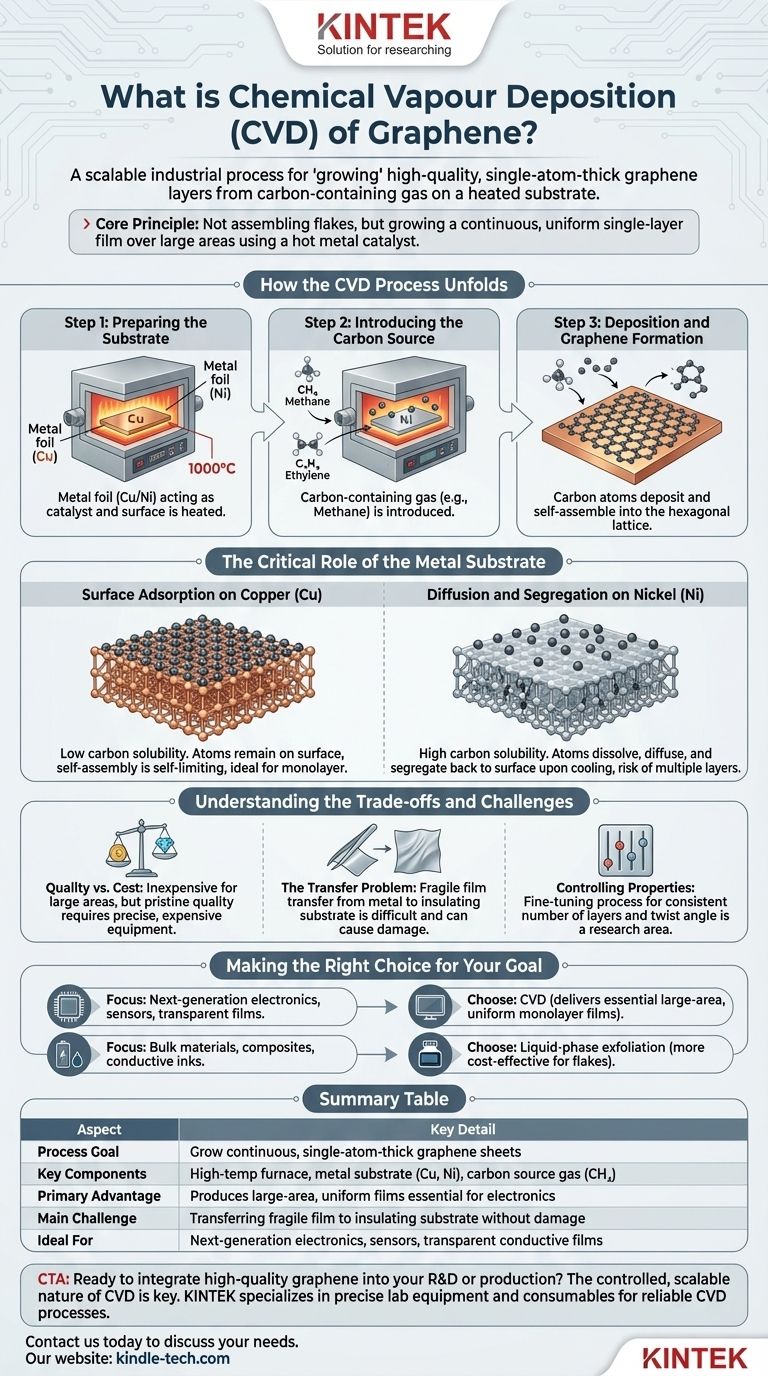
In essence, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a scalable industrial process for "growing" high-quality, single-atom-thick layers of graphene. It involves introducing a carbon-containing gas onto a heated substrate, typically a metal foil, where the gas decomposes and the carbon atoms arrange themselves into the characteristic honeycomb lattice. This method is the most promising and widely used technique for producing the large-area, uniform graphene films required for electronic applications.
The core principle of CVD is not about assembling flakes, but about growing a continuous sheet. By breaking down carbon-based gases on a hot metal catalyst, engineers can form a uniform, single-layer film over large areas, a feat that is difficult with other methods.
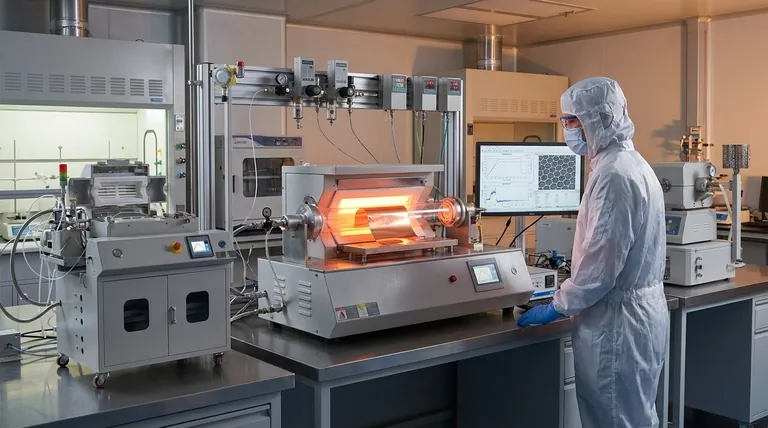

How the CVD Process Unfolds
The CVD method is a carefully controlled sequence of events that takes place inside a high-temperature furnace. Each step is critical to the quality of the final graphene film.
Step 1: Preparing the Substrate
The process begins with a substrate, which acts as both a catalyst and a surface for growth. Foils of metals like copper (Cu) or nickel (Ni) are common choices. This substrate is placed inside a reaction chamber and heated to a high temperature, typically around 1000°C.
Step 2: Introducing the Carbon Source
Once the substrate is hot, a precursor gas containing carbon is introduced into the chamber. Common gases include methane (CH₄), ethylene (C₂H₄), or acetylene (C₂H₂). The versatility of CVD allows for various carbon sources, including liquids, solids, and even waste plastics.
Step 3: Deposition and Graphene Formation
At these high temperatures, the hydrocarbon gas decomposes. The carbon atoms are freed and begin to deposit onto the surface of the hot metal substrate. These atoms then arrange themselves into the stable, hexagonal lattice structure that defines graphene.
The Critical Role of the Metal Substrate
The choice of metal substrate is not arbitrary; it fundamentally changes how the graphene layer forms. The key difference lies in how well the metal dissolves carbon at high temperatures.
Surface Adsorption on Copper (Cu)
Copper has a very low carbon solubility. This means carbon atoms do not dissolve into the bulk metal. Instead, they remain on the surface and self-assemble. This process is largely self-limiting, typically stopping once a complete single layer of graphene has formed, making copper the ideal substrate for producing high-quality monolayer graphene.
Diffusion and Segregation on Nickel (Ni)
In contrast, nickel has a high carbon solubility. At high temperatures, carbon atoms dissolve and diffuse into the bulk of the nickel foil. When the system is cooled, the solubility drops, and the absorbed carbon "precipitates" or segregates back to the surface, forming the graphene layer. This process is harder to control and can result in multiple layers or less uniform films.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While CVD is the leading method for high-quality graphene production, it is essential to understand its practical limitations.
Quality vs. Cost
CVD is considered relatively inexpensive for producing large-area films compared to methods like mechanical exfoliation ("the scotch tape method"). However, achieving pristine, defect-free graphene still requires expensive equipment and precise control over process parameters like temperature, pressure, and gas flow.
The Transfer Problem
Graphene is grown on a metal foil, but for most electronic applications, it needs to be on an insulating substrate like silicon. The process of transferring the fragile, single-atom-thick film from the metal to its final destination is a major challenge. This step can introduce wrinkles, tears, and contamination, degrading the material's exceptional properties.
Controlling the Final Properties
The electrical characteristics of the graphene are highly dependent on factors like the number of layers and the twist angle between them if multiple layers form. Fine-tuning the CVD process to control these factors with perfect consistency remains a significant area of research and development.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a graphene production method depends entirely on the requirements of the end-use application.
- If your primary focus is next-generation electronics, sensors, or transparent conductive films: CVD is the only viable method because it delivers the essential large-area, high-quality, and uniform monolayer films.
- If your primary focus is on bulk materials like composites, conductive inks, or battery additives: Methods like liquid-phase exfoliation are often more cost-effective, as the absolute perfection of a single-layer sheet is less critical than producing large quantities of graphene flakes.
Ultimately, CVD's strength lies in its unique ability to grow a continuous, high-quality graphene sheet, making it the foundational production technique for the future of electronics.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Goal | Grow continuous, single-atom-thick graphene sheets |
| Key Components | High-temperature furnace, metal substrate (e.g., Cu, Ni), carbon source gas (e.g., CH₄) |
| Primary Advantage | Produces large-area, uniform films essential for electronics |
| Main Challenge | Transferring the fragile film to an insulating substrate without damage |
| Ideal For | Next-generation electronics, sensors, transparent conductive films |
Ready to integrate high-quality graphene into your R&D or production?
The controlled, scalable nature of Chemical Vapor Deposition is key to unlocking graphene's potential in advanced applications. KINTEK specializes in the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for reliable CVD processes, serving the exacting needs of materials science and electronics laboratories.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve consistent, high-quality graphene growth for your most innovative projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production



















