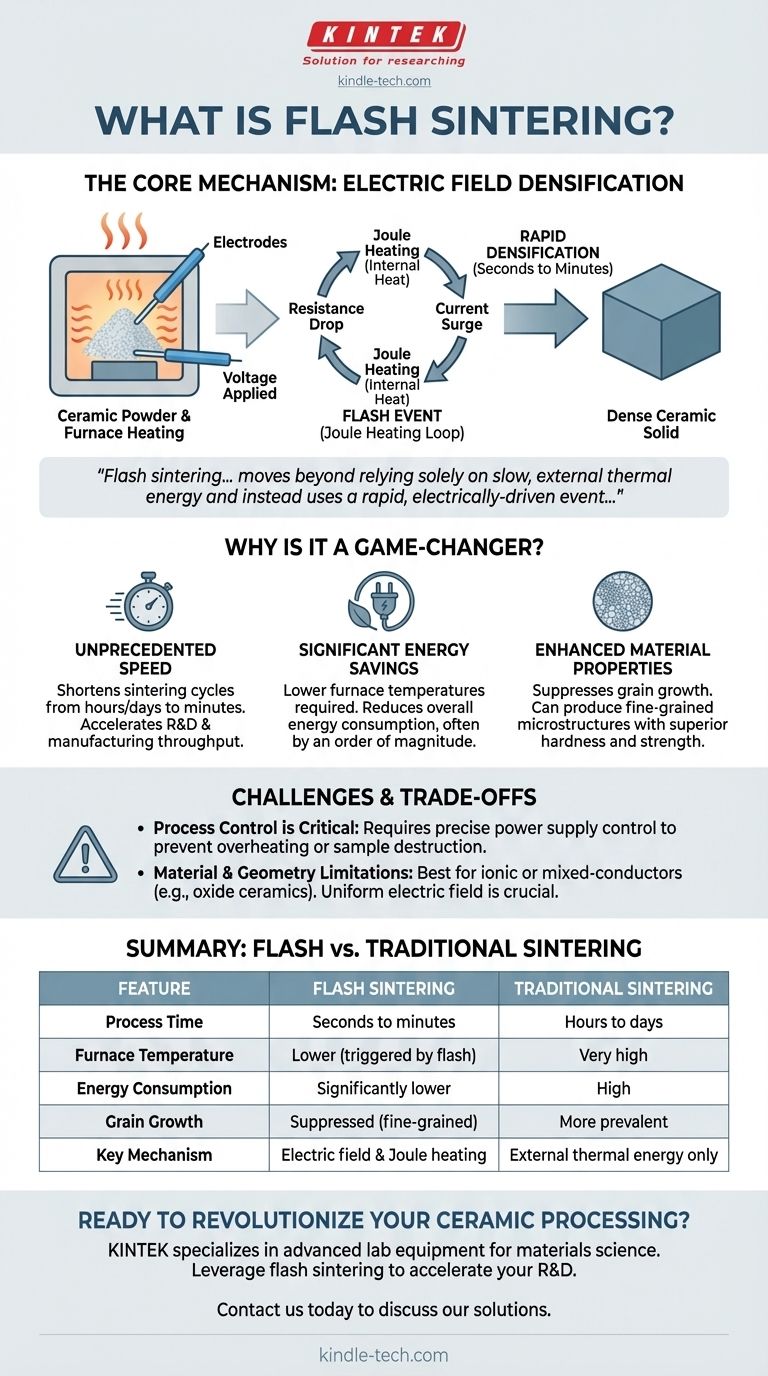
At its core, flash sintering is an advanced materials processing technique that uses an electric field to dramatically accelerate the densification of a ceramic powder. While the material is being heated in a furnace, applying a voltage triggers a sudden, non-linear surge in electrical conductivity and current, generating intense internal heat—known as Joule heating—that fuses the material into a dense solid in mere seconds.
Flash sintering represents a fundamental shift in how we process ceramic materials. It moves beyond relying solely on slow, external thermal energy and instead uses a rapid, electrically-driven event to achieve densification at lower furnace temperatures and in a fraction of the time.
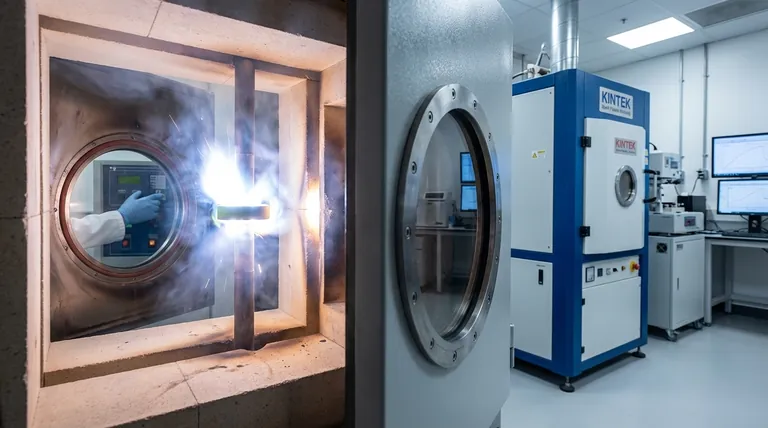

How Flash Sintering Works: The Core Mechanism
To truly grasp its potential, you must understand the sequence of events that defines the "flash" phenomenon. It is a process controlled by a powerful positive feedback loop.
The Setup: Combining Heat and Electricity
The process begins with a standard furnace setup, but with a critical addition: two electrodes are placed in contact with the material being sintered (often a ceramic "green body," or pressed powder).
The furnace provides initial, conventional heating, while a power supply connected to the electrodes applies a constant electric field across the sample.
Reaching the Threshold: The Tipping Point
As the furnace temperature slowly rises, the material's electrical resistivity begins to decrease. For many ceramics, this is a natural property.
At a specific onset temperature, the material becomes sufficiently conductive for a small but meaningful electrical current to flow through it. This is the critical tipping point for the entire process.
The "Flash" Event: A Runaway Effect
The moment current begins to flow, Joule heating (heat generated by electrical resistance) starts to warm the material from the inside.
This creates a powerful feedback loop: a slight increase in internal temperature further decreases the material's resistivity, which allows more current to flow, which in turn generates even more Joule heating. This thermal runaway effect causes a near-instantaneous, exponential spike in conductivity and temperature.
Rapid Densification: From Powder to Solid
This intense, internally generated heat causes the material's particles to fuse together and eliminate porosity with extreme speed.
The entire densification process, which could take many hours in a conventional furnace, is completed in a matter of seconds to minutes once the flash event is triggered.
Why is Flash Sintering a Game-Changer?
The unique mechanism of flash sintering provides three distinct advantages over traditional methods, making it a disruptive technology in materials science.
Unprecedented Speed
The most obvious benefit is speed. By shortening sintering cycles from many hours or even days down to a few minutes, it dramatically accelerates research, development, and potential manufacturing throughput.
Significant Energy Savings
Because the "flash" provides the majority of the thermal energy required for densification, the furnace itself does not need to reach the extremely high temperatures typical of conventional sintering.
This, combined with the incredibly short processing time, results in a substantial reduction in overall energy consumption—often by an order of magnitude or more.
Enhanced Material Properties
The rapid heating and cooling cycle helps suppress grain growth, a common issue in slow, high-temperature sintering that can degrade mechanical properties.
Flash sintering often produces materials with exceptionally fine-grained microstructures, which can lead to superior hardness, strength, and other desirable characteristics.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, flash sintering is not a universal solution and requires careful control to be effective.
Process Control is Critical
The same thermal runaway that makes the process so fast can also lead to catastrophic failure. If the power supply is not precisely controlled to limit the current after the flash event, the sample can be overheated, melted, or even destroyed.
Material and Geometry Limitations
The technique works best for materials that exhibit the necessary temperature-dependent electrical conductivity, primarily ionic or mixed-conductors like many oxide ceramics (e.g., zirconia, ceria).
Furthermore, the sample's geometry and the quality of the electrode contact are crucial for ensuring a uniform electric field. Non-uniformities can cause "hot spots" and uneven densification.
Is Flash Sintering Right for Your Application?
Choosing a sintering technique depends entirely on your end goal. Flash sintering offers compelling advantages for specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is rapid manufacturing or prototyping: Flash sintering offers a significant speed advantage for producing dense ceramic components quickly.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and cost reduction: The lower furnace temperatures and dramatically shorter cycle times can lead to substantial operational savings.
- If your primary focus is developing advanced materials: The unique, non-equilibrium conditions can create novel, fine-grained microstructures with potentially superior properties.
By understanding its unique mechanism, you can leverage flash sintering to move beyond the traditional time and energy constraints of ceramic processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Flash Sintering | Traditional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Process Time | Seconds to minutes | Hours to days |
| Furnace Temperature | Lower (triggered by flash event) | Very high |
| Energy Consumption | Significantly lower | High |
| Grain Growth | Suppressed (fine-grained structure) | More prevalent |
| Key Mechanism | Electric field & Joule heating | External thermal energy only |
Ready to revolutionize your ceramic processing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment for innovative materials science. Our solutions are designed to help you leverage cutting-edge techniques like flash sintering to accelerate your R&D and achieve superior results.
Whether you're developing advanced materials, focusing on energy efficiency, or speeding up prototyping, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your goals.
Contact us today to discuss how our specialized lab equipment and consumables can power your next breakthrough in ceramic technology.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance



















