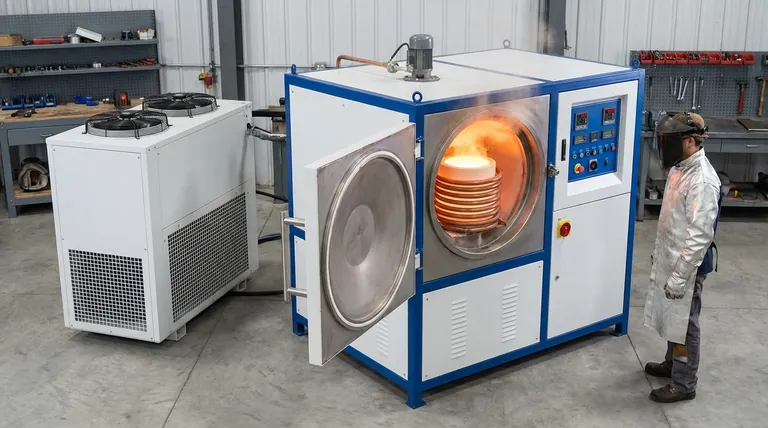
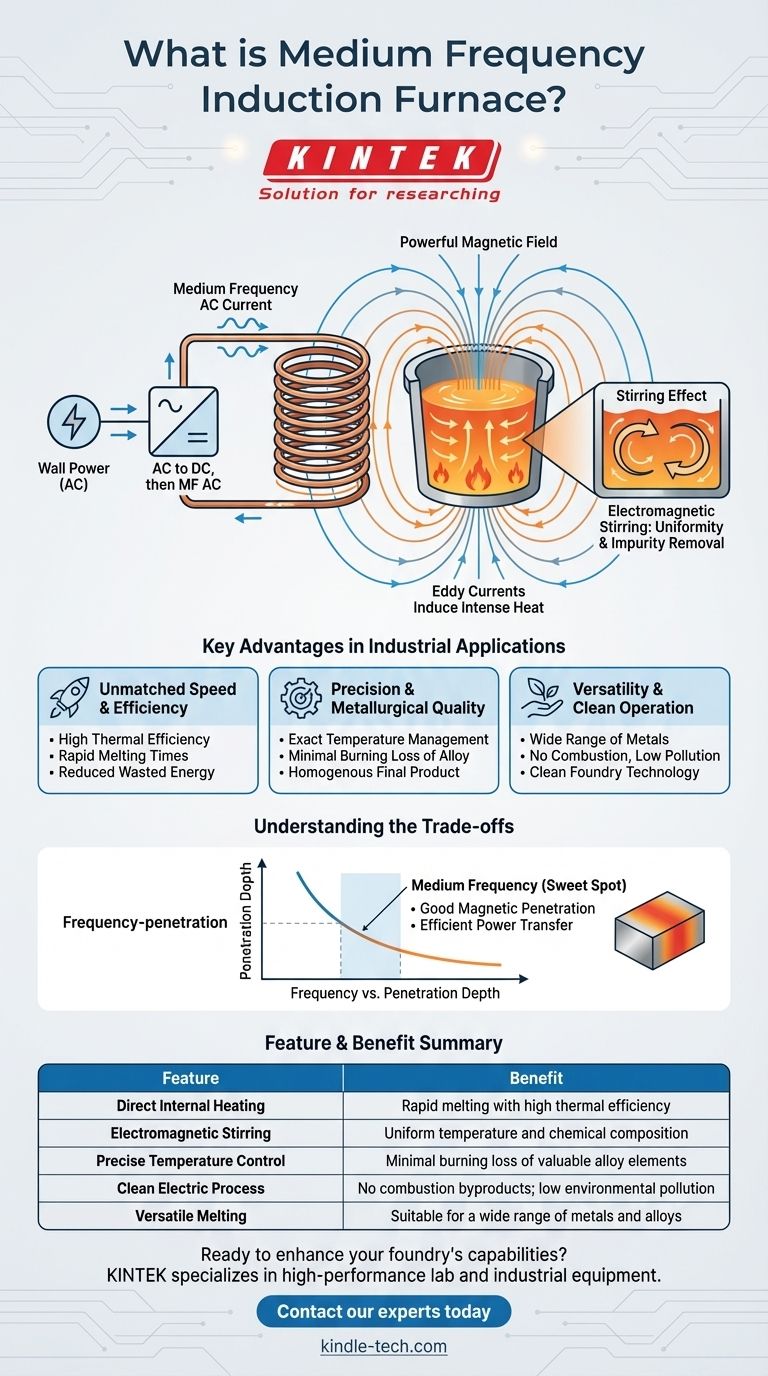
At its core, a medium frequency induction furnace is an advanced electrical furnace that melts metal without any direct contact or combustion. It works by converting standard electrical power into a medium frequency current, which is fed into a copper coil. This coil generates a powerful magnetic field that induces large electrical currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the metal charge, causing it to heat up and melt rapidly.
A medium frequency induction furnace represents a fundamental shift in melting technology, moving away from external heat sources to a process that generates heat directly inside the target material. This principle of electromagnetic induction delivers unparalleled speed, efficiency, and metallurgical control.

The Core Principle: How Induction Creates Heat
To understand the value of this technology, we must first understand its unique method of generating heat. The entire process is based on two fundamental physical principles: electromagnetic induction and the thermal effect of current.
From Wall Power to Medium Frequency Current
The furnace's power supply is the first critical component. It takes standard three-phase alternating current (AC) from the power grid and converts it into direct current (DC). This DC is then transformed into a precisely controlled, single-phase, medium frequency AC current.
The Power of Electromagnetic Induction
This specialized current is sent through a large, water-cooled copper coil that surrounds the crucible holding the metal. As the current flows, it generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within the coil.
Generating Heat with Eddy Currents
This magnetic field passes through the metal placed inside the crucible. According to the laws of electromagnetic induction, the fluctuating magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents, called eddy currents, to flow within the metal itself.
The metal has natural electrical resistance. As these large eddy currents flow against this resistance, they generate intense heat, a phenomenon known as the thermal effect of current. This is what causes the metal to heat up and eventually melt.
The Inherent Stirring Effect
The same magnetic forces that generate the eddy currents also create a stirring action within the molten metal. This electromagnetic stirring is a significant advantage, as it ensures the liquid metal has a uniform temperature and chemical composition, while also helping to move impurities to the surface to be removed as scum.
Key Advantages in Industrial Applications
The unique working principle of the medium frequency induction furnace provides several distinct advantages over traditional fuel-fired or other electric furnace types.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
Because heat is generated directly within the metal charge, the process has extremely high thermal efficiency. There is very little wasted energy, which results in significantly shorter melting times compared to furnaces that must transfer heat from an external source.
Precision and Metallurgical Quality
The power input can be controlled with extreme precision, allowing for exact temperature management. This, combined with the lack of combustion byproducts, leads to minimal burning loss of valuable alloy elements. The stirring effect further guarantees a homogenous, high-quality final product.
Versatility and Clean Operation
Induction furnaces can melt a very wide range of metals and alloys. As an entirely electric process with no combustion, it produces very little environmental pollution in the form of dust, smoke, or harmful gases, making it a much cleaner technology for the modern foundry.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the design of these furnaces is built around a specific set of physical principles. The choice of "medium frequency" is a deliberate engineering trade-off.
The Frequency-Penetration Balance
The frequency of the alternating current in the coil dictates how deeply the magnetic field penetrates the metal charge. Lower frequencies penetrate deeper, while higher frequencies tend to heat just the surface.
The "Sweet Spot" for Melting
Medium frequency is the optimal balance for most melting applications. It is low enough to achieve good magnetic penetration into the chunks of metal in the crucible but high enough to transfer power efficiently and create a strong stirring effect for metallurgical quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a melting technology depends entirely on your operational priorities. A medium frequency induction furnace excels in specific areas.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and alloy control: The precise temperature management, clean melting environment, and inherent stirring action make this the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, on-demand melting: The rapid heating and high electrical efficiency allow for faster turnaround times than nearly any other method.
- If your primary focus is reducing environmental impact: The lack of combustion and emissions makes it one of the cleanest and most sustainable melting technologies available.
This technology empowers foundries to produce high-quality metals with exceptional speed, precision, and environmental responsibility.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Direct Internal Heating | Rapid melting with high thermal efficiency |
| Electromagnetic Stirring | Uniform temperature and chemical composition |
| Precise Temperature Control | Minimal burning loss of valuable alloy elements |
| Clean Electric Process | No combustion byproducts; low environmental pollution |
| Versatile Melting | Suitable for a wide range of metals and alloys |
Ready to enhance your foundry's capabilities with advanced melting technology?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab and industrial equipment, including induction furnaces. Our solutions are designed to deliver the speed, precision, and clean operation your laboratory or production facility requires.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a medium frequency induction furnace can optimize your metal melting process and help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys



















