In essence, carbonization is a thermal decomposition process that transforms organic materials, like wood or agricultural waste, into a carbon-rich substance called charcoal. It works by heating the material in a low-oxygen environment, which drives off volatile compounds like water, methane, and hydrogen, leaving behind almost pure carbon.
The core principle of carbonization is not to burn the material, but to "cook" it without sufficient oxygen. This controlled heating breaks down complex organic matter, systematically removing everything that isn't carbon.

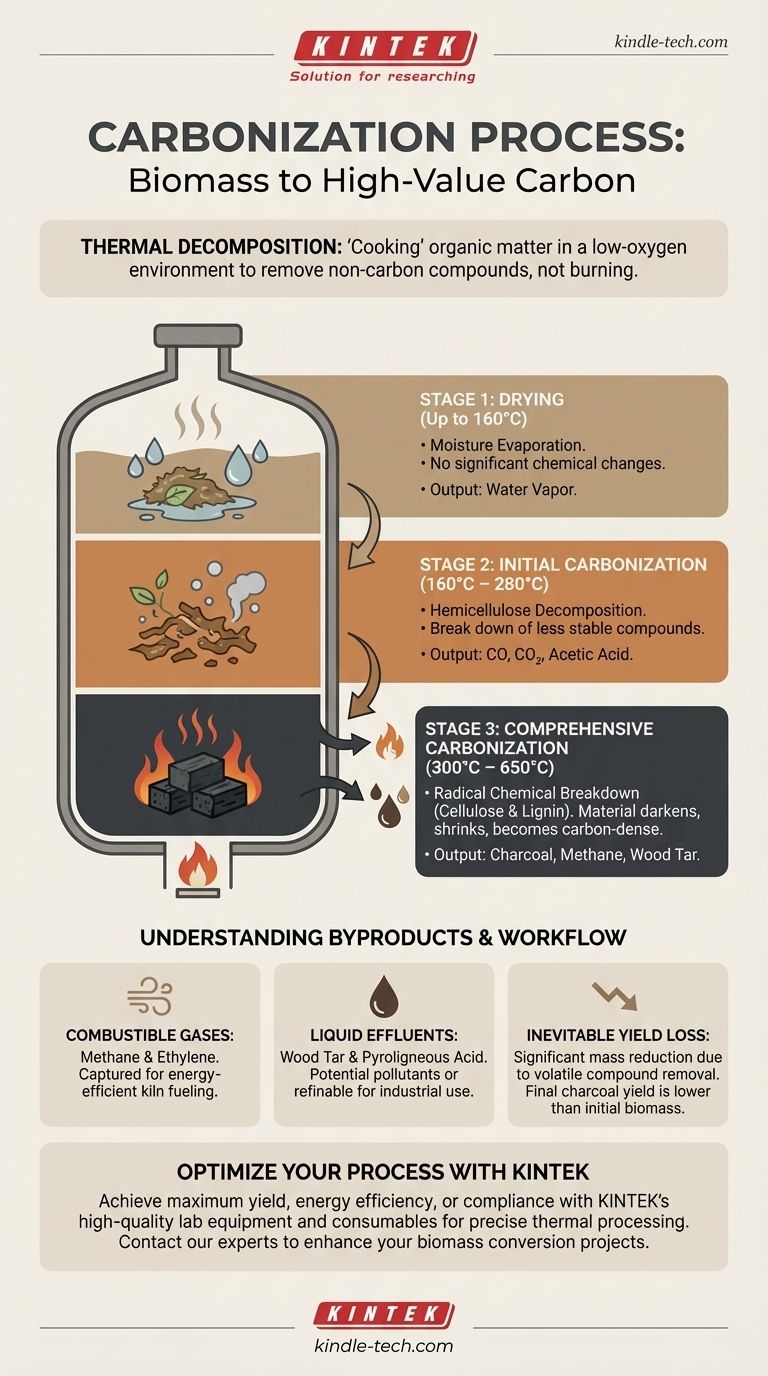
The Core Mechanism: Thermal Decomposition
To truly understand carbonization, you must first grasp the concept of thermal decomposition, also known as pyrolysis. This is the foundation of the entire process.
What is Thermal Decomposition?
Thermal decomposition is a chemical breakdown caused by heat. Instead of reacting with oxygen (burning), the material's own chemical bonds become unstable at high temperatures and break apart into simpler molecules.
The Role of an Oxygen-Free Environment
The key to successful carbonization is limiting oxygen. Sealing the material in a kiln or stove prevents combustion. If ample oxygen were present, the material would simply burn away into ash. By starving the process of oxygen, we ensure it decomposes into charcoal instead.
The Three Stages of Carbonization
The transformation from raw biomass to charcoal happens in distinct stages, dictated by rising temperatures inside the kiln.
Stage 1: Drying (Up to 160°C)
The initial phase is focused entirely on removing moisture. As the temperature rises to 160°C, any water within the biomass evaporates.
At this stage, there are no significant chemical changes. The material is simply being prepared for the decomposition that follows.
Stage 2: Initial Carbonization (160°C – 280°C)
Once the material is dry, true decomposition begins. The least stable organic compounds start to break down.
Specifically, a component called hemicellulose decomposes, releasing gases like carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and small amounts of acetic acid.
Stage 3: Comprehensive Carbonization (300°C – 650°C)
This is the main and most aggressive stage of the process. The temperature climbs significantly, causing a radical chemical breakdown of the remaining organic matter, primarily cellulose and lignin.
During this phase, a large volume of byproducts is released, including flammable gases like methane and ethylene, as well as liquids like wood tar and more acetic acid. The material darkens, shrinks, and becomes the carbon-dense product we know as charcoal.
Understanding the Byproducts and Trade-offs
The substances released during carbonization are not just waste; they are a critical part of the process with significant implications.
Combustible Gases
The methane and ethylene produced in Stage 3 are flammable. In modern carbonization systems, these gases are often captured and redirected to help fuel the kiln, creating a more energy-efficient, self-sustaining process.
Liquid Effluents
The process also creates liquids like wood tar (a complex mixture of organic compounds) and pyroligneous acid (primarily acetic acid and methanol). These byproducts can be environmental pollutants if not managed correctly, but they can also be collected and refined for various industrial uses.
The Inevitable Yield Loss
It is critical to understand that carbonization fundamentally reduces mass. A significant portion of the initial material's weight is lost as water vapor and volatile compounds. The final charcoal yield is always much lower than the starting weight of the biomass.
The Practical Workflow
While the chemistry is complex, the physical steps of the process are straightforward.
1. Loading and Sealing
The raw biomass (e.g., wood logs, briquettes) is loaded into a specialized oven or kiln. The container is then sealed to restrict airflow and create the necessary low-oxygen environment.
2. Heating and Decomposition
An external heat source initiates the process. As the internal temperature rises through the three stages, the biomass transforms into charcoal. In many systems, the process becomes self-sustaining once the flammable gases are released and ignited.
3. Cooling and Extraction
After the decomposition is complete, the charcoal must be allowed to cool down completely, still in a sealed, oxygen-free environment. Introducing oxygen while the charcoal is still hot would cause it to ignite. Once cool, it can be safely removed.
Applying This to Your Goal
Your approach to carbonization will depend on what you want to achieve.
- If your primary focus is maximum charcoal yield: Prioritize precise temperature control and ensuring the kiln is perfectly sealed to prevent any loss of product to combustion.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Design a system to capture and reuse the combustible gases produced during Stage 3 to minimize external fuel consumption.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: You must have a clear plan for safely managing or refining the liquid byproducts like wood tar and acidic liquids.
Ultimately, carbonization is a powerful and controlled method for refining organic matter into a stable, high-energy form of carbon.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Temperature Range | Key Process | Main Outputs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Drying | Up to 160°C | Moisture evaporation | Water vapor |
| 2. Initial Carbonization | 160°C – 280°C | Hemicellulose decomposition | CO, CO2, acetic acid |
| 3. Comprehensive Carbonization | 300°C – 650°C | Cellulose & lignin breakdown | Charcoal, methane, wood tar |
Ready to optimize your carbonization process?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processing. Whether your goal is maximum charcoal yield, energy efficiency, or environmental compliance, our solutions provide the control and reliability you need.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our kilns and laboratory systems can enhance your biomass conversion projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is graphite used for heat transfer? For Superior In-Plane Thermal Conductivity
- What is the temperature of atomic absorption in graphite furnace? Mastering the Multi-Stage Heating Program
- Is graphite good for high temperature? Unlock Its Full Potential in Controlled Atmospheres
- What is isostatic graphite? The Ultimate Material for High-Tech and High-Temperature Applications
- What is the difference between extruded and isostatic graphite? A Guide to Choosing the Right Material
- What is the process of isostatic graphite manufacturing? Achieve Unmatched Material Uniformity and Performance
- What is the function of the graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat for Analysis & Materials Processing
- What is the temperature of graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry? Mastering the Multi-Stage Heating Program



















