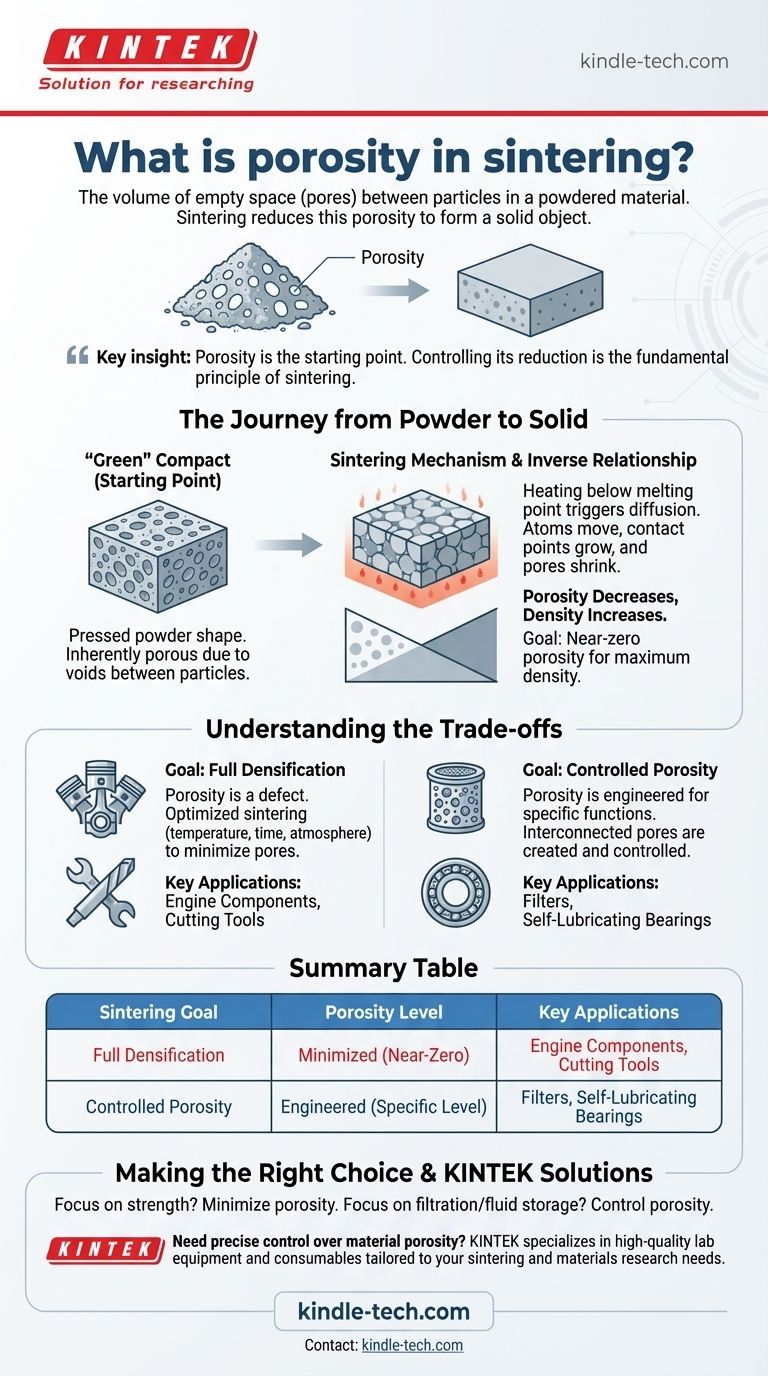
In the context of manufacturing, porosity refers to the volume of empty space, or pores, that exists between the individual particles of a powdered material. During the sintering process, the primary objective is to heat this powdered mass to systematically reduce this porosity, causing the particles to bond and form a dense, solid object.
Porosity is the starting point, not the end goal, of most sintering operations. Understanding and controlling the reduction of these pores is the fundamental principle behind using sintering to transform loose powder into a strong, functional component.
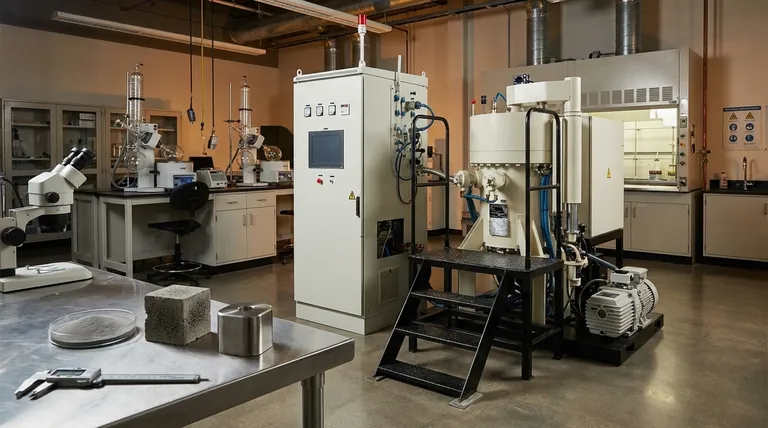

The Journey from Powder to Solid
Sintering is a thermal process that converts a compact made of powder into a coherent, solid mass. The evolution of porosity is the central story of this transformation.
The Starting Point: The 'Green' Compact
Before sintering begins, the material exists as a "green" compact. This is simply powder that has been pressed into a desired shape.
Because it is composed of discrete particles, this green compact is inherently porous. These voids between particles are what define its initial porosity.
The Mechanism of Pore Reduction
Sintering involves heating the green compact to a high temperature, but one that remains below the material's melting point.
At this temperature, a process called diffusion begins. Atoms move across the boundaries of the particles, causing the points of contact between them to grow and fuse. This atomic transport pulls the particle centers closer together, effectively shrinking and eliminating the pores.
The Inverse Relationship: Porosity and Density
Porosity and density are inversely related. As the pores are eliminated during sintering, the empty space within the material decreases.
Consequently, the density of the material increases. The ultimate goal for many structural parts is to approach the theoretical maximum density of the material, which corresponds to near-zero porosity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While sintering is often used to eliminate porosity, it can also be used to create materials where a specific level of porosity is a desirable feature. The goal dictates the process.
The Goal of Full Densification
For most structural applications, such as engine components or cutting tools, porosity is a defect. Pores act as stress concentration points and reduce the material's overall strength, ductility, and fatigue resistance.
In these cases, the sintering process is optimized with specific temperatures, times, and atmospheres to reduce porosity as much as possible.
The Value of Controlled Porosity
In other applications, porosity is engineered into the final part. These pores are intentionally created and controlled to serve a specific function.
For example, porous sintered materials are used for filters, where the interconnected pores allow fluids to pass through while trapping contaminants. They are also used for self-lubricating bearings, where the pores act as a reservoir for oil.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to porosity in sintering depends entirely on the desired properties of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and mechanical integrity: Your goal is to minimize porosity by optimizing the sintering cycle to achieve the highest possible density.
- If your primary focus is filtration or fluid storage: Your goal is to control the sintering process to create a specific, stable, and interconnected network of pores.
Mastering the sintering process is a matter of mastering the control of porosity.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Goal | Porosity Level | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Full Densification | Minimized (Near-Zero) | Engine Components, Cutting Tools |
| Controlled Porosity | Engineered (Specific Level) | Filters, Self-Lubricating Bearings |
Need precise control over material porosity for your lab's projects? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your sintering and materials research needs. Whether you're developing dense structural components or innovative porous materials, our expertise ensures you achieve consistent, reliable results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve high-density NTC ceramics with superior stability.
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance
- How does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace facilitate the high densification of Al-30%Sc alloys?



















