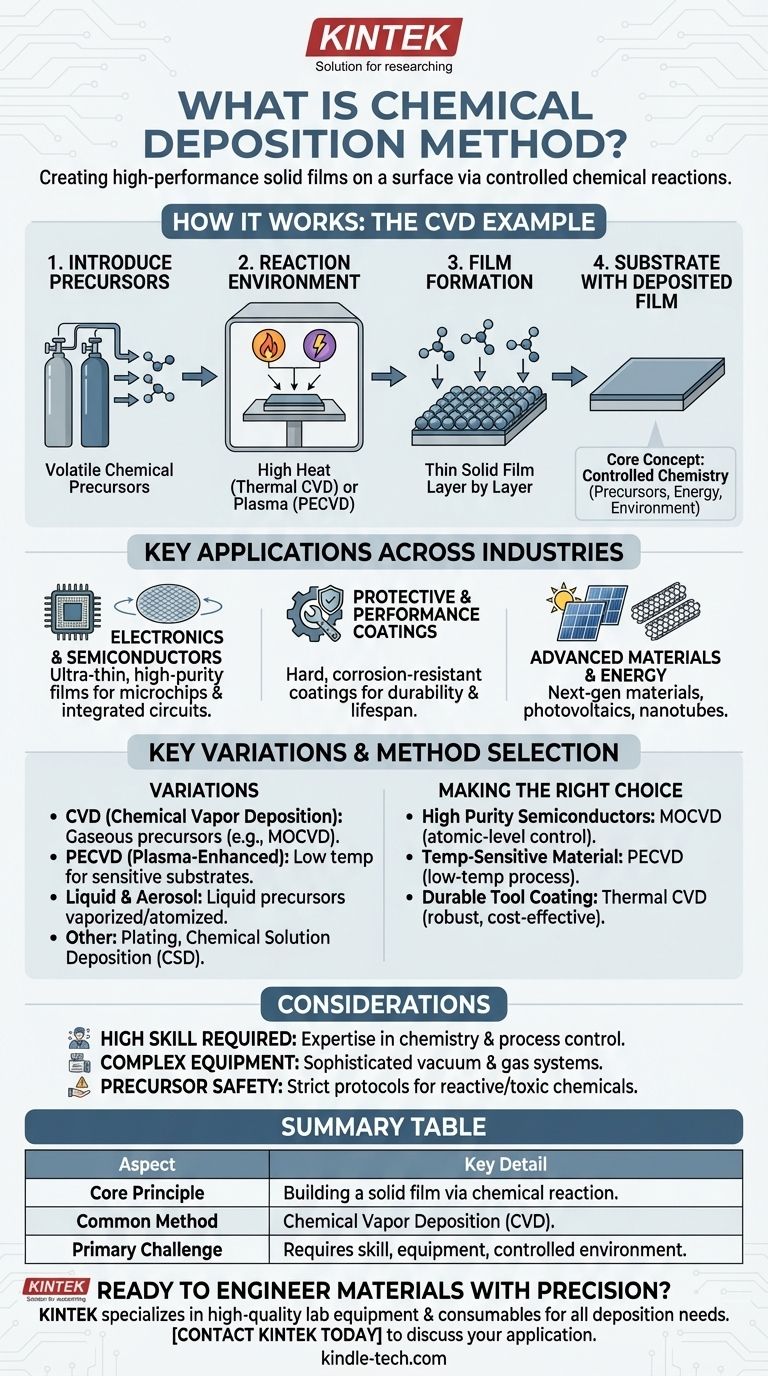
In essence, chemical deposition is a family of processes used to create a high-performance solid film on a surface (known as a substrate) through a chemical reaction. It involves introducing chemical precursors, which react and deposit a new layer onto the substrate, effectively building a thin film from the bottom up. This method is fundamental to manufacturing advanced materials across numerous industries.
The core concept behind all chemical deposition techniques is controlled chemistry. By carefully managing chemical precursors, energy, and the environment, you can grow a thin, solid film with highly specific properties onto a target material.

How Chemical Deposition Works: The CVD Example
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is one of the most common forms of chemical deposition and serves as an excellent model for understanding the fundamental principles of the process.
The Core Principle
The goal of CVD is to expose a target object, or substrate, to volatile chemical precursors. These precursors decompose or react near the substrate's surface, depositing a thin, solid film of the desired material.
Introducing the Precursors
The process begins by introducing precursor chemicals, often in a gaseous state, into a reaction chamber. These precursors contain the specific elements that will make up the final film.
The Reaction Environment
The substrate is placed inside a controlled environment, typically a vacuum chamber. An energy source, such as high heat (Thermal CVD) or plasma (PECVD), is applied. This energy triggers the chemical reaction needed for deposition.
Film Formation on the Substrate
The energy causes the precursor gases to react and solidify onto the substrate's surface. This process builds the film layer by layer, allowing for precise control over its thickness and final properties.
Key Applications Across Industries
Chemical deposition is not an abstract laboratory technique; it is a critical manufacturing process for many of the technologies we rely on.
Electronics and Semiconductors
This is perhaps the most well-known application. Chemical deposition is used to lay down the ultra-thin, high-purity films of silicon, dielectrics, and metals that form the basis of microchips and integrated circuits.
Protective and Performance Coatings
The process is used to apply extremely hard and corrosion-resistant coatings to materials like cutting tools and engine components. These coatings dramatically increase durability and lifespan.
Advanced Materials and Energy
Chemical deposition is essential for fabricating next-generation materials. It is used to grow carbon nanotubes and nanowires and to deposit the critical photovoltaic layers in thin-film solar cells.
Understanding the Key Variations
"Chemical deposition" is an umbrella term for several distinct methods, each suited for different materials and applications.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
As discussed, CVD is a highly versatile method that uses gaseous precursors. Sub-types like Metalorganic CVD (MOCVD) are staples in the semiconductor industry.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
This important variant uses plasma to energize the chemical reaction instead of high heat. This allows for deposition on temperature-sensitive substrates, like certain plastics, that would be damaged by traditional CVD.
Liquid and Aerosol-Based Methods
Techniques like Direct Liquid Injection and Aerosol-Assisted CVD use liquid precursors. These are vaporized or atomized into a mist before entering the reaction chamber, offering flexibility in precursor choice.
Other Deposition Categories
Beyond vapor-based methods, the field also includes plating (like electroless nickel plating) and Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD), where a liquid precursor solution is applied to the surface and then heated to form the film.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While powerful, chemical deposition is a complex process with specific requirements that dictate its feasibility and success.
Requirement for High Skill
These are not simple "plug-and-play" operations. Achieving a high-quality, uniform film requires deep expertise in chemistry, materials science, and process control.
Environmental and Equipment Demands
Most chemical deposition methods require sophisticated equipment, such as vacuum chambers and precise gas-handling systems. Maintaining this controlled environment is critical and can be costly.
Precursor Selection and Safety
The choice of chemical precursors is paramount as it dictates the film's properties. Many of these chemicals are highly reactive, toxic, or flammable, demanding strict safety protocols.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct deposition method depends entirely on your material, substrate, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-purity semiconductor films: Methods like Metalorganic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD) provide the atomic-level control required for complex electronic devices.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is the clear choice, as its low-temperature process prevents damage to the underlying substrate.
- If your primary focus is a durable, wear-resistant tool coating: Traditional thermal CVD is a robust and cost-effective method for applying hard ceramic layers to metals.
Ultimately, understanding the principles of chemical deposition empowers you to engineer materials with precision for nearly any advanced application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Building a solid film on a substrate via a chemical reaction. |
| Common Method | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). |
| Key Applications | Semiconductors, protective coatings, solar cells, nanomaterials. |
| Primary Challenge | Requires high skill, specialized equipment, and controlled environments. |
Ready to engineer materials with precision?
Chemical deposition is a complex process requiring the right equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your deposition needs, from research to production.
Whether you are developing next-generation semiconductors or applying durable protective coatings, our solutions can help you achieve superior results.
Contact KINTALK today to discuss your specific application and discover the perfect deposition solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings



















