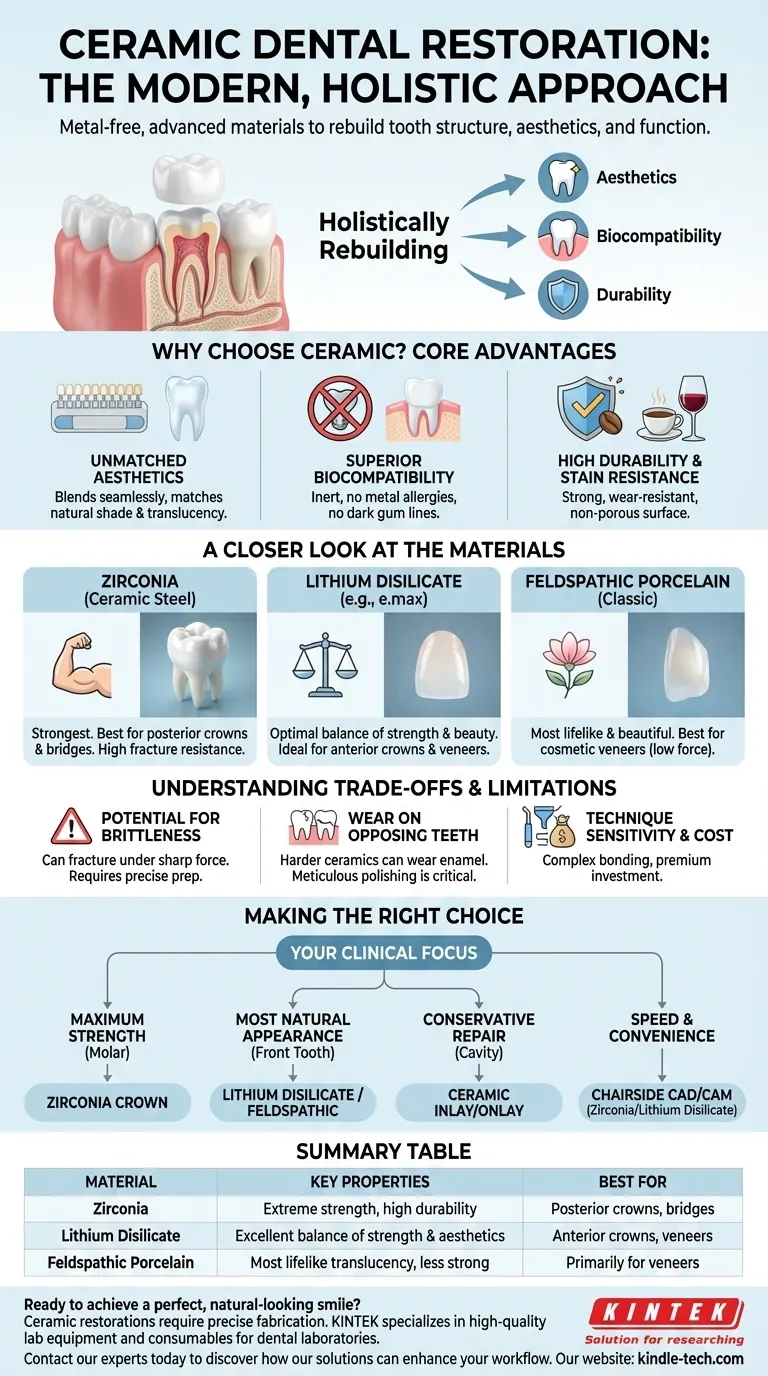
In modern dentistry, ceramic restorations are advanced, metal-free materials used to repair or replace damaged tooth structure. These restorations, which include crowns, veneers, inlays, and bridges, are crafted from high-strength dental ceramics to precisely mimic the color, translucency, and function of natural teeth. They are the cornerstone of aesthetic and biocompatible dental reconstruction.
The core shift in restorative dentistry is from simply "filling a space" to "holistically rebuilding" a tooth. Ceramic restorations achieve this by offering a unique combination of lifelike aesthetics, excellent biocompatibility, and robust durability, making them a superior choice for a wide range of clinical situations.
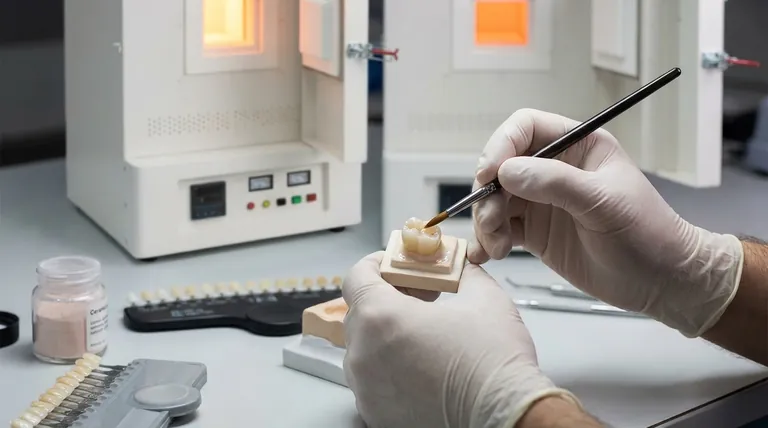

Why Choose Ceramic? The Core Advantages
The preference for ceramic materials over traditional options like metal amalgam or gold is driven by three primary factors.
Unmatched Aesthetics
Ceramics can be manufactured to match the specific shade, translucency, and character of a patient's natural teeth. This allows the restoration to blend seamlessly, making it virtually indistinguishable from the surrounding dentition—a critical factor for front teeth.
Superior Biocompatibility
Dental ceramics are inert, meaning they do not react with the body's tissues. This eliminates the risk of metal allergies (seen with some alloys), metallic taste, or the dark "gum line tattoo" that can occur with porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) crowns.
High Durability and Stain Resistance
Modern ceramic materials are incredibly strong and wear-resistant. Unlike composite resin, their non-porous surface is highly resistant to staining from coffee, tea, and wine, ensuring the restoration maintains its color for years.
A Closer Look at the Materials
The term "ceramic" encompasses several distinct materials, each with specific properties suited for different applications.
Zirconia (Zirconium Dioxide)
Often called "ceramic steel," zirconia is the strongest ceramic material available. Its exceptional fracture resistance makes it the ideal choice for posterior crowns and multi-unit bridges that must withstand immense chewing forces. While traditionally more opaque, newer formulations offer improved translucency.
Lithium Disilicate (e.g., IPS e.max)
Lithium disilicate strikes an optimal balance between strength and beauty. It is significantly stronger than older porcelains but possesses outstanding translucency and optical properties. This makes it the go-to material for highly aesthetic single crowns, veneers, and inlays, especially on visible teeth.
Feldspathic Porcelain
This is the original, classic porcelain used in dentistry. While it is the most beautiful and lifelike ceramic, it is also the most brittle. Today, its use is primarily limited to cosmetic veneers on front teeth where chewing forces are minimal and aesthetics are the absolute priority.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While ceramics offer numerous benefits, a balanced assessment requires understanding their limitations.
Potential for Brittleness
Unlike metals, which can bend or deform under pressure, ceramics are brittle and can fracture if subjected to a sharp, excessive force. Proper tooth preparation by the clinician and material selection are crucial to mitigate this risk.
Wear on Opposing Teeth
Because some ceramics (especially early forms of zirconia) are harder than natural tooth enamel, they can cause wear on the opposing teeth over time. Polishing the ceramic surface meticulously is a critical step to minimize this effect.
Technique Sensitivity and Cost
Bonding a ceramic restoration to a tooth is a more complex and moisture-sensitive procedure than cementing a metal crown. This, combined with higher material and lab fabrication costs, generally makes ceramic restorations a more premium investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Restoration
Selecting the appropriate material is a clinical decision based on the specific functional and aesthetic demands of your case.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength for a back molar: A full-contour Zirconia crown is often the most durable and reliable option.
- If your primary focus is the most natural appearance for a front tooth: A Lithium Disilicate or Feldspathic Porcelain restoration provides the best aesthetic outcome.
- If your primary focus is a conservative repair for a cavity: A ceramic inlay or onlay preserves more natural tooth structure than a full crown.
- If your primary focus is speed and convenience: A practice with chairside CAD/CAM technology (like CEREC) can design, mill, and deliver a Zirconia or Lithium Disilicate crown in a single appointment.
Ultimately, understanding the properties of each ceramic material empowers you and your clinician to select a restoration that perfectly balances function, longevity, and aesthetics.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Properties | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Zirconia | Extreme strength, high durability | Posterior crowns, bridges (back teeth) |
| Lithium Disilicate | Excellent balance of strength & aesthetics | Anterior crowns, veneers (front teeth) |
| Feldspathic Porcelain | Most lifelike translucency, less strong | Primarily for veneers on front teeth |
Ready to achieve a perfect, natural-looking smile?
Ceramic restorations require precise fabrication for optimal results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for dental laboratories, providing the tools needed to create durable and aesthetically superior ceramic crowns, veneers, and bridges.
Contact our experts today to discover how our solutions can enhance your dental restoration workflow and help you deliver the best possible care to your patients.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering process of coating? Building Durable, Solid Layers from Powder
- How do you sterilize glassware without an autoclave? A Step-by-Step Guide to Dry Heat Sterilization
- Why is a muffle furnace or oven used for thermal annealing after silver nanowire deposition? Unlock Peak Conductivity
- What is the importance of precise programmed temperature control in a high-temperature furnace? Master Co-Sintering
- How do high-temperature furnaces and ceramic crucibles impact Li-ion battery stability? Master Precision Synthesis














