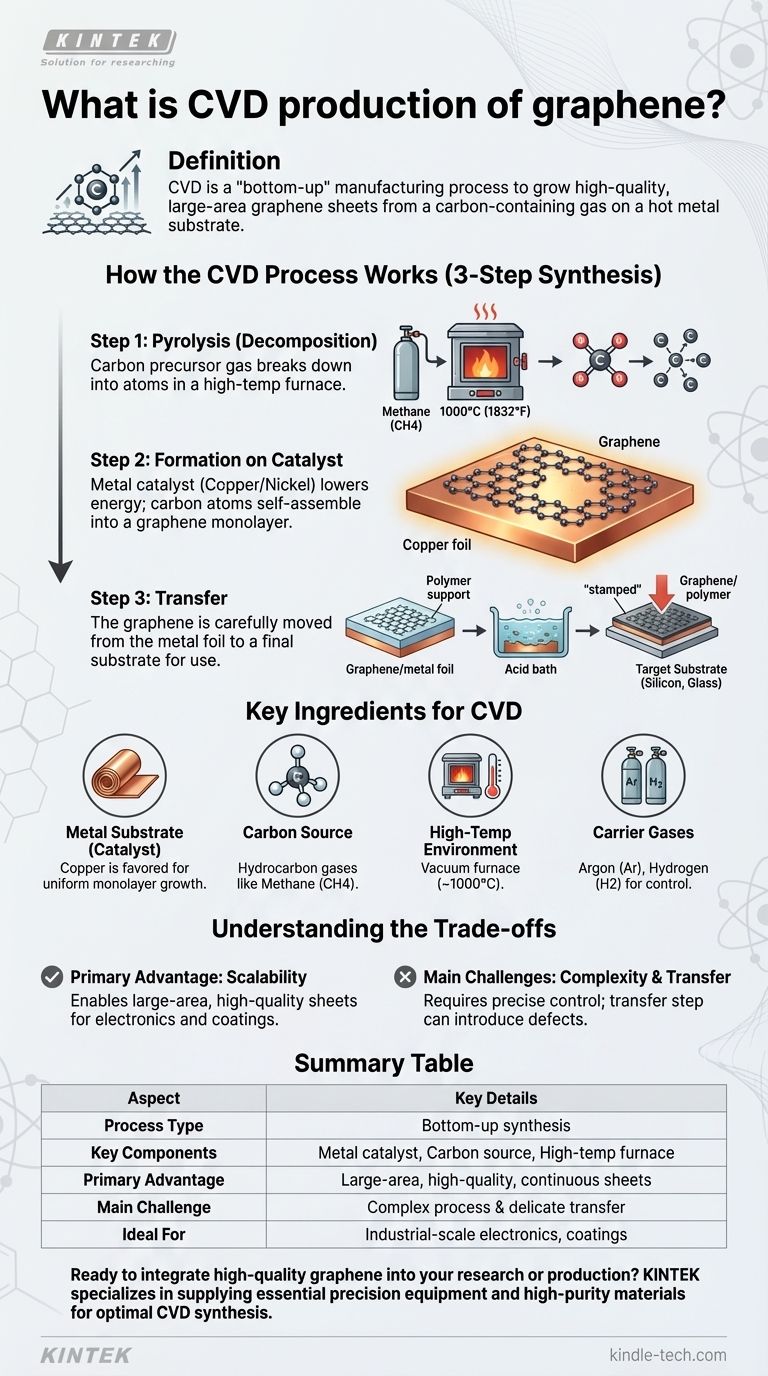
In essence, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a "bottom-up" manufacturing process used to grow high-quality, large-area sheets of graphene. It involves heating a metal substrate, like copper foil, inside a furnace and introducing a carbon-containing gas, such as methane. At very high temperatures, this gas breaks down, and the resulting carbon atoms assemble themselves into a single atomic layer of graphene on the surface of the metal.
The core concept of CVD is using a hot, gaseous chemical reaction to "grow" a perfect, continuous film of graphene on a temporary metallic surface. While it is the premier method for industrial-scale production, it is a complex process that requires a delicate transfer step to move the finished graphene to its final destination.
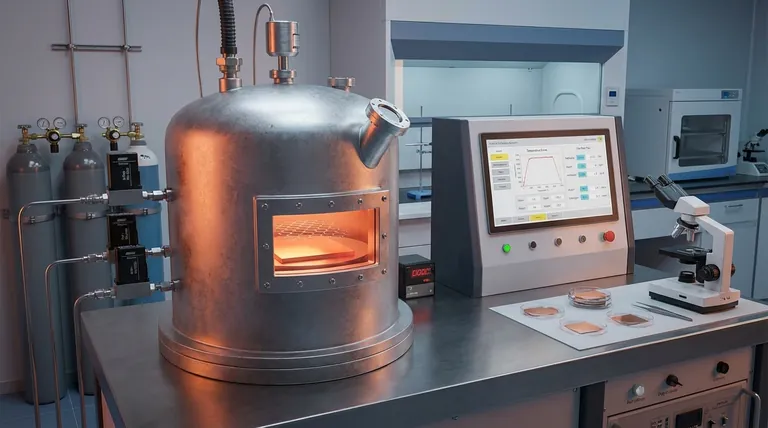

How the CVD Process Works: A Step-by-Step Synthesis
The creation of graphene via CVD is fundamentally a two-stage process that occurs within a controlled, high-temperature environment.
Step 1: Decomposing the Carbon Source (Pyrolysis)
The process begins by placing a metal substrate, typically a thin foil of copper (Cu) or nickel (Ni), into a sealed furnace.
This furnace is heated to extreme temperatures, often around 1000°C (1832°F). A carbon-containing gas, known as the precursor, is then introduced. Methane (CH4) is a very common choice.
The intense heat causes the precursor gas to decompose in a process called pyrolysis, breaking the chemical bonds and releasing individual carbon atoms into the chamber.
Step 2: Graphene Formation on the Catalyst
The metal substrate is not just a surface to grow on; it acts as a catalyst. It lowers the energy required for the carbon atoms to arrange themselves into graphene's signature hexagonal lattice.
These free-floating carbon atoms land on the hot metal surface and self-assemble, atom by atom, into a continuous, one-atom-thick sheet of graphene.
Process conditions like gas flow rate, temperature, and duration are precisely controlled to manage the quality and number of graphene layers grown.
Step 3: Transfer to the Final Substrate
A critical and often overlooked step is that the graphene sheet is now bonded to the metal foil it grew on. To be used in an application like a sensor or screen, it must be moved.
This involves coating the graphene with a polymer support layer, chemically etching away the metal catalyst underneath, and then carefully "stamping" the graphene film onto a target substrate like silicon, glass, or plastic.
The Key Ingredients for CVD Graphene
Successfully producing CVD graphene requires a precise recipe of four essential components.
The Metal Substrate (Catalyst)
Copper and nickel are the most common catalysts. Copper is particularly favored for growing large, uniform monolayer (single-layer) graphene sheets.
The Carbon Source
This is the feed material that supplies the carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon gases like methane, ethane, or acetylene are standard precursors.
The High-Temperature Environment
A vacuum-sealed tube furnace capable of reaching and maintaining temperatures around 1000°C is necessary to drive the chemical reaction.
Carrier Gases
Inert gases like Argon (Ar) and Hydrogen (H2) are used to control the pressure within the chamber and help facilitate the chemical reactions on the catalyst's surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
CVD is a powerful technique, but it comes with distinct advantages and challenges that are important to understand.
The Primary Advantage: Scalability
CVD is effectively the only method capable of producing large-area, high-quality graphene sheets on an industrial scale. This makes it essential for applications in electronics, transparent conductive films, and advanced coatings.
The Challenge: Process Complexity
The process is delicate. It requires precise and stable control over temperature, pressure, and gas flow rates. Any fluctuation can introduce defects into the graphene lattice, compromising its exceptional properties.
The Challenge: The Transfer Step
Moving the ultrathin graphene film from the metal foil to a final substrate is a major engineering hurdle. This transfer process can introduce wrinkles, tears, and contamination, which can degrade the performance of the final device.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a graphene production method depends entirely on the intended use case.
- If your primary focus is large-scale electronics or creating uniform films: CVD is the definitive and leading industry method for producing the necessary large, continuous sheets.
- If your primary focus is R&D, small-scale testing, or creating composite materials: Other methods, like liquid-phase exfoliation of graphite, may be far simpler and more cost-effective if you only need small graphene flakes or a powder.
Ultimately, CVD is the critical technology enabling graphene's transition from a laboratory marvel to a real-world industrial material.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Bottom-up synthesis |
| Key Components | Metal catalyst (e.g., Copper), Carbon source (e.g., Methane), High-temperature furnace (~1000°C) |
| Primary Advantage | Produces large-area, high-quality, continuous graphene sheets |
| Main Challenge | Complex process requiring precise control and a delicate transfer step |
| Ideal For | Industrial-scale applications like electronics, transparent conductive films, and coatings |
Ready to integrate high-quality graphene into your research or production?
The complex CVD process demands precision equipment and reliable consumables to achieve optimal results. KINTEK specializes in supplying the essential lab equipment and high-purity materials—from tube furnaces to metal substrates and gases—that empower researchers and manufacturers to perfect their graphene synthesis.
Let KINTEK be your trusted partner in advanced materials development. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can accelerate your graphene innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance



















