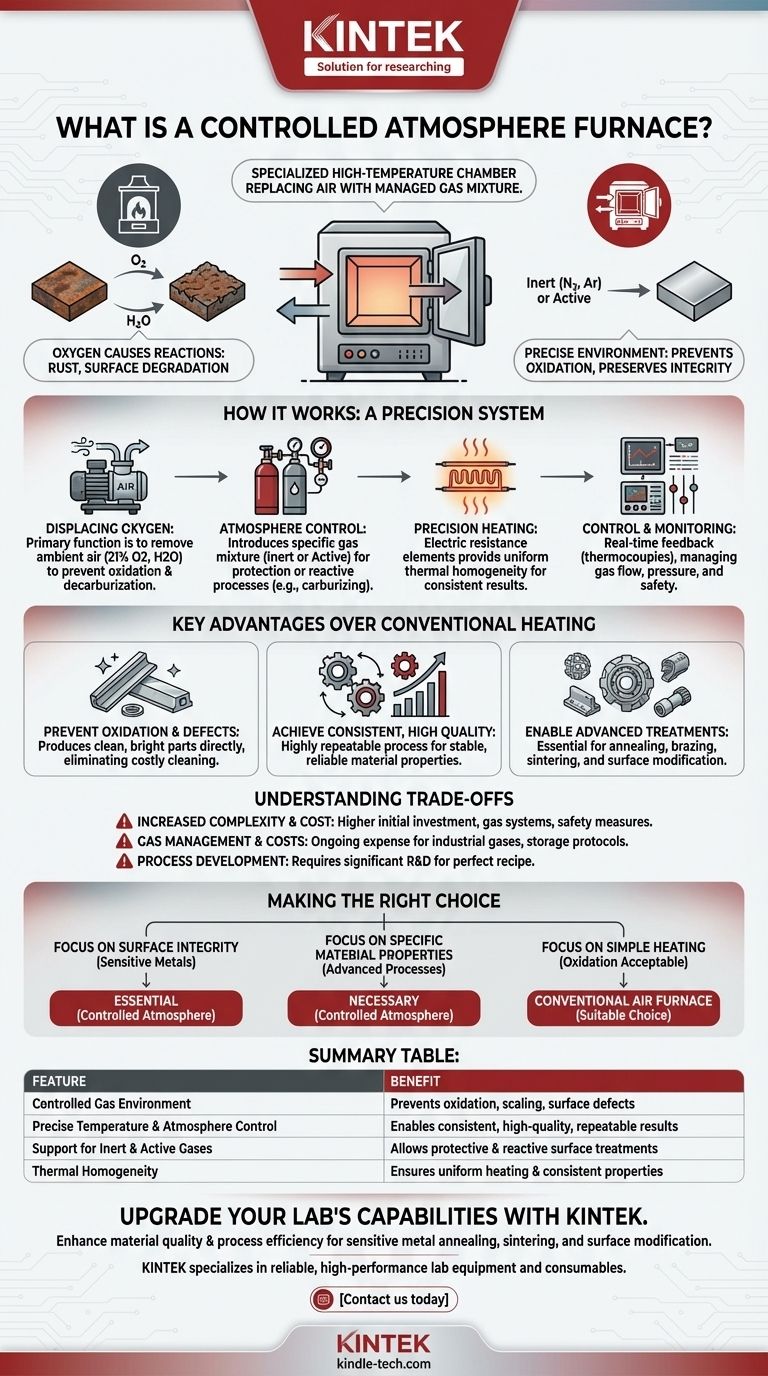
At its core, a controlled atmosphere furnace is a specialized high-temperature chamber that replaces the normal air inside with a carefully managed gas mixture. This precise control over the internal environment allows materials to be heated and cooled without undergoing unwanted chemical reactions, such as oxidation or scaling, that would occur in the presence of oxygen.
The fundamental problem with heating materials in air is that oxygen causes undesirable reactions like rust and surface degradation. A controlled atmosphere furnace solves this by creating a protective, non-reactive (or selectively reactive) environment, ensuring the material's integrity and final properties are preserved.

How a Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Works
A controlled atmosphere furnace is more than just a hot box; it is a precision system where the environment is as critical as the temperature. Each component works together to achieve a highly specific outcome.
The Core Principle: Displacing Oxygen
The primary function is to remove ambient air, which contains roughly 21% oxygen and variable amounts of water vapor, from the heating chamber.
This air is replaced with a specific gas or a blend of gases. This prevents oxidation, decarburization (the loss of carbon from steel), and other chemical changes that could compromise the material's quality.
The Atmosphere Control System: The Critical Component
This is the heart of the furnace. The system introduces a specific gas mixture to create the desired environment.
Gases can be inert, like nitrogen or argon, which simply protect the material from reacting. They can also be active, designed to intentionally react with the material's surface, such as in carburizing or nitriding processes. Precise measurement and control of this gas flow are essential for success.
The Heating System: Precision and Uniformity
Heating is typically accomplished with electric resistance wire elements. These elements generate heat when electricity passes through them.
The furnace is designed to distribute this heat evenly through radiation, ensuring thermal homogeneity. This means the entire part reaches the target temperature uniformly, preventing inconsistencies in the final product.
The Control and Monitoring Systems
Modern furnaces rely on sophisticated control systems. Temperature sensors (like thermocouples) provide real-time feedback, allowing the system to maintain a precise temperature profile.
These systems also manage the gas flow, pressure, and safety interlocks, ensuring the process is both repeatable and safe for operators.
Key Advantages Over Conventional Heating
Using a controlled atmosphere provides significant benefits compared to heating materials in a standard air furnace. The value lies in the quality and consistency of the final product.
Preventing Oxidation and Surface Defects
This is the most significant advantage. For materials like steel, copper, and other alloys, heating in air creates a layer of oxide scale. This scale must often be cleaned off in a separate, costly step. A controlled atmosphere furnace produces clean, bright parts directly from heat treatment.
Achieving Consistent, High-Quality Results
By eliminating the variable of ambient air, the process becomes highly repeatable. This ensures that every part processed has the same material properties, from surface hardness to internal structure. The result is stable, reliable material quality.
Enabling Advanced Heat Treatments
Processes like annealing, brazing, and sintering are dramatically improved when oxygen is removed. Furthermore, advanced surface modification treatments are only possible in a controlled atmosphere where specific reactive gases can be introduced to alter the material's chemistry.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, this technology is not always the necessary choice. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Increased Complexity and Cost
Atmosphere furnaces are more complex and have a higher initial investment cost than simple air furnaces. They require gas delivery systems, flow controllers, and more sophisticated safety measures.
Gas Management and Operating Costs
The ongoing cost of industrial gases can be significant, especially for large-scale operations. Proper storage, handling, and safety protocols for gases like hydrogen or ammonia add another layer of operational requirements.
Process Development
Developing the perfect "recipe"—the exact combination of temperature, time, and gas composition—for a specific material and desired outcome can require significant research and development. It is not always a plug-and-play solution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use a controlled atmosphere furnace should be driven by the required quality of your final product.
- If your primary focus is surface integrity and preventing oxidation: A controlled atmosphere furnace is essential for processing sensitive metals to achieve a clean, scale-free finish.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific material properties: The precise environmental control is necessary for advanced processes like carburizing, nitriding, or bright annealing.
- If your primary focus is simple heating where surface oxidation is acceptable: A less complex and more affordable conventional air furnace may be a perfectly suitable choice.
By controlling the atmosphere, you gain direct control over your material's final quality and performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Controlled Gas Environment | Prevents oxidation, scaling, and surface defects |
| Precise Temperature & Atmosphere Control | Enables consistent, high-quality results and repeatable processes |
| Support for Inert & Active Gases | Allows for both protective and reactive surface treatments (e.g., carburizing) |
| Thermal Homogeneity | Ensures uniform heating and consistent material properties |
Upgrade your lab's capabilities with a controlled atmosphere furnace from KINTEK.
Whether you're working on sensitive metal annealing, advanced sintering, or surface modification processes, our furnaces deliver the precise environmental control you need to prevent oxidation and achieve superior, repeatable results.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory needs with reliable, high-performance solutions.
Contact us today to discuss how a controlled atmosphere furnace can enhance your material quality and process efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes



















