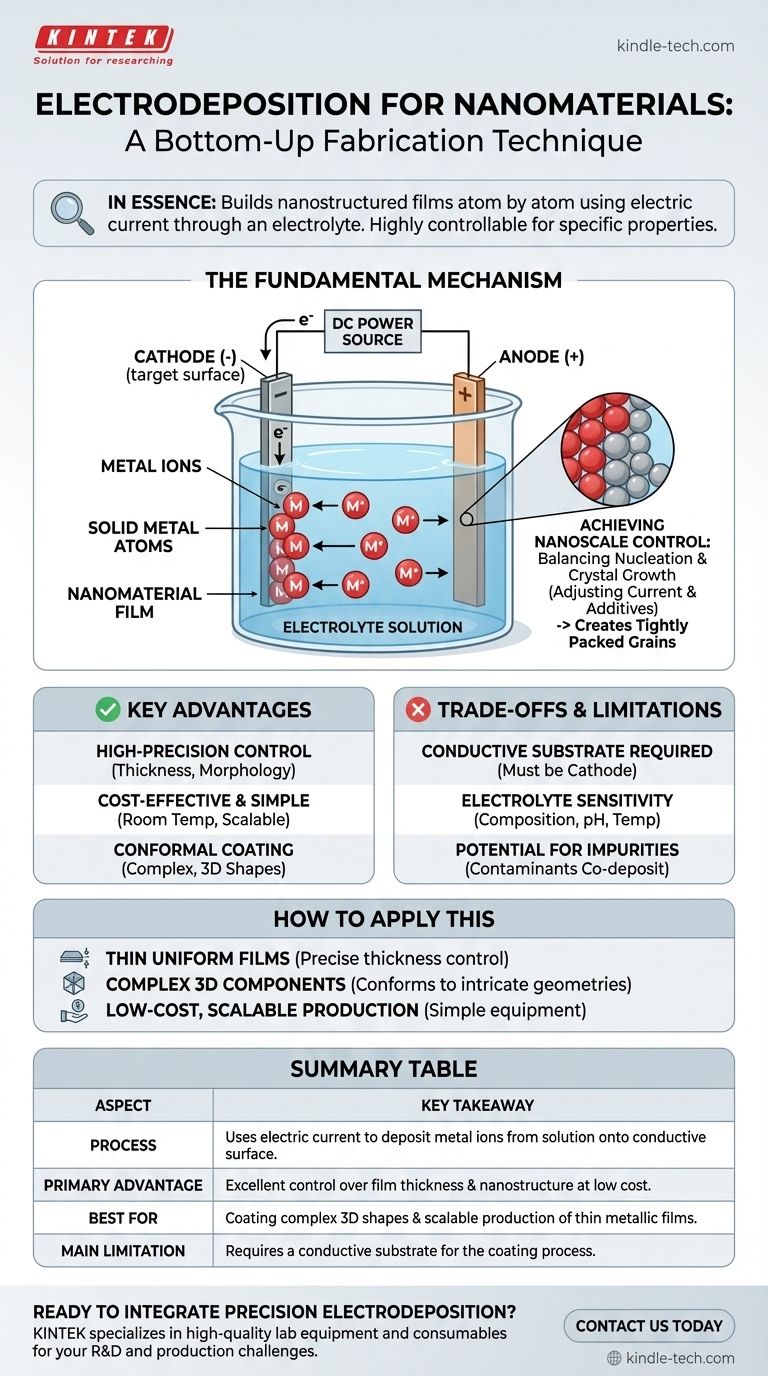
In essence, electrodeposition for nanomaterials is a bottom-up fabrication technique that uses an electric current to build nanostructured films or coatings atom by atom. It involves passing a current through a conductive solution (an electrolyte), causing dissolved metal ions to deposit onto a target surface (the electrode), forming a thin film with controlled nanoscale features.
The critical insight is that electrodeposition moves beyond simple coating; it is a highly controllable process where manipulating electrical parameters and solution chemistry allows you to precisely manage crystal formation, enabling the creation of materials with specific nanoscale textures and properties.
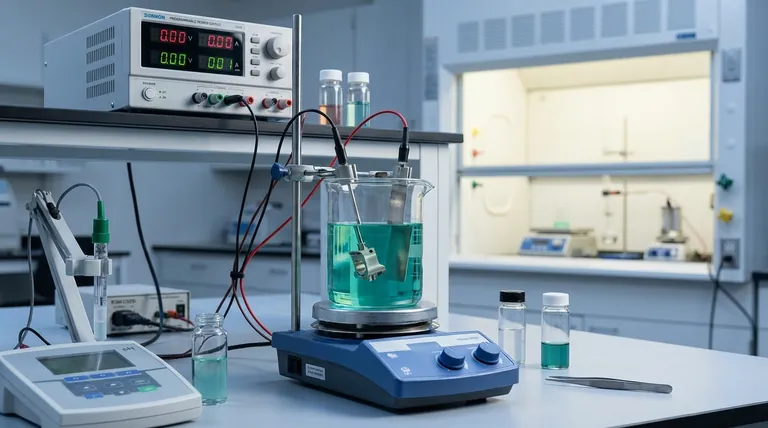

The Fundamental Mechanism: From Ions to Nanostructures
To understand how electrodeposition works at the nanoscale, we must look at the core components and the electrochemical reactions they facilitate. The process is governed by simple principles but allows for complex outcomes.
The Core Components
The setup consists of three primary parts: two electrodes (a cathode and an anode) and an electrolyte. The electrolyte is a liquid solution containing the dissolved ions of the material you wish to deposit, such as copper or gold ions.
The Electrochemical Reaction
When a direct current (DC) is applied, the electrode you want to coat is made the cathode (negative electrode). The positively charged metal ions in the electrolyte are attracted to this negative surface.
The Deposition Process
At the cathode's surface, the metal ions gain electrons in a process called reduction. This neutralizes their charge, causing them to precipitate out of the solution and deposit onto the surface as solid metal atoms.
Achieving Nanoscale Control
The key to creating nanostructures, rather than a simple bulk coating, lies in controlling the balance between two competing processes: nucleation (the formation of new crystal seeds) and crystal growth (the expansion of existing crystals). By adjusting factors like current density and additives in the electrolyte, you can favor rapid nucleation, which leads to a film composed of very small, tightly packed grains—a nanostructured material.
Key Advantages of Electrodeposition
This method is not just a laboratory curiosity; it is a practical and widely used technique in nanotechnology for several compelling reasons.
High-Precision Control
Electrodeposition offers excellent control over film thickness, which can be managed down to the nanometer scale by precisely controlling the total charge passed during the process. The morphology and grain size of the material can also be tuned.
Cost-Effectiveness and Simplicity
Compared to high-vacuum techniques like physical or chemical vapor deposition, electrodeposition equipment is relatively inexpensive and operates at or near room temperature and pressure. This makes it more accessible and easier to scale for industrial production.
Conformal Coating on Complex Shapes
One of the most significant advantages of electrodeposition is its ability to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes. Because the deposition is driven by the electric field, it can reach into intricate geometries that line-of-sight methods cannot.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No technique is perfect, and it is crucial to understand the limitations of electrodeposition to use it effectively.
Requirement for a Conductive Substrate
The most fundamental limitation is that the material to be coated (the substrate) must be electrically conductive to act as the cathode. While techniques exist to metallize non-conductive surfaces first, this adds an extra step and complexity.
Electrolyte Sensitivity
The outcome of the deposition is highly sensitive to the composition of the electrolyte. Factors like ion concentration, pH, temperature, and the presence of organic additives must be meticulously controlled to ensure reproducible results.
Potential for Impurities
Contaminants present in the electrolyte bath can be co-deposited along with the target material. This can introduce impurities into the final film, potentially altering its electrical, mechanical, or chemical properties.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice to use electrodeposition will depend entirely on your end goal. The technique's versatility is one of its greatest strengths.
- If your primary focus is creating thin, uniform metallic films: Electrodeposition is an excellent choice, allowing you to control thickness precisely by managing current and time.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D components with a nanostructured layer: This method is superior to many alternatives due to its ability to conform to intricate geometries.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, scalable production of nanomaterials: The relatively simple equipment and operating conditions make electrodeposition highly suitable for industrial applications.
By controlling electrical and chemical parameters, electrodeposition provides a powerful and accessible tool for engineering materials from the atom up.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Process | Uses electric current to deposit metal ions from a solution onto a conductive surface. |
| Primary Advantage | Excellent control over film thickness and nanostructure at a low cost. |
| Best For | Coating complex 3D shapes and scalable production of thin metallic films. |
| Main Limitation | Requires a conductive substrate for the coating process. |
Ready to integrate precision electrodeposition into your nanomaterial research or production?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need to master this technique. Whether you are scaling up a process or require precise control for R&D, our solutions are designed to meet your laboratory's specific challenges.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your project with reliable equipment and expert consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Gold Disc Electrode
People Also Ask
- What technical advantages do current converters and polarity reversal provide? Enhance EC System Longevity & Efficiency
- How does a standard three-electrode electrolytic cell system analyze Montmorillonite & TiO2? Enhance Data Precision
- What are the sterilization and heating precautions for a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Ensure Safe Operation and Accurate Results
- What experimental conditions does a three-electrode electrolytic cell provide? Optimize Precise Corrosion Analysis
- Why is an external cooling system necessary for an electrolytic reactor? Prevent Coating Failure in Aluminum PEO
- What is the typical experimental system used with a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Achieve Precise Electrochemical Control
- What are the operational procedures and safety precautions during an experiment with an acrylic electrolytic cell? Essential Guide for Lab Safety
- How does a standard electrolytic cell ensure accuracy in HER testing? Achieve Reliable SnO2/MoS2 Catalyst Performance



















