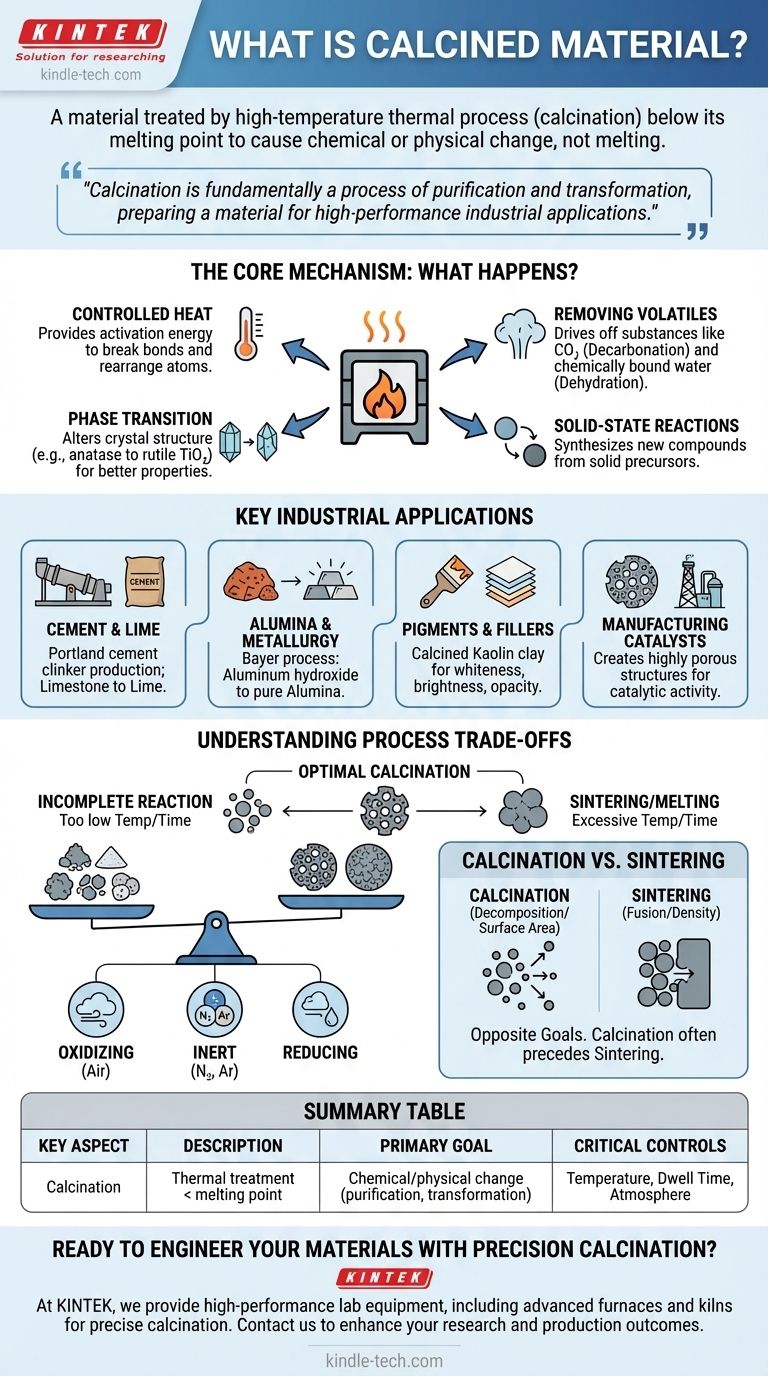
In material science, a calcined material is one that has undergone a high-temperature thermal treatment process known as calcination. This process is conducted below the material's melting point in a controlled atmosphere. The primary purpose is not to melt the substance, but to heat it intensely to cause a chemical or physical change, such as removing volatile components or transforming its crystalline structure.
Calcination is fundamentally a process of purification and transformation. It uses controlled heat to break chemical bonds, drive off impurities, and re-engineer a material’s internal structure, preparing it for a specific, high-performance industrial application.

The Core Mechanism: What Happens During Calcination?
Calcination is a precise thermal process that fundamentally alters a material. The change is driven by carefully controlled variables to achieve a specific outcome.
The Role of Controlled Heat
The essence of calcination is applying heat that is high enough to initiate a reaction but low enough to avoid melting the material. This thermal energy provides the activation energy needed to break chemical bonds and rearrange atoms.
Removing Volatile Components
A primary goal of calcination is to decompose a compound by driving off volatile substances.
- Decarbonation: This involves removing carbon dioxide (CO₂). The most common example is heating limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) to produce lime (calcium oxide, CaO), a critical ingredient in cement manufacturing.
- Dehydration: This is the removal of chemically bound water molecules from a mineral's crystal structure, often called "water of crystallization."
Inducing a Phase Transition
Heat can also force a material to change its crystal structure (polymorphic transformation) without altering its chemical formula. This new phase often possesses more desirable properties. For instance, anatase titanium dioxide can be calcined to form rutile titanium dioxide, which has a higher refractive index and is preferred as a white pigment.
Promoting Solid-State Reactions
Calcination can also be used to synthesize a new compound entirely by reacting two or more solid precursors at high temperatures. The heat facilitates the diffusion of atoms between the solids, forming a new material.
Key Industrial Applications
Calcination is not an abstract laboratory technique; it is a foundational process in numerous large-scale industries.
Cement and Lime Production
The production of Portland cement clinker is one of the largest applications of calcination. A mixture of limestone and clay is heated in a rotary kiln to over 1400°C, driving off CO₂ and forming the complex silicates that give cement its binding properties.
Alumina and Metallurgy
In the Bayer process, aluminum hydroxide is calcined at over 1100°C to produce alumina (aluminum oxide, Al₂O₃). This highly pure, stable alumina is the primary raw material used to produce aluminum metal through electrolysis.
Pigments and Fillers
Calcined kaolin clay is a critical functional additive in paper, paint, and plastics. The process removes water, increases the clay's whiteness and brightness, and creates a more structured particle that improves opacity and durability.
Manufacturing Catalysts
Many industrial catalysts are created by calcining a precursor material. The heat decomposes the precursor and creates a highly porous structure with a large surface area, which is essential for maximizing catalytic activity in processes like petroleum refining.
Understanding the Process Trade-offs
Achieving the desired outcome with calcination requires precise control. Mismanaging the process can render the material useless.
Temperature and Dwell Time
These are the most critical variables. Insufficient temperature or time will result in an incomplete reaction. Conversely, excessive temperature or time can cause sintering—the unwanted fusing of particles, which reduces surface area and porosity—or even outright melting.
The Importance of Atmosphere
The gas environment inside the kiln is crucial.
- Oxidizing (Air): Used when the goal is to burn off organic impurities or promote oxidation.
- Inert (Nitrogen, Argon): Used to prevent unwanted reactions, such as oxidation, when a pure phase change is the only goal.
- Reducing: Used in specific metallurgical applications to remove oxygen.
Calcination vs. Sintering
These two thermal processes are often confused but have opposite goals. Calcination typically aims to decompose a material or increase its surface area. Sintering aims to fuse particles together to increase density and reduce porosity. In many processes, calcination is a necessary first step before a separate, higher-temperature sintering step.
Applying This to Your Goal
The specific objective of calcination dictates the required process parameters. Understanding your goal is the key to controlling the outcome.
- If your primary focus is purification or decomposition: Your goal is to apply just enough heat for a specific duration to drive off a volatile component like H₂O or CO₂ without causing sintering.
- If your primary focus is creating a new crystal phase: Your goal is to hold the material at a specific transition temperature to allow the atomic structure to fully rearrange.
- If your primary focus is increasing porosity for a catalyst: Your goal is to carefully decompose a precursor, creating a "skeletal" structure with a high surface area while strictly avoiding sintering.
Ultimately, calcination is a powerful and versatile tool for engineering the fundamental properties of materials on an industrial scale.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Chemical/physical change via heat, below melting point |
| Common Changes | Removal of volatiles (CO₂, H₂O), phase transitions |
| Main Industries | Cement production, metallurgy, pigments, catalysts |
| Critical Controls | Temperature, dwell time, atmosphere (air, inert, reducing) |
Ready to Engineer Your Materials with Precision Calcination?
Calcination is a critical step for achieving the exact material properties your application demands. Whether you are developing advanced catalysts, producing high-purity ceramics, or processing minerals, the right thermal treatment is key to your success.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including advanced furnaces and kilns designed for precise calcination processes. Our solutions help researchers and industry professionals in materials science, chemistry, and metallurgy achieve consistent, reliable results.
Let KINTEK be your partner in material transformation.
Contact us today to discuss your specific calcination needs and discover how our expertise can enhance your research and production outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing



















