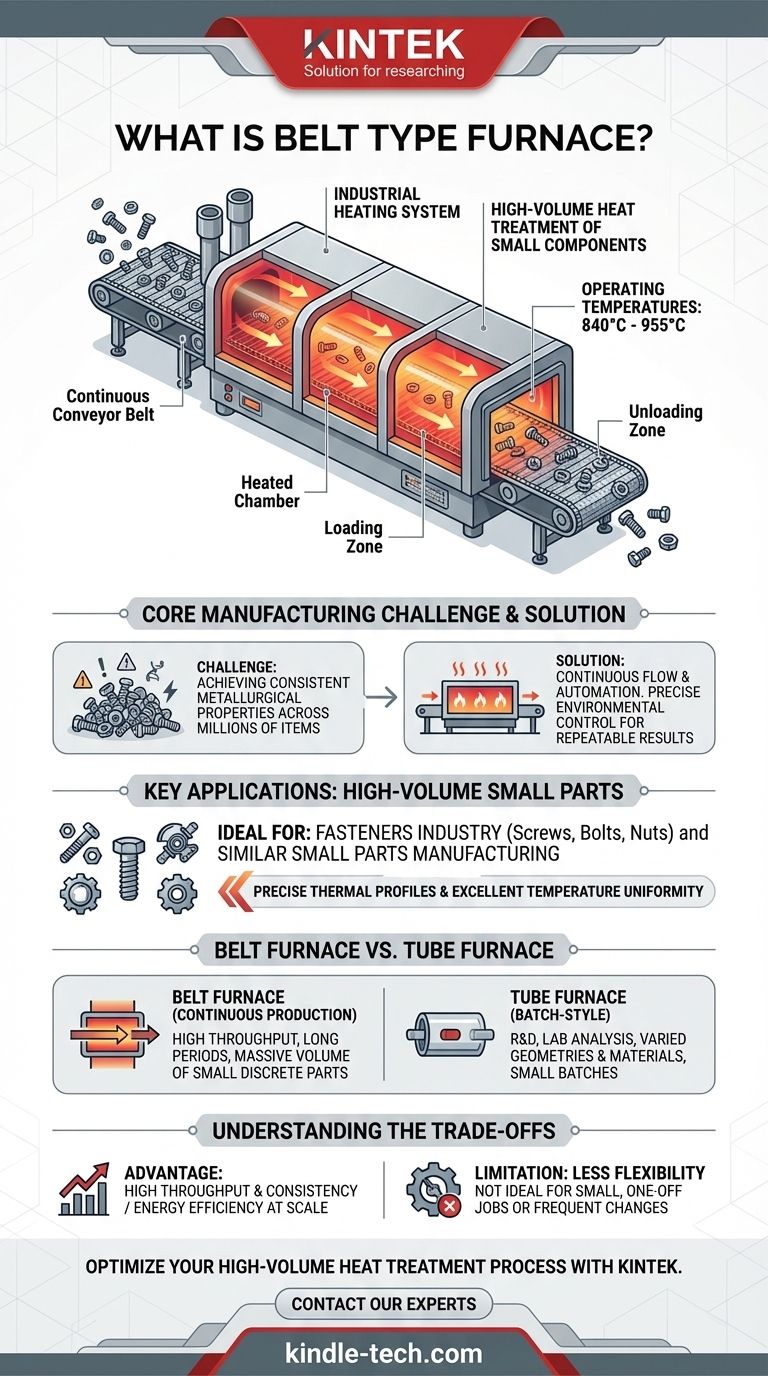
At its core, a belt type furnace is an industrial heating system that uses a continuous conveyor belt, typically made of wire mesh, to move parts through a heated chamber. This design is specifically engineered for the high-volume heat treatment of many small, individual components, such as screws, nuts, and bolts. It allows for consistent and controlled processing in applications like hardening, carbonitriding, and carburizing at temperatures between 840°C and 955°C.
The critical distinction of a belt furnace is its continuous-flow operation. Unlike batch furnaces that process one load at a time, a belt furnace is designed to be an integrated part of a production line, prioritizing high throughput and process uniformity for large quantities of small parts.

How a Belt Furnace Solves a Core Manufacturing Challenge
The primary challenge in mass-producing small metal components is achieving consistent metallurgical properties across millions of individual items. A belt furnace is designed to solve this problem through automation and precise environmental control.
The Continuous Flow Principle
The heart of the system is the conveyor belt. Parts are loaded onto the belt at a controlled rate, which then transports them through various heating and cooling zones within the furnace. This continuous movement ensures that every part experiences the exact same thermal profile, leading to highly predictable and repeatable results.
Key Applications: High-Volume Small Parts
Belt furnaces excel in scenarios where the workload consists of many small, separate items. The mesh belt allows for even heating and ensures that the controlled atmosphere (if used) can circulate freely around each component. This makes it ideal for the fasteners industry (screws, bolts, nuts) and other similar small parts manufacturing.
Achieving Precise Thermal Profiles
Modern belt furnaces offer excellent temperature uniformity, often referred to as an "equal temperature field." This means the temperature is consistent across the width of the belt, preventing hot or cold spots. This precision is critical for advanced heat treatments like carbonitriding, where both temperature and atmosphere composition must be tightly managed to achieve the desired surface hardness.
Belt Furnace vs. Other Common Designs (like Tube Furnaces)
Choosing the right furnace technology depends entirely on the process requirements. Comparing a belt furnace to a different type, like a tube furnace, highlights its specific purpose.
Process Type: Continuous vs. Batch
A belt furnace is built for continuous production. It is meant to run for long periods, processing a steady stream of parts.
A tube furnace, by contrast, is primarily a batch-style furnace. It is better suited for laboratory analysis, research and development, or processing single items, powders, or small, specific loads that require a contained tubular chamber.
Part Geometry and Volume
Belt furnaces are optimized for high volumes of small, discrete parts that can be spread evenly on the belt.
Tube furnaces are more versatile for varied geometries and materials. They can handle powders, wires, or single components that might be too large or awkwardly shaped for a belt. They are not, however, designed for the high-throughput needs of mass production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the belt furnace design involves specific advantages and limitations that are crucial to understand.
Advantage: High Throughput and Consistency
The biggest benefit is the ability to process a massive number of parts with exceptional consistency. The automated, continuous nature removes the variability inherent in manual loading and batch processing, resulting in higher yields and lower per-unit costs at scale.
Advantage: Energy Efficiency at Scale
Once at operating temperature, a continuous belt furnace is highly energy-efficient. Because it doesn't need to be repeatedly heated and cooled like a batch furnace, it maintains a stable thermal state, saving significant energy during long production runs.
Limitation: Less Flexibility
The primary trade-off is a lack of flexibility. Belt furnaces are not ideal for small, one-off jobs or for manufacturers who frequently change the type of part or heat treatment process. Their setup and optimization are geared toward long-term, stable production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace technology is a strategic decision based on your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production of small, similar parts: A belt furnace is the optimal choice for its throughput, consistency, and efficiency at scale.
- If your primary focus is versatile lab analysis, R&D, or processing small, varied batches: A tube furnace or another type of batch furnace offers the necessary flexibility.
Ultimately, the right furnace is the one that best matches the scale and requirements of your specific thermal processing task.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Belt Furnace | Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Continuous | Batch |
| Ideal For | High-volume small parts (screws, nuts) | R&D, lab analysis, varied materials |
| Throughput | Very High | Low to Medium |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
Optimize your high-volume heat treatment process with KINTEK.
Are you manufacturing small components like screws, nuts, or bolts and need consistent, high-throughput heat treatment? KINTEK specializes in industrial belt furnaces designed for precision hardening, carburizing, and carbonitriding at scale. Our solutions deliver the uniform temperature control and automation you need to enhance production efficiency and part quality.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK belt furnace can integrate into your production line and drive your manufacturing success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data



















