At its core, corrosion is the natural degradation of a refined metal into a more chemically stable form, such as its oxide or sulfide. Within an electrochemical cell, this process is not merely a surface reaction but a complete circuit where the metal essentially self-destructs by creating a tiny, unwanted battery on its own surface.
Corrosion is an electrochemical process because it involves the four essential components of a battery: an anode (where the metal is lost), a cathode, an electrolyte (like water), and a metallic path, all working together to break the metal down.
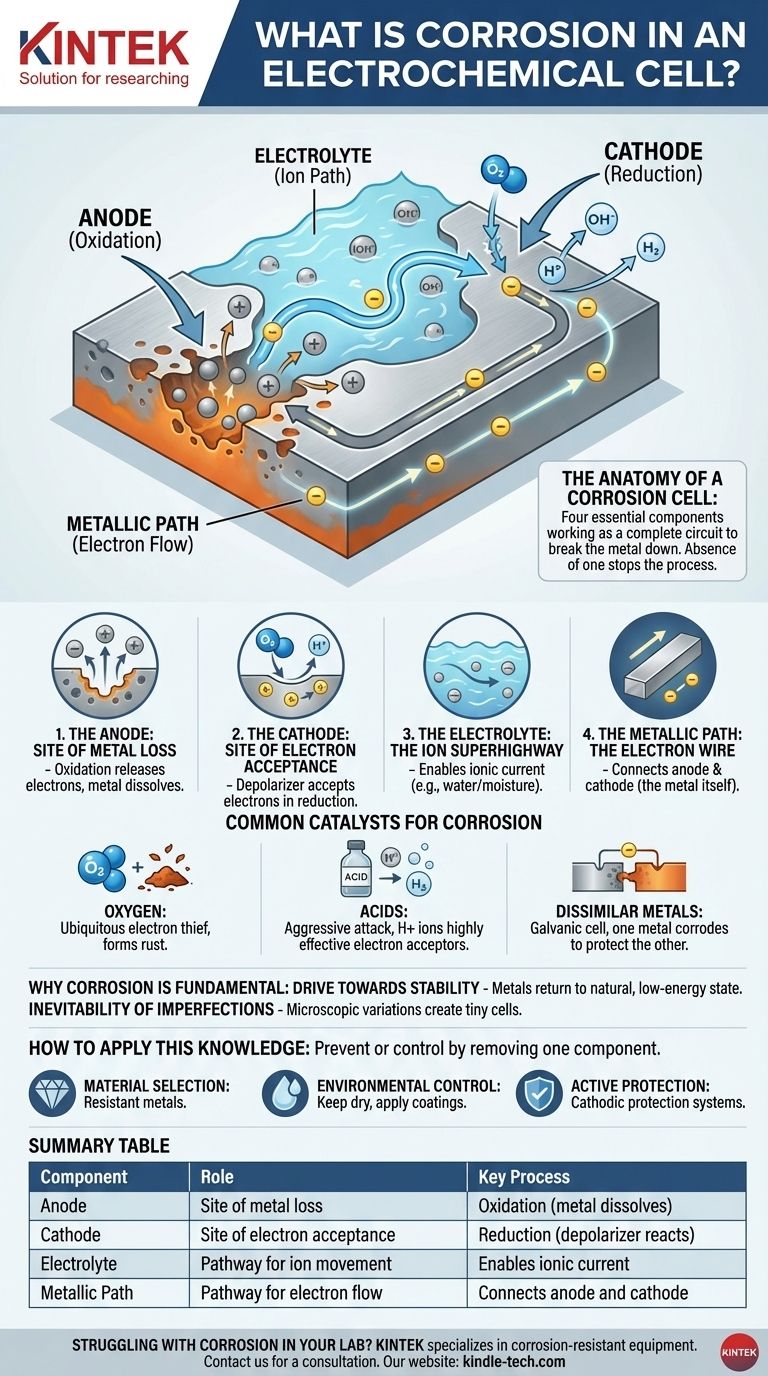
The Anatomy of a Corrosion Cell
To understand corrosion is to understand the four components it requires to function. The absence of any one of these components will stop the process entirely.
The Anode: The Site of Metal Loss
The anodic site is the specific point on the metal surface where corrosion occurs. Here, metal atoms undergo oxidation, losing electrons and transforming into positively charged ions that dissolve into the surrounding water or moisture. This is the physical act of the metal being eaten away.
The Cathode: The Site of Electron Acceptance
The electrons released from the anode travel through the metal to a different location, the cathodic site. Here, a substance in the environment—known as a depolarizer—accepts these electrons in a reduction reaction. This depolarizer is a critical ingredient.
The Electrolyte: The Ion Superhighway
Water, even in microscopic amounts like humidity, acts as the electrolyte. It provides a medium for the dissolved metal ions (from the anode) and other ions to travel, completing the electrical circuit. Without an electrolyte, the ions have no way to move, and the circuit is broken.
The Metallic Path: The Electron Wire
The body of the metal itself serves as the metallic path. It provides a conductive pathway for the electrons to travel from the anode to the cathode. This is why the anodic and cathodic sites can be right next to each other or far apart on the same piece of metal.
Common Catalysts for Corrosion
The rate and severity of corrosion are often dictated by the availability and type of the depolarizer (the electron acceptor) at the cathode.
Oxygen: The Ubiquitous Electron Thief
In most common environments, dissolved oxygen is the primary electron acceptor. This is why water and oxygen together are so destructive to metals like iron, leading to the formation of rust (iron oxide).
Acids: An Aggressive Attack
Acids dramatically accelerate corrosion. The hydrogen ions (H+) in an acidic solution are highly effective electron acceptors, creating hydrogen gas at the cathode. This process is typically much faster and more aggressive than oxygen-driven corrosion.
Dissimilar Metals: The Galvanic Cell
When two different metals are in electrical contact within an electrolyte, they create a galvanic cell. The less noble, more active metal will become the anode and corrode rapidly, while the more noble metal becomes the cathode and is protected. This is why you see sacrificial zinc anodes on boat hulls to protect the steel.
Why Corrosion is a Fundamental Process
Corrosion is not a flaw; it is a natural and spontaneous process driven by fundamental laws of thermodynamics. Understanding this inevitability is key to managing it.
The Drive Towards Stability
Refined metals like aluminum and steel are man-made materials held in a high-energy state. Corrosion is simply the process of that metal returning to its natural, low-energy state, similar to the ore from which it was extracted. The metal is releasing its stored energy.
The Inevitability of Imperfections
No metal surface is perfectly uniform. Microscopic variations in composition, stress from manufacturing, or even differences in oxygen exposure create tiny anodic and cathodic sites all over the surface. These imperfections are all that is needed to initiate thousands of microscopic corrosion cells.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Understanding that corrosion is an electrochemical cell gives you a clear framework for preventing or controlling it. The strategy is always to remove one of the four essential components.
- If your primary focus is material selection: Use metals that are naturally resistant to forming an electrochemical cell in their service environment, or avoid connecting dissimilar metals.
- If your primary focus is environmental control: Eliminate the electrolyte by keeping the metal dry or applying a waterproof coating (like paint) to block moisture from reaching the surface.
- If your primary focus is active protection: Intentionally create a more powerful electrochemical cell where your structural metal is forced to be the cathode. This is the principle behind both sacrificial anodes and cathodic protection systems.
By viewing corrosion as a simple circuit, you can systematically diagnose its cause and effectively interrupt its destructive path.

Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Corrosion Cell | Key Process |
|---|---|---|
| Anode | Site of metal loss | Oxidation (metal dissolves) |
| Cathode | Site of electron acceptance | Reduction (depolarizer reacts) |
| Electrolyte | Pathway for ion movement | Enables ionic current (e.g., water) |
| Metallic Path | Pathway for electron flow | Connects anode and cathode (the metal itself) |
Struggling with corrosion in your lab equipment?
Corrosion can compromise your experiments, damage sensitive instrumentation, and lead to costly downtime. KINTEK specializes in corrosion-resistant lab equipment and consumables, helping you protect your investments and ensure the integrity of your research.
Our experts can help you select the right materials and solutions to interrupt the corrosion circuit in your specific laboratory environment.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and discover how we can help you combat corrosion and enhance your lab's performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Flat Corrosion Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Thin-Layer Spectral Electrolysis Electrochemical Cell
People Also Ask
- What experimental conditions does a three-electrode electrolytic cell provide? Optimize Precise Corrosion Analysis
- What is the primary benefit of micro-electrochemical cells? Maximize Research with Minimal Reagents
- What is the purpose of purging the electrolyte with high-purity inert gases? Ensure Reliable Microbial Electrochemistry
- What are the standard opening specifications for sealed and unsealed all-quartz electrolytic cells? Optimize Your Electrochemistry Setup
- What are the core functions of an electrolytic cell and electrode system in MOF synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Films
- What regular maintenance checks are required for the electrolytic cell system? Ensure Data Accuracy & Equipment Longevity
- What are the advantages of electro-deposition? Achieve Precision Coatings on Complex Shapes
- What are the procedures for after using a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Ensure Equipment Longevity and Data Accuracy



















