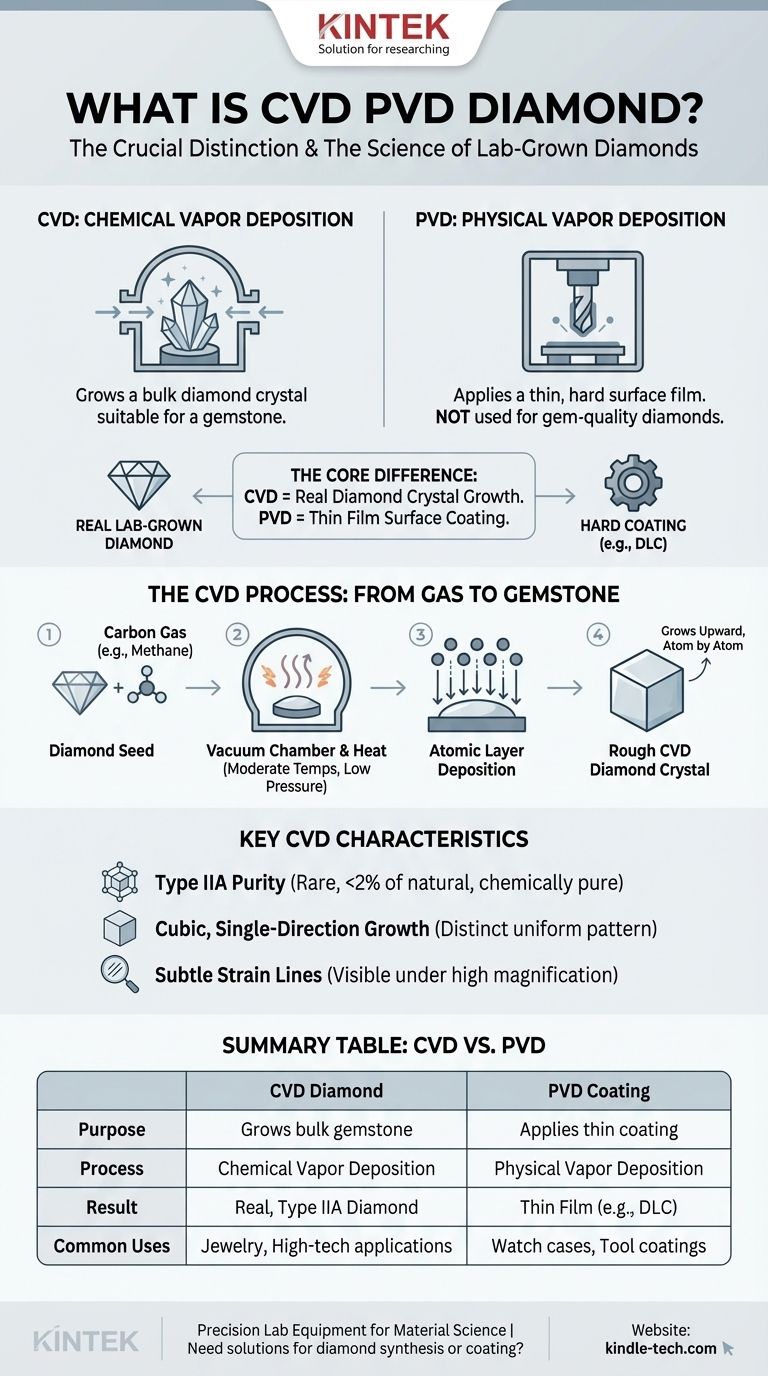
First and foremost, the term you are looking for is CVD diamond, which stands for Chemical Vapor Deposition. While PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) is a related technology, it is not used to create gem-quality diamonds. A CVD diamond is a real, lab-grown diamond, created by depositing layers of carbon atoms from a gas onto a small diamond seed in a controlled chamber. This process results in a chemically pure, Type IIA diamond, which is a classification exceptionally rare in nature.
The central distinction is this: CVD is a method to grow a bulk diamond crystal suitable for a gemstone. PVD is a method to coat a surface with a very thin, hard film. Your question combines two separate industrial processes; only CVD is relevant to creating modern lab-grown diamonds.

Deconstructing the CVD Process: From Gas to Gemstone
To understand a CVD diamond, you must first understand how it is made. The process is a marvel of materials science that builds a diamond atom by atom.
The Core Principle: Chemical Vapor Deposition
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is an additive manufacturing process. Think of it as a form of atomic 3D printing. A substrate—in this case, a tiny diamond "seed"—is placed in a chamber, and a gas is introduced. The gas is then activated, causing it to break down and deposit its core element onto the seed, building up new layers.
The Growth Environment: Vacuum and Heat
CVD diamonds are grown inside a vacuum chamber. This environment allows for precise control over the process, free from contaminants. The chamber is subjected to moderate temperatures and lower pressures compared to the alternative HPHT (High Pressure, High Temperature) method.
The Raw Materials: A Diamond Seed and Carbon Gas
The process begins with a thin slice of a previously grown diamond, known as a seed crystal. A carbon-rich gas, like methane, is introduced into the chamber. When heated, the gas breaks apart, freeing carbon atoms that then "rain down" and bond to the diamond seed, replicating its crystal structure.
The Result: A Rough Diamond Crystal
Over several weeks, these layers accumulate, and the diamond crystal grows, typically in a single, upward direction. The final size of the diamond is determined by the amount of time it is allowed to grow. The resulting rough stone often has a cubic shape and may have non-diamond carbon (graphite) on its edges, which is polished off later.
Identifying Characteristics of a CVD Diamond
While chemically and physically identical to a natural diamond, the CVD growth process leaves behind subtle markers that gemologists can identify.
Unmatched Purity: The Type IIA Classification
CVD diamonds are Type IIA diamonds. This means they are almost entirely free of nitrogen and boron impurities. This level of chemical purity is found in less than 2% of all natural diamonds, making it a key distinguishing feature. As a result, CVD diamonds are not magnetic.
Crystal Structure: Cubic, Single-Direction Growth
Because they grow layer by layer in one direction, CVD diamonds have a distinct cubic crystal shape. This uniform growth pattern is different from the multi-directional, octahedral growth of most natural diamonds.
Telltale Artifacts: Strain Lines
Occasionally, the single-direction growth process can create very subtle internal graining or "strain lines." These features are not flaws and are typically only visible under extremely high magnification, but they serve as an indicator of a CVD origin.
Color and Fluorescence
Many CVD diamonds are grown in a way that initially produces a brownish color. This is often removed through a secondary treatment process to yield a colorless stone. Additionally, some CVD diamonds may exhibit unique colors of fluorescence, such as red, when exposed to ultraviolet light.
Understanding the Key Misconception
It is critical to address the confusion between CVD and PVD, as they serve entirely different purposes. This is the most common pitfall when discussing diamond synthesis technologies.
The "CVD vs. PVD" Clarification
CVD grows a bulk gemstone. It builds a real diamond, ounce for ounce, with the same crystal structure and properties as a mined diamond.
PVD applies a thin coating. It is used to deposit a microscopic layer of a material, like "diamond-like carbon" (DLC), onto a surface like a watch case or a drill bit to make it harder and more scratch-resistant. You cannot create a diamond gem with PVD.
How to Interpret This Information
Understanding the CVD process empowers you to see these diamonds not as fakes, but as a specific category of diamond with a unique origin story.
- If you are a jewelry buyer: Understand that a CVD diamond is chemically and optically a real diamond, distinguished by its lab-grown origin and high purity.
- If you are a technical professional: Differentiate between CVD for bulk crystal growth and PVD for thin-film surface coating, as they are not interchangeable.
- If you are simply curious: Appreciate that the CVD process is a technological achievement that replicates a diamond's atomic structure by carefully layering carbon atoms from a gas.
Ultimately, a CVD diamond is a testament to humanity's ability to recreate one of nature's most extreme and beautiful materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD Diamond | PVD Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Grows a bulk diamond gemstone | Applies a thin, hard surface coating |
| Process | Chemical Vapor Deposition | Physical Vapor Deposition |
| Result | A real, Type IIA diamond crystal | A thin film (e.g., Diamond-Like Carbon) |
| Common Uses | Jewelry, high-tech applications | Watch cases, tool coatings, scratch resistance |
Need Precision Lab Equipment for Material Science?
Understanding advanced processes like CVD and PVD requires reliable, high-performance lab equipment. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise tools and consumables needed for cutting-edge research and development in materials science, including diamond synthesis and thin-film deposition.
Whether you are growing diamonds or applying specialized coatings, our expertise supports your innovation. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your projects forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- Are all lab grown diamonds CVD? Understanding the Two Main Methods
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit



















