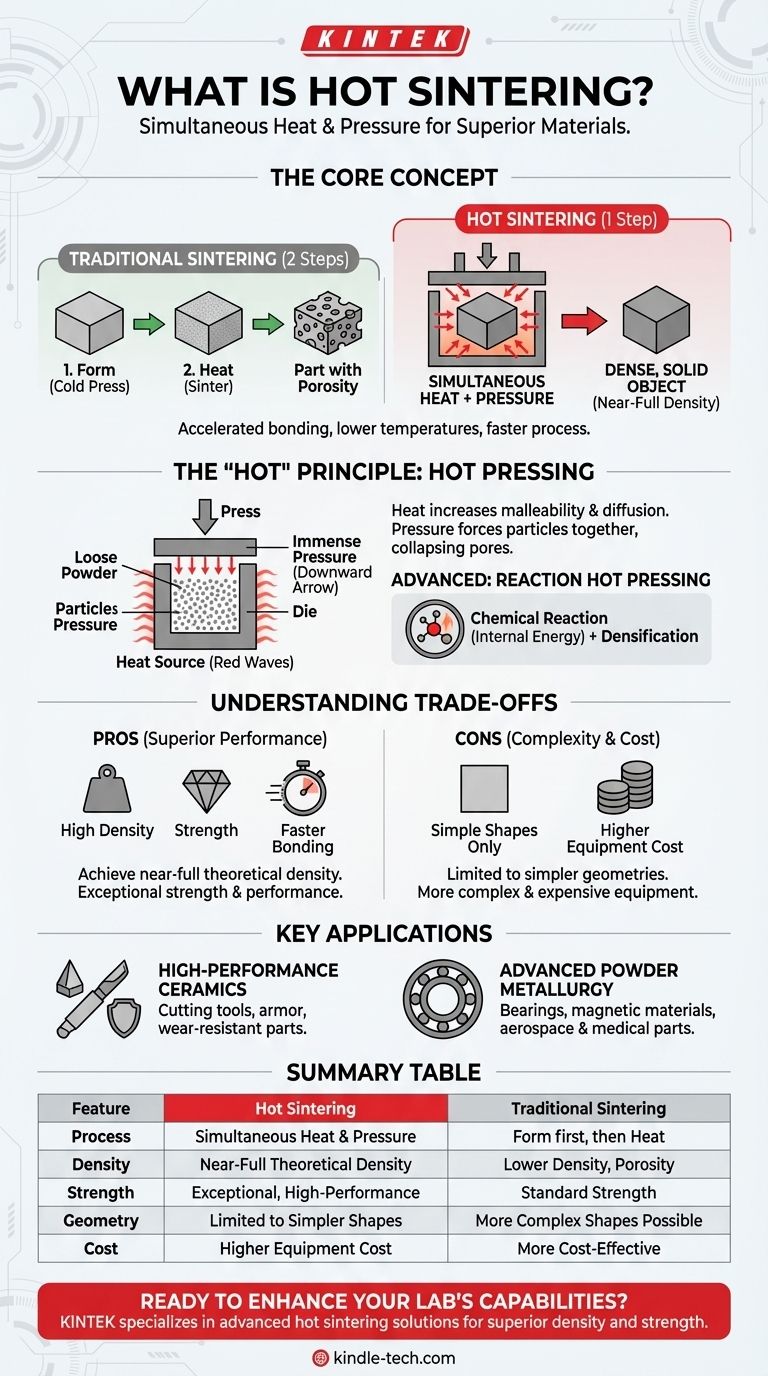
At its core, hot sintering is a manufacturing process that consolidates a powder-like material into a solid, dense object by applying high temperature and high pressure at the same time. Unlike traditional sintering where an object might be formed first and then heated, hot sintering combines these steps into a single, more efficient operation to create materials with superior properties.
The critical distinction of hot sintering is its simultaneous application of heat and pressure. This combination accelerates the bonding between material particles, allowing for the creation of denser, stronger components at lower temperatures and in less time than conventional methods.

What is Sintering Fundamentally?
The Goal: Fusing Particles Without Melting
Sintering is a thermal treatment for bonding particles of a material into a coherent, solid mass. This is accomplished using heat that is below the material's melting point.
The energy from the heat causes the atoms on the surfaces of the particles to diffuse, creating "necks" or bridges between them. Over time, these necks grow, pulling the particles closer together and eliminating the empty space, or porosity, between them.
Why Not Just Melt the Material?
Sintering is essential for materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten or many ceramics, where melting them would be impractical and incredibly energy-intensive. It also provides precise control over the final product's microstructure, which is critical for performance.
The "Hot" in Hot Sintering: A Combined Force
The defining feature of hot sintering is the synergy between thermal energy (heat) and mechanical energy (pressure). This simultaneous action dramatically enhances the consolidation process.
The Principle of Hot Pressing
Hot pressing is the most common form of hot sintering. A loose powder is placed into a die, which is then heated while a press applies immense pressure.
The heat makes the material particles more malleable and accelerates atomic diffusion. The external pressure then physically forces the particles together, collapsing pores and speeding up the bonding process far more effectively than heat alone.
An Advanced Example: Reaction Hot Pressing
Some advanced techniques take this a step further. Reaction hot pressing utilizes the energy from a chemical reaction occurring within the powder itself as an additional driving force for densification. This clever approach can further reduce the required external temperature, making it possible to create highly dense, advanced ceramics that would otherwise be very difficult to produce.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Superior Density vs. Geometric Complexity
The primary benefit of hot sintering is its ability to achieve near-full theoretical density, resulting in materials with exceptional strength and performance.
However, the process is often limited to simpler shapes. Because the part is typically formed inside a rigid die, complex geometries like those produced by 3D printing or injection molding are much more difficult to achieve with hot pressing.
Cost and Equipment
The equipment required for hot sintering—a furnace integrated with a powerful mechanical press—is more complex and expensive than a standard sintering furnace. This generally reserves the process for high-value components where maximum performance is non-negotiable.
Key Applications of Hot Sintering
High-Performance Ceramics
Hot sintering is crucial for producing dense, robust ceramic components used in demanding applications. This includes cutting tools, armor, and wear-resistant parts where even microscopic pores could lead to failure.
Advanced Powder Metallurgy
In the field of metals, the process is used to create specialized parts from metal powders. This includes self-lubricating bearings, strong magnetic materials, and structural components for aerospace and medical industries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is maximum density and material performance: Hot sintering is the superior choice for creating components with minimal porosity and exceptional strength.
- If you are working with difficult-to-sinter materials: The combined force of heat and pressure can effectively consolidate advanced ceramics or refractory metals that resist conventional sintering.
- If your design involves complex geometry and cost is a major factor: A traditional "press-and-sinter" approach or an additive manufacturing method might be a more practical solution.
Ultimately, choosing hot sintering is a decision to prioritize final material quality and performance over process simplicity and geometric freedom.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Sintering | Traditional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Simultaneous heat and pressure | Form first, then heat |
| Density | Near-full theoretical density | Lower density, more porosity |
| Strength | Exceptional, high-performance | Standard strength |
| Geometry | Limited to simpler shapes | More complex shapes possible |
| Cost | Higher equipment cost | More cost-effective |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with high-performance materials?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for hot sintering processes. Whether you're working with high-performance ceramics or advanced metal powders, our expertise ensures you achieve superior density and strength for your critical components.
Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs and drive your research forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why is precise temperature control necessary for SiC/Cu Vacuum Hot Pressing? Mastering the Cu9Si Interface Phase
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Achieve 99.1% Density in CuW30 Composites
- What conditions does a Vacuum Hot Pressing Furnace provide for Copper-MoS2-Mo composites? Achieve Peak Densification
- What is the significance of precise temperature control in melt infiltration? Achieve High-Performance Li-Alloy Electrodes



















