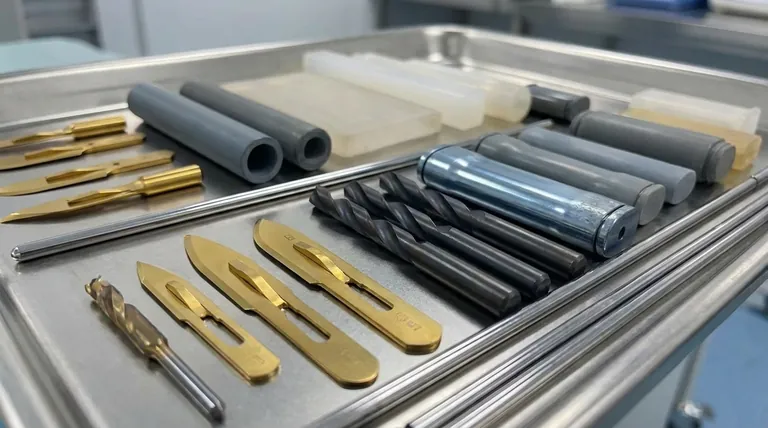
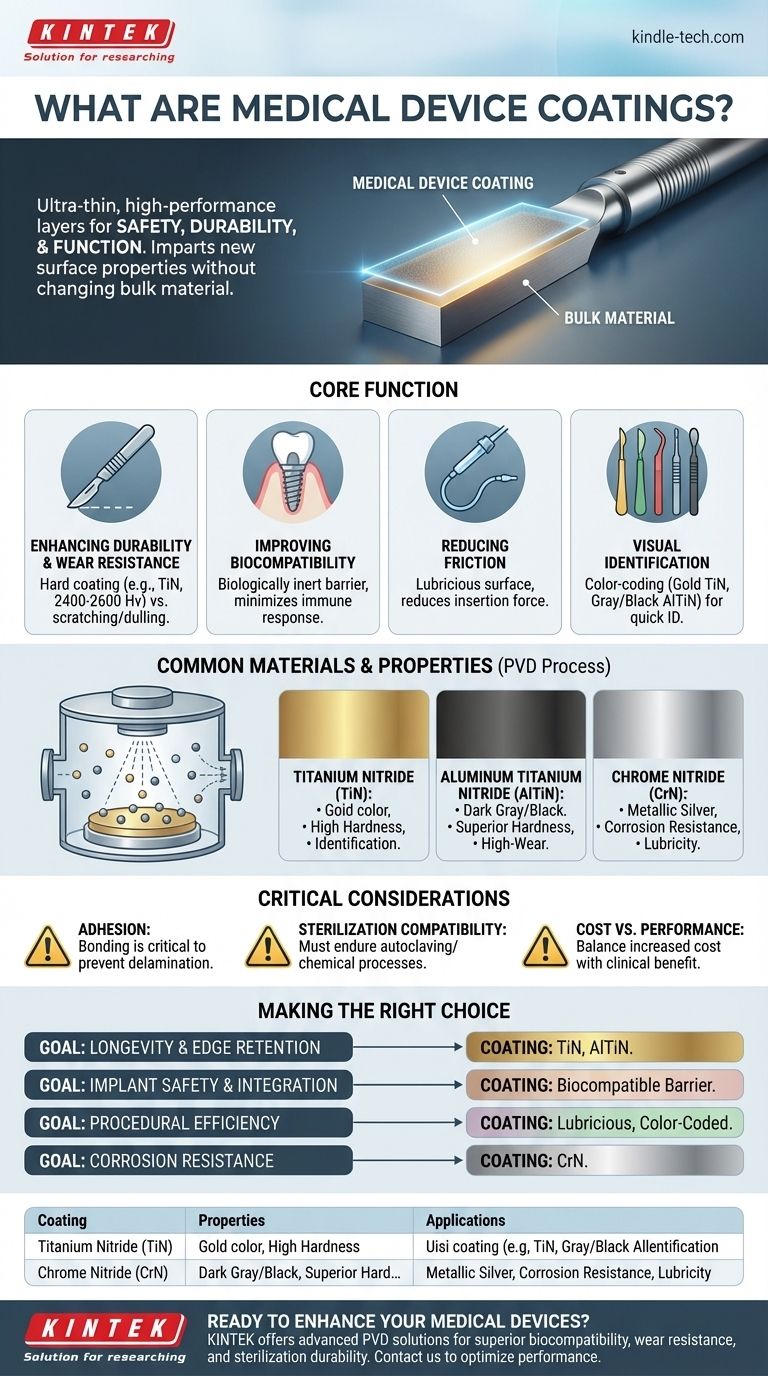
In essence, medical device coatings are ultra-thin, high-performance layers of material applied to the surface of medical instruments, implants, and equipment. They are not merely for aesthetics; they are a critical engineering feature designed to fundamentally enhance a device's safety, durability, and overall function within a clinical setting.
The core purpose of a medical coating is to impart new, desirable properties to a device's surface without changing the underlying bulk material. This allows engineers to select a base material for its strength or cost, and then add a specialized coating to provide biocompatibility, wear resistance, or lubricity.

The Core Functions of Medical Coatings
A coating is chosen to solve a specific problem. Understanding these core functions is key to appreciating their value in modern medicine.
Enhancing Durability and Wear Resistance
Many surgical instruments, such as scalpels and bone saws, must maintain a sharp edge through repeated use and sterilization cycles.
A hard coating dramatically increases the surface's resistance to scratching and dulling. For example, Titanium Nitride (TiN), a common coating, has a Vickers hardness of 2,400 to 2,600 Hv, making it significantly harder than the stainless steel beneath it.
Improving Biocompatibility
The materials used in implants, like titanium or cobalt-chrome alloys, can sometimes provoke a response from the body's immune system.
Coatings can act as a biologically inert barrier between the implant and the patient's tissue. This minimizes the risk of adverse reactions and improves the long-term success of the device.
Reducing Friction
For devices that are inserted into the body, such as catheters or guidewires, high friction can cause tissue damage and make procedures more difficult.
Lubricious coatings create an extremely slick surface, which can reduce the force needed for insertion and improve patient comfort and safety.
Aiding in Visual Identification
In a fast-paced surgical environment, quickly identifying the correct instrument is critical.
Coatings can be used for color-coding. The distinct gold color of Titanium Nitride (TiN) or the gray/black of Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) helps surgeons and staff instantly differentiate between instruments.
Common Coating Materials and Properties
The specific material chosen for a coating dictates its performance. The coatings are typically applied in a vacuum chamber using a process like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), which deposits the material atom by atom to create a very thin—yet durable—film.
Titanium Nitride (TiN)
This is a workhorse material in the medical field. It provides an excellent combination of high hardness for wear resistance and a distinctive gold color for identification. Its typical thickness is between 0.0001 and 0.0002 inches.
Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN)
This coating is even harder than TiN and offers superior performance in high-wear applications, such as orthopedic drills or saws. It typically has a dark gray or black finish.
Chrome Nitride (CrN)
Valued for its excellent corrosion resistance and lubricity, Chrome Nitride is often used on instruments that require a smooth surface finish and must withstand harsh sterilization processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While coatings offer significant advantages, they are an engineered solution with inherent complexities and considerations.
Adhesion is Critical
The single most important factor for a coating is its ability to bond to the underlying device. If the coating chips or flakes off (a failure known as delamination), it can compromise the device's function and potentially harm the patient.
Sterilization Compatibility
A coating must be able to endure the sterilization methods used in hospitals, such as high-pressure steam (autoclaving) or chemical sterilization, without degrading or losing its properties. Not all coatings are compatible with all methods.
Cost vs. Performance
Adding a high-performance coating increases the manufacturing cost of a device. The decision to use one must be balanced against the clinical benefit it provides, such as extending the life of an expensive instrument or improving the safety of an implant.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal coating is entirely dependent on the specific application and the primary problem you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is instrument longevity and edge retention: Prioritize coatings with the highest hardness, such as Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN).
- If your primary focus is implant safety and integration: Select a coating specifically proven for its biocompatibility and ability to create an inert barrier.
- If your primary focus is procedural efficiency: Look for coatings that provide high lubricity for smoother device movement or distinct colors for rapid instrument identification.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance: Choose a stable and non-reactive coating like Chrome Nitride (CrN) that can withstand repeated, harsh cleaning cycles.
Ultimately, medical coatings transform standard devices into specialized, high-performance tools that are safer and more effective for both the clinician and the patient.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium Nitride (TiN) | High hardness (2,400-2,600 Hv), gold color | Surgical instruments, cutting tools |
| Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) | Superior hardness, dark gray/black finish | Orthopedic drills, high-wear tools |
| Chrome Nitride (CrN) | Excellent corrosion resistance, lubricity | Instruments requiring smooth surfaces |
Ready to enhance your medical devices with precision coatings? KINTEK specializes in advanced PVD coating solutions for laboratory and medical equipment. Our coatings deliver superior biocompatibility, wear resistance, and sterilization durability—ensuring your instruments and implants meet the highest clinical standards. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your device performance and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Square Bidirectional Pressure Mold for Lab Use
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Carbon Graphite Plate Manufactured by Isostatic Pressing Method
People Also Ask
- Why is a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) Required for NaSICON? Achieve Maximum Green Density and Ionic Conductivity
- How does a Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) improve W-Cu densification? Achieve Near-Theoretical Density with High Pressure
- What is a pressing die? The Precision Tool for Shaping Powder into Solid Pellets
- What is the function of high-strength pressure molds for nanostructured copper powders? Achieve High Purity Densification
- What are molds used for? Unlock Mass Production of Precision Parts













