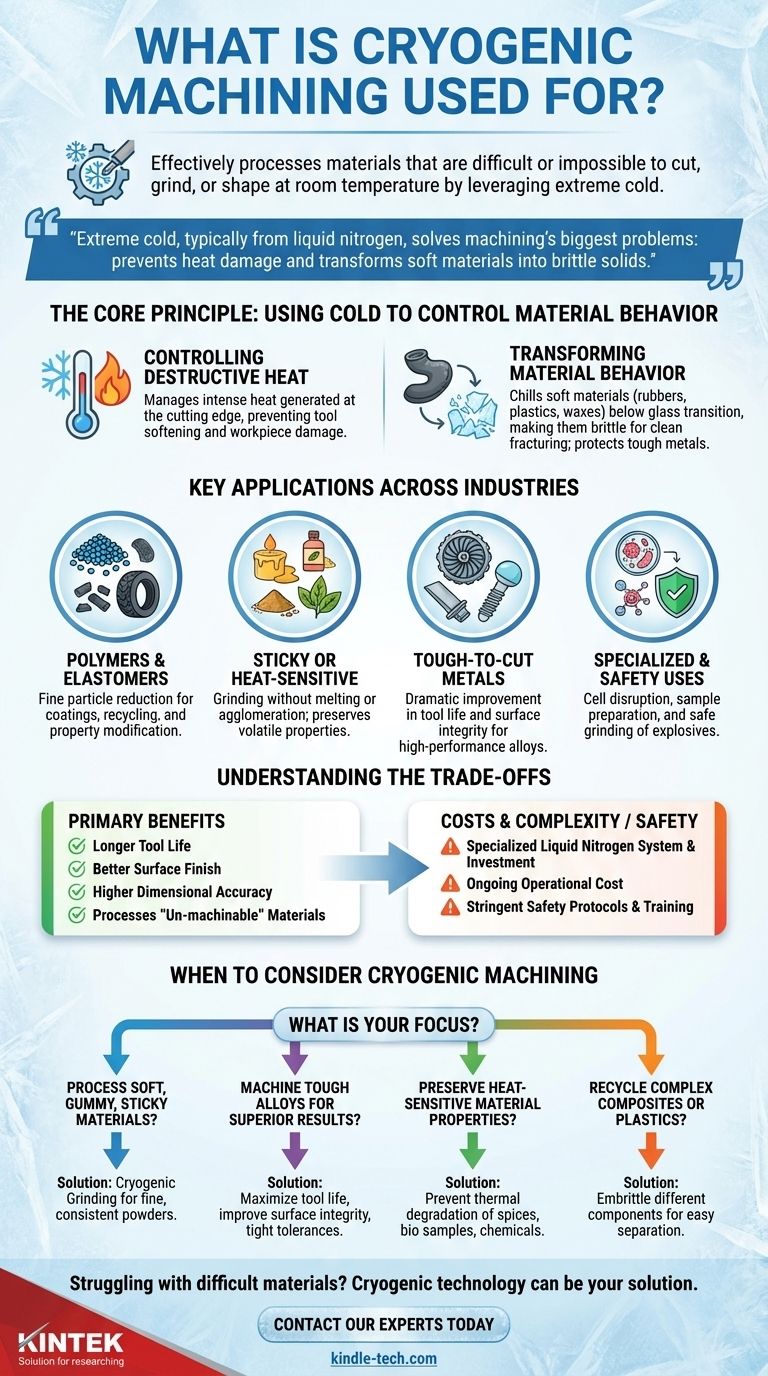
In short, cryogenic machining is used to effectively process materials that are difficult or impossible to cut, grind, or shape at room temperature. It leverages extreme cold to alter a material's properties, making soft materials brittle and controlling the intense heat generated when cutting hard metals, thereby improving tool life, surface finish, and overall efficiency.
The core principle is simple: extreme cold, typically from liquid nitrogen, solves two of machining's biggest problems. It prevents heat from damaging the tool and workpiece, and it transforms soft, gummy materials into hard, brittle solids that can be fractured cleanly.
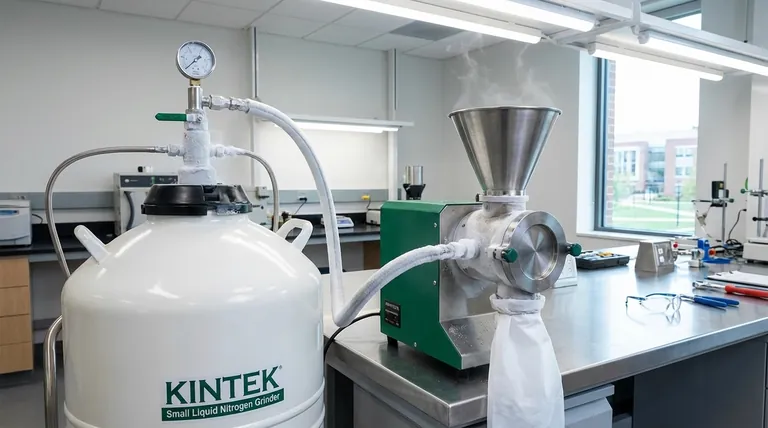

The Core Principle: Using Cold to Control Material Behavior
Traditional machining is a battle against heat and material deformation. Cryogenic machining changes the rules of that battle by introducing extreme cold to the cutting zone, fundamentally altering how the material and cutting tool interact.
The Problem of Destructive Heat
In conventional machining, the friction between the cutting tool and the workpiece generates immense heat. This heat can soften the cutting tool, causing it to wear out quickly, and can also damage the surface of the part being made, reducing its quality and dimensional accuracy.
Making Soft Materials Hard
Many materials, like rubber, certain plastics (nylon, PVC), waxes, and adhesives, are too soft or sticky to machine conventionally. They tend to melt, smear, or deform rather than chip away cleanly. Cryogenic cooling chills these materials below their glass transition temperature, making them hard and brittle like glass, allowing them to be cleanly ground or shattered into fine powders.
Protecting Tough Materials
When machining very hard metals and alloys, the goal isn't to make the material harder, but to manage the extreme heat generated at the tool's cutting edge. Cryogenic cooling extracts this heat with incredible efficiency, keeping the tool hard and sharp while preventing metallurgical damage to the workpiece surface.
Key Applications Across Industries
The unique capabilities of cryogenic machining lend themselves to a surprisingly diverse range of applications where conventional methods fail or underperform.
Processing Polymers and Elastomers
This is one of the most common uses. Cryogenic grinding is essential for the fine particle size reduction of thermoplastics and elastomers. It's used to create powders for coatings, recycle waste rubber and plastic, and modify polymer properties.
Handling Sticky or Heat-Sensitive Materials
Materials like adhesives and waxes are easily ground into powders when frozen, as the cold prevents them from becoming pliable and sticky. Similarly, spices are cryo-ground to preserve their volatile oils and flavoring components, which would be lost due to the heat of traditional grinding.
Machining Tough-to-Cut Metals
For high-performance alloys used in aerospace and medical implants, cryogenic cooling is emerging as a superior method. It dramatically improves tool life and the surface integrity of the finished part, which is critical for components under high stress.
Specialized Scientific and Safety Uses
The technology is also applied in highly specific fields. It is used in microbiology for cell disruption to extract proteins from tissues, for preparing food or even human teeth samples for chemical analysis, and to safely grind explosive materials well below their ignition temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, cryogenic machining is a specialized process with clear benefits and notable complexities. It is not a universal replacement for traditional cooling methods.
The Primary Benefits
The advantages are clear and measurable: longer tool life, better surface finish, and higher dimensional accuracy. It enables the processing of materials that are otherwise "un-machinable" and can lead to increased productivity in niche applications.
The Costs and Complexity
The primary drawback is the cost and complexity of the system. It requires a specialized delivery system for the cryogenic fluid (typically liquid nitrogen) and significant capital investment. The ongoing cost of liquid nitrogen is a major operational expense compared to conventional coolants.
Safety and Handling
Working with cryogenic liquids requires stringent safety protocols. Technicians need specific training to handle materials at such low temperatures to prevent severe cold burns and to ensure proper ventilation, as evaporating nitrogen can displace oxygen in enclosed spaces.
When to Consider Cryogenic Machining
The decision to use cryogenic machining should be driven by the specific material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is processing soft, gummy, or sticky materials: Cryogenic grinding is the ideal solution to achieve fine, consistent powders without melting or agglomeration.
- If your primary focus is machining tough alloys with superior results: Use it to maximize tool life, improve surface integrity, and maintain tight dimensional tolerances.
- If your primary focus is preserving the properties of a heat-sensitive material: It is the best method to grind materials like spices, biological samples, or certain chemicals without thermal degradation.
- If your primary focus is recycling complex composites or plastics: Use it to embrittle different components, making them easier to fracture and separate for recovery.
Ultimately, cryogenic machining is a powerful tool for solving specific, challenging material processing problems that are beyond the reach of conventional methods.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Polymers & Elastomers | Creates fine powders from soft, gummy materials without melting. |
| Tough Metals & Alloys | Extends tool life and improves surface integrity by controlling heat. |
| Heat-Sensitive Materials | Preserves properties of spices, biological samples, and chemicals. |
| Sticky Materials (Adhesives, Waxes) | Prevents agglomeration for clean, fine grinding. |
| Specialized Uses (Safety, Recycling) | Safely grinds explosives and recycles composites by embrittlement. |
Struggling to machine difficult materials? Cryogenic technology can be the solution for your toughest material processing challenges, from improving surface finishes on medical implants to creating fine polymer powders. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables to meet your specific laboratory needs. Contact our experts today to discover how we can enhance your lab's capabilities and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP for Small Workpiece Production 400Mpa
People Also Ask
- Why is cryogenic grinding used? To pulverize tough, heat-sensitive materials effectively.
- What are the benefits of cryogenic machining? Boost Tool Life, Finish, and Productivity
- What is the meaning of cryomilling? Achieve Nanoscale Grain Refinement for Superior Materials
- What is the role of a cryogenic grinder in PET recycling? Transform Waste into High-Reactive Micron Powders
- What is the primary function of a cryogenic ball milling system? Achieve Perfect Polymer Composite Powders
- What is the process of cryo milling? Achieve Nanoscale Powder & Superior Material Properties
- What is the specific utility of cryomilling for Cantor alloys? Unlock High-Strength Nanocrystalline Structures
- What is freeze grinding? Achieve Precise Powdering of Tough, Heat-Sensitive Materials



















