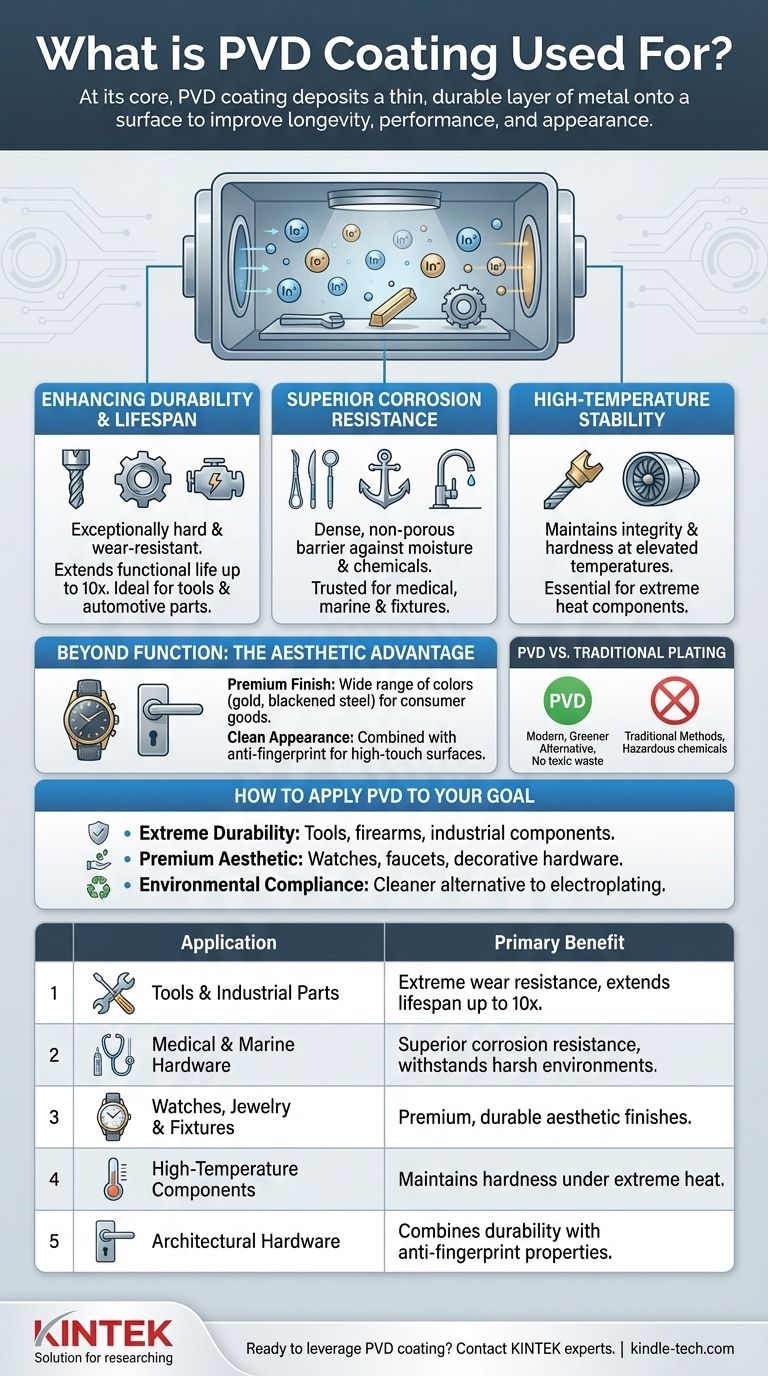
At its core, PVD coating is used to deposit a thin, durable layer of metal onto a surface. This advanced process is found across numerous industries to dramatically improve a product's longevity, performance, and appearance, from medical surgical tools and automotive engine parts to high-end watches and kitchen faucets. It serves as both a protective shield and an aesthetic enhancement.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is not just a single-purpose solution. It uniquely solves the engineering challenge of simultaneously demanding extreme surface hardness, corrosion resistance, and a premium finish, all while being a more environmentally responsible process than traditional methods like chrome plating.

Why PVD Is Chosen for Demanding Applications
The decision to use PVD coating stems from its ability to impart superior physical properties to a product's surface, fundamentally changing its performance characteristics.
Enhancing Durability and Lifespan
PVD coatings are exceptionally hard and highly resistant to wear and abrasion. This makes them ideal for objects subjected to intense friction or use.
By applying this coating, the functional life of a product can be extended by up to ten times. This is critical for high-performance items like drill bits, machine tools, and internal automotive components.
Superior Corrosion Resistance
The deposited metal layer is dense and non-porous, creating an effective barrier against moisture, chemicals, and oxidation.
This property is why PVD is trusted for surgical tools that must withstand repeated sterilization, marine hardware exposed to saltwater, and kitchen and bath fixtures in constant contact with water.
High-Temperature Stability
PVD coatings maintain their integrity and hardness even at elevated temperatures. This is a significant advantage over many other surface treatments.
This stability is essential for applications like high-temperature cutting tools and components within an engine that experience extreme heat during operation.
Beyond Function: The Aesthetic Advantage
While PVD is an engineering solution, its value is equally tied to its ability to produce flawless, decorative finishes. It allows manufacturers to achieve specific looks without compromising on durability.
Achieving a Premium Finish
PVD can deposit a wide range of colors and finishes, including those that mimic expensive materials like gold, brass, or blackened steel.
This is commonly used on consumer goods like watches, jewelry, eyeglass frames, and door hardware to provide a luxury appearance on a more cost-effective base metal.
Maintaining a Clean Appearance
For high-touch surfaces, PVD can be combined with an anti-fingerprint (AF) coating in the same process. This integrated layer resists oils and smudges far more effectively than a simple spray-on treatment.
This dual benefit makes it a popular choice in architecture for door handles, panels, and fixtures in public spaces.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: PVD vs. Traditional Plating
No technology exists in a vacuum. The most significant trade-off to understand with PVD is how it compares to older, more conventional methods.
A Modern, Greener Alternative
The primary advantage of PVD is its environmental profile. Unlike traditional electroplating (such as chrome plating), the PVD process does not produce toxic chemical waste or water pollution.
This makes it a more sustainable and responsible choice for manufacturers, aligning with modern environmental and safety standards.
Thin-Film Precision
PVD applies an extremely thin—yet very hard—coating, typically only a few microns thick. It conforms precisely to the underlying surface without altering the part's dimensions or details.
This is a benefit for precision components, but it's important to recognize that PVD is a surface finish, not a method for adding structural bulk or repairing significant surface damage.
How to Apply PVD to Your Goal
Your reason for choosing PVD will dictate its application. Consider which primary benefit you need to leverage.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and wear resistance: PVD is the superior choice for tools, firearms, and industrial components that must withstand intense physical stress.
- If your primary focus is a premium aesthetic with strong longevity: Use PVD for consumer goods like watches, faucets, and decorative hardware where appearance and resistance to daily use are critical.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: Select PVD as a modern, cleaner alternative to traditional electroplating methods that involve hazardous chemicals.
By understanding its unique blend of performance, aesthetics, and sustainability, you can leverage PVD coating to create products that are more durable, beautiful, and responsible.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Benefit of PVD Coating |
|---|---|
| Tools & Industrial Parts | Extreme wear resistance, extends lifespan up to 10x |
| Medical & Marine Hardware | Superior corrosion resistance, withstands harsh environments |
| Watches, Jewelry & Fixtures | Premium, durable aesthetic finishes (e.g., gold, black) |
| High-Temperature Components | Maintains hardness and integrity under extreme heat |
| Architectural Hardware | Combines durability with anti-fingerprint properties |
Ready to leverage PVD coating for your products?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface treatment and materials science. Whether you are developing more durable industrial tools, corrosion-resistant medical devices, or aesthetically superior consumer goods, our solutions can support your R&D and quality control processes.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior product performance and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- How does hot pressing work? Achieve Maximum Density for Advanced Materials
- What is hot press moulding? Achieve Superior Density and Complex Shapes with Heat and Pressure
- What is vacuum lamination? Achieve a Flawless, Durable Finish on Complex Shapes
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot stamping? Unlock Ultra-High Strength for Automotive Parts
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use



















