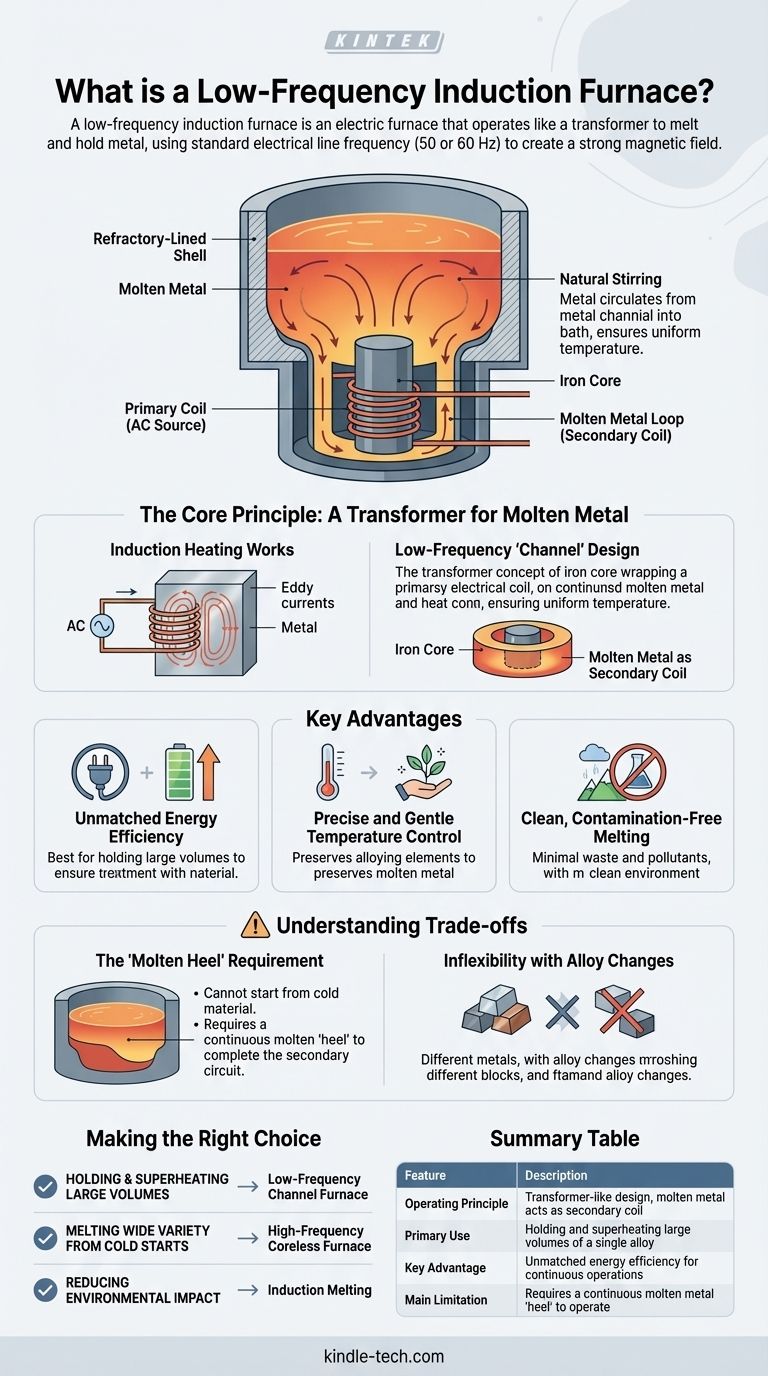
In short, a low-frequency induction furnace is an electric furnace that operates like a transformer to melt and hold metal. It uses a standard electrical line frequency (typically 50 or 60 Hz) to create a strong magnetic field, which induces a powerful heating current within a loop of molten metal. This design is distinct from high-frequency furnaces and is exceptionally efficient for large-scale, continuous operations.
The most critical concept to understand is that a low-frequency furnace, often a channel furnace, functions as a live transformer where the primary coil and iron core are part of the furnace, and the molten metal itself forms the secondary coil. This makes it highly efficient for holding liquid metal but requires a continuous molten "heel" to operate.
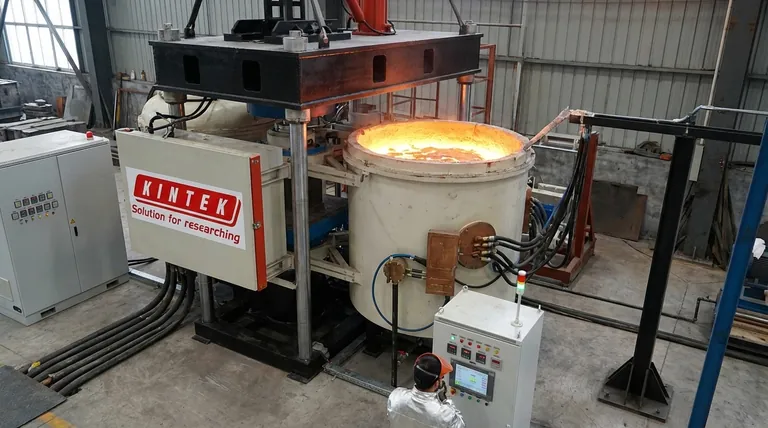

The Core Principle: A Transformer for Molten Metal
To understand a low-frequency furnace, it's essential to first grasp the basic principle of induction and then see how this specific design applies it.
How Induction Heating Works
All induction furnaces operate on the principle of electromagnetism. An alternating current (AC) flows through a copper coil, creating a fluctuating magnetic field. When conductive material like metal is placed within this field, the field induces powerful internal electrical currents called eddy currents. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates intense, rapid heat.
The Low-Frequency "Channel" Design
A low-frequency furnace refines this principle. It consists of a main refractory-lined shell to hold the bulk of the molten metal. Attached to this shell is an induction unit.
This unit contains an iron core with a primary electrical coil wound around it. A channel of molten metal from the main bath loops around this same iron core, acting as the secondary coil of a transformer. When AC is applied to the primary coil, it induces a massive current in the molten metal loop, generating heat.
Natural Stirring and Temperature Uniformity
The intense heat generated in the narrow channel causes the metal there to circulate into the main bath. This movement creates a gentle, continuous stirring action. This natural circulation ensures the entire melt has a uniform temperature and a consistent alloy composition.
Key Advantages of the Low-Frequency Approach
The unique design of low-frequency furnaces provides several distinct operational benefits, particularly in foundry and industrial settings.
Unmatched Energy Efficiency
For holding large volumes of molten metal at a specific temperature for long periods, the direct transformer-like coupling is extremely energy-efficient. It consumes significantly less power for holding applications compared to other furnace types.
Precise and Gentle Temperature Control
The heat is generated directly within the metal, not by an external flame or electric arc. This allows for very precise temperature regulation, which is critical for preserving valuable and easily oxidized alloying elements.
Clean, Contamination-Free Melting
Because there is no combustion, no fuel is introduced into the melt. This eliminates a major source of contamination. The process produces minimal waste, smoke, or pollutants, leading to a cleaner product and a safer working environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, the low-frequency furnace is a specialized tool with critical operational constraints that make it unsuitable for certain applications.
The "Molten Heel" Requirement
This is the most significant limitation. A low-frequency channel furnace cannot start melting from solid, cold material. It requires a continuous loop of molten metal—a "heel"—to complete the secondary circuit. This means the furnace must be started with a pre-melted charge and can never be fully emptied during operation.
Inflexibility with Alloy Changes
Due to the molten heel requirement, these furnaces are best suited for applications dedicated to a single metal alloy. Switching alloys is a difficult and time-consuming process that involves draining the furnace and restarting with a new molten heel.
Slower Melting of Cold Material
While exceptionally efficient at holding and superheating, these furnaces are generally slower at melting large batches of cold scrap compared to high-frequency coreless furnaces. Their primary strength lies in maintaining, not just creating, a molten state.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on your operational needs and production goals.
- If your primary focus is holding and superheating large, continuous volumes of a single alloy: The energy efficiency of a low-frequency channel furnace is almost certainly your best option.
- If your primary focus is melting a wide variety of alloys from cold starts in different batch sizes: A high-frequency coreless induction furnace provides the necessary flexibility.
- If your primary focus is reducing environmental impact and ensuring high metal purity: Any form of induction melting offers a massive advantage over traditional combustion-based furnaces.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is about matching the tool's inherent strengths to your specific metallurgical task.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Transformer-like design; molten metal acts as secondary coil. |
| Primary Use | Holding and superheating large volumes of a single alloy. |
| Key Advantage | Unmatched energy efficiency for continuous operations. |
| Main Limitation | Requires a continuous molten metal "heel" to operate. |
Optimize your foundry or lab with the right furnace technology. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust solutions for laboratory needs. Whether you're melting, holding, or superheating metals, our expertise ensures you get the most efficient and reliable equipment. Contact us today to discuss how our induction furnaces can enhance your productivity and metal purity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- Why is a small pressure applied during SiCf/TB8 debinding? Master Fiber Alignment in Vacuum Hot Pressing
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- What are the advantages of using a Vacuum Hot-Pressing Furnace for Ti-6Al-4V? Achieve Forged-Like Strength & Purity
- How does the mechanical pressure from a vacuum hot-pressing furnace facilitate the densification of B4C/Al composites?
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity


















