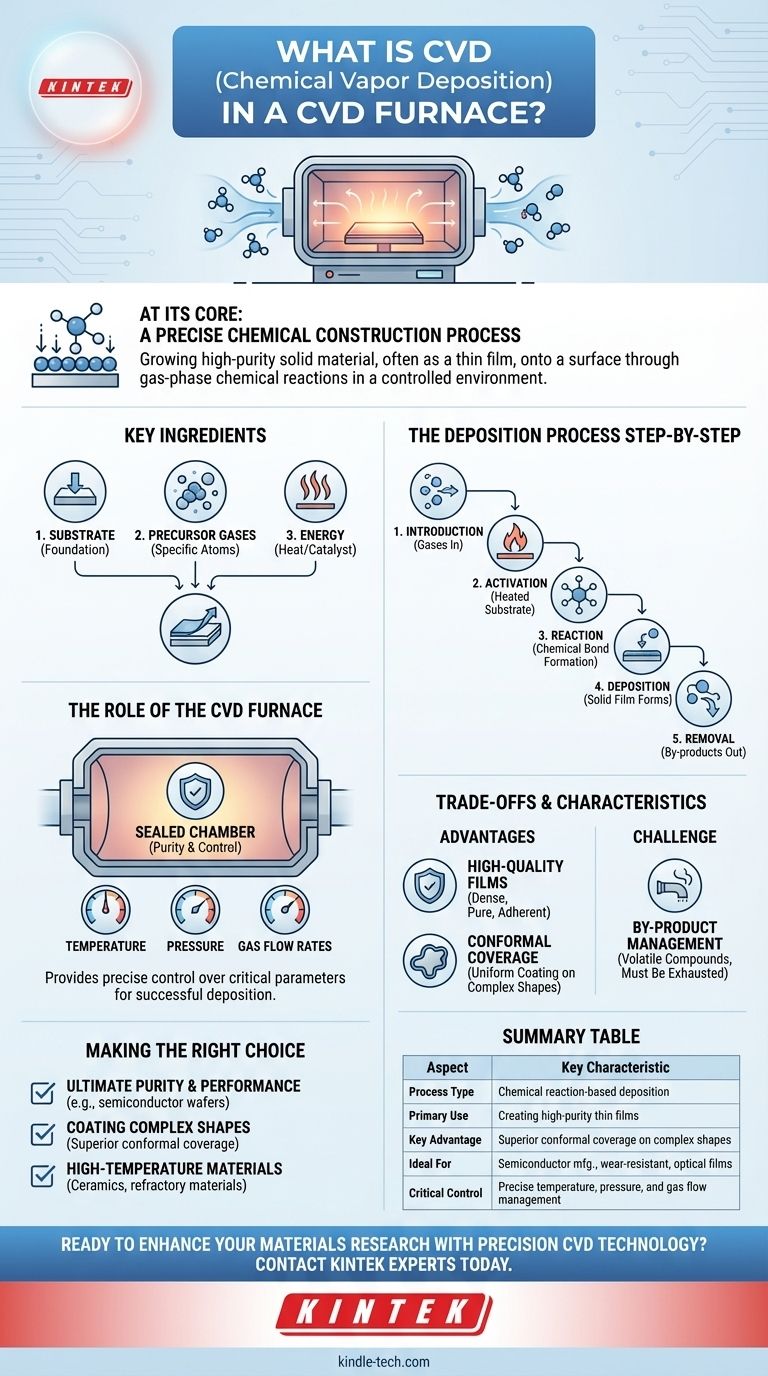
At its core, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a sophisticated process for "growing" a high-purity solid material, often as a thin film, onto a surface. Inside a specialized CVD furnace, volatile precursor gases are introduced and heated, causing them to undergo a chemical reaction or decomposition that deposits a solid layer onto a target object, known as a substrate. This method essentially builds new materials one molecule at a time.
Chemical Vapor Deposition should be understood not as a simple coating technique, but as a precise chemical construction process. It leverages gas-phase reactions in a highly controlled environment to create superior, high-performance solid materials directly on a substrate's surface.

How CVD Fundamentally Works
To grasp the process, it's best to break it down into its essential components and sequence of events. The entire operation is a carefully choreographed chemical reaction at a microscopic level.
The Key Ingredients
The CVD process requires three primary components:
- The Substrate: This is the base material or object that will receive the new film. It acts as the foundation upon which the solid material is grown.
- Precursor Gases: These are volatile chemical compounds in a gas or vapor state. They contain the specific atoms (e.g., silicon, carbon, titanium) needed to create the desired solid film.
- Energy: Typically in the form of heat from the furnace, this energy is the catalyst. It provides the activation energy required to break chemical bonds in the precursor gases and drive the deposition reaction.
The Deposition Process Step-by-Step
The process inside the CVD furnace follows a clear sequence:
- Introduction: One or more precursor gases are fed into the furnace's reaction chamber, which is often held under a vacuum.
- Activation: The substrate is heated to a precise reaction temperature, which in turn heats the precursor gases flowing over its surface.
- Reaction: The heat triggers a chemical reaction. The precursor gases either decompose (break apart) or react with other gases near the hot substrate.
- Deposition: As a result of this reaction, a new, solid material forms and bonds chemically to the substrate's surface, creating a dense and uniform thin film.
- Removal: The reaction also creates volatile by-products (waste gases), which are continuously removed from the chamber by a gas flow or vacuum system.
Why a "Chemical" Reaction is Crucial
The term "chemical" is key. This is not simply condensation, where a gas turns into a liquid or solid. CVD involves the creation of an entirely new solid material through chemical bond formation, resulting in a film that is strongly adhered to the substrate.
The Role of the CVD Furnace
The furnace is much more than a simple oven; it is the self-contained environment where the entire process is managed. Its primary function is to provide precise control over the conditions necessary for a successful deposition.
More Than Just Heat
While providing uniform, stable heat is the furnace's most obvious job, it also serves as a sealed reaction chamber. This containment is critical for maintaining purity and controlling the chemical environment.
Controlling Critical Parameters
To achieve a high-quality film, the furnace system must meticulously manage several variables:
- Temperature: Determines the rate and type of chemical reaction.
- Pressure: The vacuum level affects the purity of the environment and the path of the gas molecules.
- Gas Flow Rates: Precisely controls the supply of precursor gases, directly influencing the composition and growth rate of the film.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Characteristics
Like any advanced manufacturing process, CVD has distinct advantages and inherent challenges that make it suitable for specific applications.
Primary Advantage: High-Quality Films
CVD is renowned for producing exceptionally high-quality materials. The films are typically very dense, pure, and have excellent adhesion to the substrate, making them ideal for high-performance applications.
The Challenge of By-products
Because CVD is a chemical reaction, it always produces by-products. These volatile compounds can be corrosive, toxic, or flammable, and they must be safely managed and exhausted from the system.
Conformal Coverage
A significant strength of CVD is its ability to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes. Since the precursor is a gas, it can penetrate small cavities and coat all exposed surfaces evenly, a feat that is difficult for line-of-sight deposition methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting CVD is a decision based on the required properties of the final material.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and performance: CVD is the premier choice for applications like manufacturing semiconductor wafers, optical coatings, and wear-resistant layers where material integrity is paramount.
- If your primary focus is coating complex or intricate shapes: The gas-based nature of CVD provides superior conformal coverage, ensuring a uniform film thickness even on non-flat surfaces.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature materials: CVD is commonly used to create ceramics and other refractory materials that can withstand extreme thermal environments.
Ultimately, chemical vapor deposition provides a powerful method for constructing materials from the ground up, enabling the creation of advanced films that are often impossible to achieve by other means.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Chemical reaction-based deposition |
| Primary Use | Creating high-purity thin films |
| Key Advantage | Superior conformal coverage on complex shapes |
| Ideal For | Semiconductor manufacturing, wear-resistant coatings, optical films |
| Critical Control | Precise temperature, pressure, and gas flow management |
Ready to enhance your materials research with precision CVD technology? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for laboratory needs. Our CVD furnaces deliver the exact control and reliability required for high-purity thin film deposition. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can accelerate your innovative projects in semiconductor development, advanced coatings, and material science.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- Are CVD diamonds worth it? Unlock Brilliant Value & Ethical Clarity
- What is the construction and working of chemical vapor deposition? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Fabrication
- What is the CVD method for synthetic diamonds? Grow Lab Diamonds from Gas with Precision
- How long does it take to process a CVD diamond? A Guide to the 2-4 Week Growth Cycle
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis

















