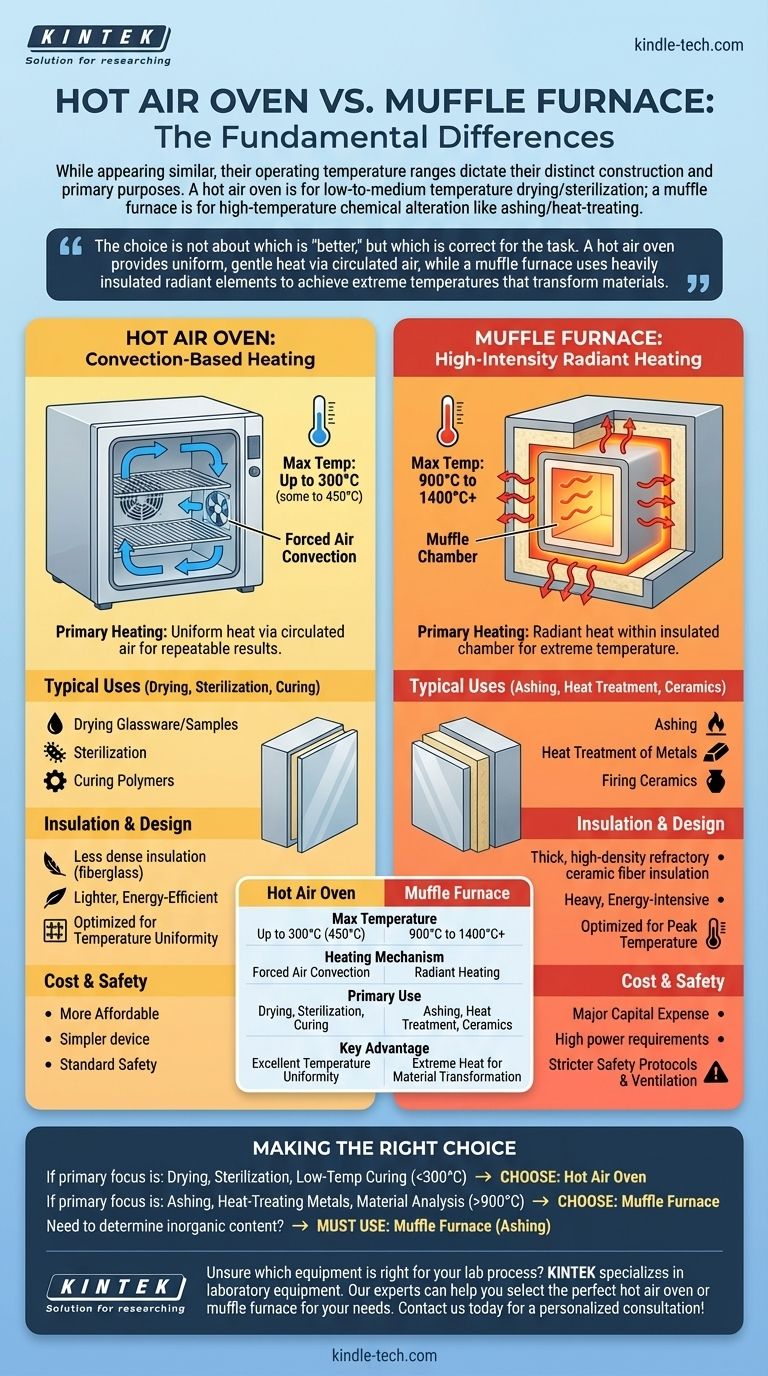
While they may appear similar, the fundamental difference between a hot air oven and a muffle furnace is their operating temperature range, which dictates their construction and primary purpose. A hot air oven is a low-to-medium temperature device used for drying and sterilization, whereas a muffle furnace is a high-temperature unit designed for processes that chemically alter materials, such as ashing or heat-treating metals.
The choice is not about which is "better," but which is correct for the task. A hot air oven provides uniform, gentle heat via circulated air, while a muffle furnace uses heavily insulated radiant elements to achieve extreme temperatures that transform materials.

The Core Difference: Temperature and Heating Mechanism
The vast difference in temperature capability stems from fundamentally different designs for generating and containing heat.
Hot Air Oven: Convection-Based Heating
A hot air oven typically operates in a range from ambient temperature up to 250°C or 300°C, with some models reaching 450°C.
Its primary heating mechanism is forced air convection. A fan actively circulates air past a heating element and throughout the chamber, ensuring a highly uniform temperature. This is critical for applications where every item must be exposed to the same conditions.
Muffle Furnace: High-Intensity Radiant Heating
A muffle furnace is built for extreme heat, with a standard operating range of 900°C to 1400°C or higher.
It uses powerful heating elements that radiate heat within a heavily insulated chamber. The term "muffle" refers to the inner chamber, which isolates the sample from direct contact with the heating elements, preventing contamination from combustion byproducts.
Application Drives the Choice
You do not use a furnace for a task that requires an oven, and vice versa. Their functions are distinct and not interchangeable.
Typical Uses for a Hot Air Oven
The focus here is on removing moisture or microbes without altering the material's chemical structure.
- Drying: Gently removing water from laboratory glassware, chemicals, or biological samples.
- Sterilization: Destroying microorganisms on heat-stable medical and lab equipment (known as dry heat sterilization).
- Curing: Hardening polymers, adhesives, or coatings at controlled, moderate temperatures.
Typical Uses for a Muffle Furnace
The goal of a furnace is to use thermal energy to induce a chemical or physical change.
- Ashing: Burning away all organic material from a sample to determine its inorganic content (ash). This is essential in food science, materials testing, and environmental analysis.
- Heat Treatment: Altering the properties of metals through processes like annealing (softening), hardening, and tempering.
- Ceramics: Firing clays and glazes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Construction
The different applications demand vastly different engineering, creating clear trade-offs in performance, safety, and cost.
Insulation and Energy Use
A muffle furnace is constructed with thick, high-density refractory ceramic fiber insulation to contain extreme heat. This makes it heavy, slow to heat up and cool down, and highly energy-intensive.
A hot air oven uses less dense insulation like fiberglass or mineral wool. This is sufficient for its lower temperature range and allows for a lighter, more energy-efficient design.
Temperature Uniformity vs. Peak Temperature
A hot air oven is optimized for temperature uniformity. The fan-driven circulation minimizes hot or cold spots, which is vital for repeatable experiments and sterilization.
A muffle furnace is optimized for achieving a peak temperature. While modern furnaces have good uniformity, their primary design priority is reaching and holding extreme heat levels safely.
Cost and Safety
Hot air ovens are relatively simple devices, making them significantly more affordable and smaller.
Muffle furnaces are a major capital expense. Their high power requirements and the extreme temperatures involved necessitate stricter safety protocols, dedicated electrical circuits, and proper ventilation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct instrument, align your primary process with the equipment's core function.
- If your primary focus is drying, sterilization, or low-temperature curing (<300°C): A hot air oven provides the necessary temperature uniformity and control for these tasks.
- If your primary focus is ashing, heat-treating metals, or material analysis (>900°C): A muffle furnace is the only tool capable of reaching the required temperatures for material transformation.
- If you need to determine the inorganic content of a sample: You must use a muffle furnace for ashing; an oven cannot achieve the temperatures needed to burn off all organic matter.
Choosing the right tool is a matter of matching the required thermal energy of your process to the equipment designed to deliver it safely and efficiently.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Air Oven | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 300°C (some to 450°C) | 900°C to 1400°C+ |
| Heating Mechanism | Forced air convection | Radiant heating |
| Primary Use | Drying, sterilization, curing | Ashing, heat treatment, ceramics |
| Key Advantage | Excellent temperature uniformity | Extreme heat for material transformation |
Unsure which equipment is right for your lab process? KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you select the perfect hot air oven or muffle furnace to meet your specific temperature and application needs, ensuring safety, efficiency, and accurate results. Contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the heat transfer of a muffle furnace? Understanding Indirect Heating for Purity
- How does a muffle work? Achieve Clean, Contamination-Free Heating for Your Lab
- What is the objective of a muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is muffle in muffle furnace? The Key to Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the point of a muffle? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processes



















