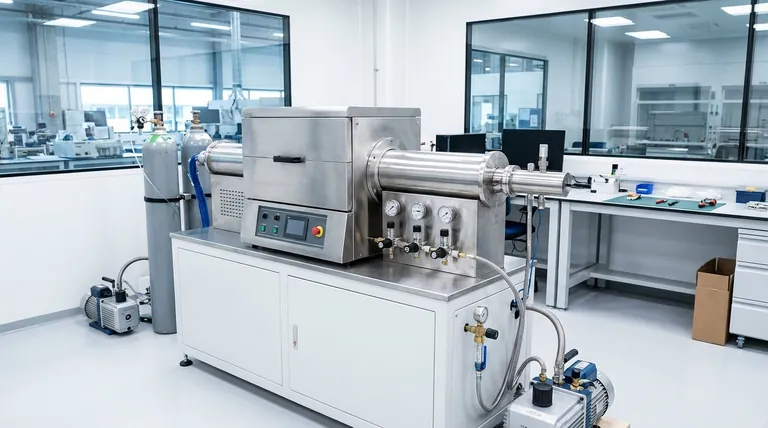
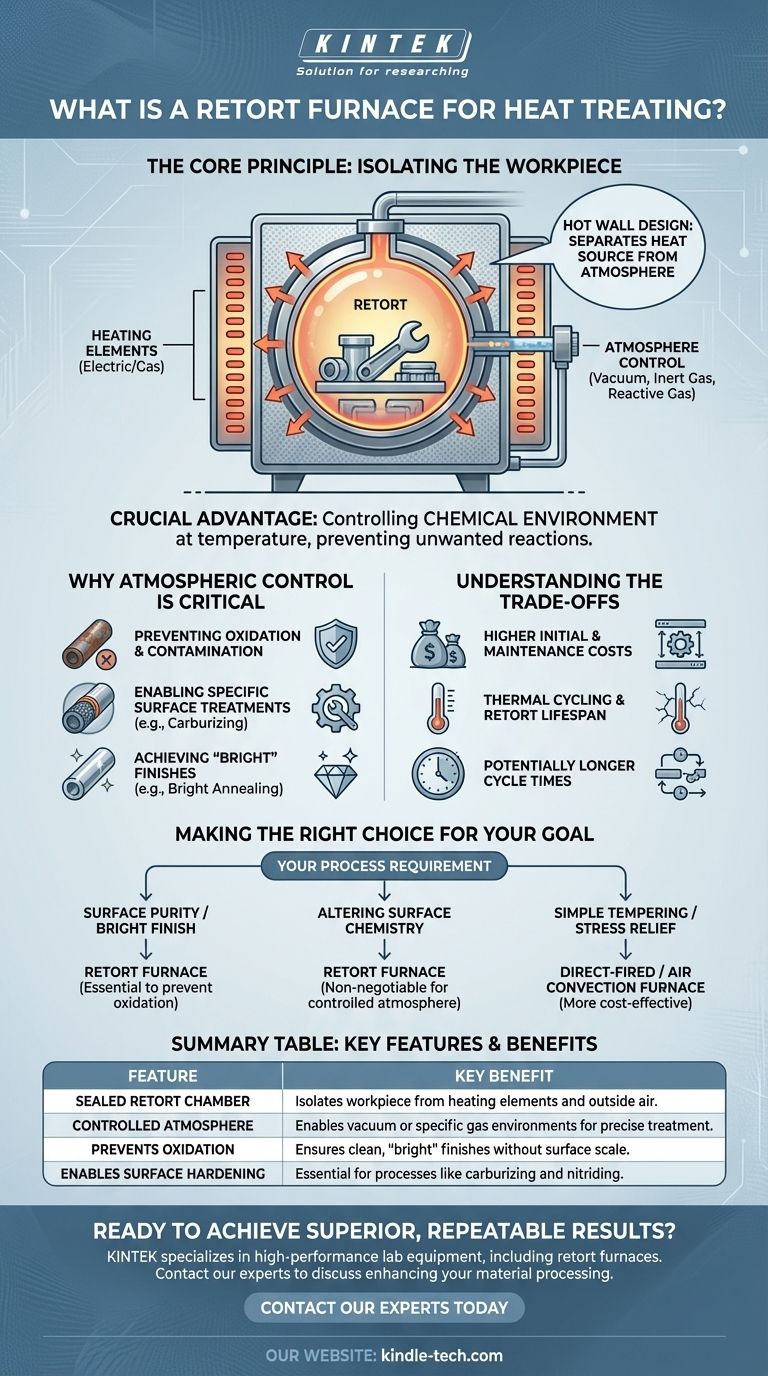
At its core, a retort furnace is a type of heat-treating furnace distinguished by its sealed inner chamber, known as the "retort." This design fundamentally separates the parts being treated from the furnace's heating elements and the outside air. This isolation is the key to creating a highly controlled atmosphere, which is critical for many advanced heat treatment processes.
The crucial advantage of a retort furnace isn't just about reaching a specific temperature; it's about controlling the chemical environment at that temperature. This prevents unwanted reactions like oxidation and enables precise changes to the material's surface properties.

The Core Principle: Isolating the Workpiece
Heat treatment relies on controlled heating and cooling to alter a material's physical and chemical properties. The retort furnace adds another layer of control by managing the atmosphere surrounding the workpiece.
What is the "Retort"?
The retort is a container, often made of a high-temperature metal alloy, that holds the parts being treated. This entire container is placed inside the main furnace chamber to be heated.
Separating Heat Source from Atmosphere
The heating elements, whether they are electric resistance coils or gas burners, are located outside the sealed retort. Heat transfers through the retort's walls to the workpiece inside.
This "hot wall" design ensures that the byproducts of combustion (in a gas furnace) or ambient air do not come into contact with the parts being treated.
Creating a Controlled Environment
With the workpiece isolated, the atmosphere inside the retort can be precisely manipulated. Air can be pumped out to create a vacuum, or specific process gases can be introduced.
This control is essential for preventing unwanted reactions and encouraging desired ones, which is impossible in a standard open-air furnace.
Why Atmospheric Control is Critical
At elevated temperatures, metals become highly reactive. Managing the atmosphere is often just as important as managing the temperature to achieve the desired outcome.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
When heated in the presence of oxygen, most metals will oxidize, forming a layer of scale on the surface. This can damage the part's finish and dimensions.
A retort furnace, by creating a vacuum or using an inert gas atmosphere, eliminates oxidation and contamination, ensuring high-quality components with clean surfaces.
Enabling Specific Surface Treatments
Processes like carburizing require the introduction of a specific carbon-rich atmosphere to change the surface chemistry of the steel, making it harder. A retort furnace is necessary to contain and control this reactive gas.
Achieving "Bright" Finishes
Processes like bright annealing are performed in a controlled atmosphere to relieve internal stresses in a material without discoloring the surface. The parts emerge from the furnace with a clean, "bright" finish, often eliminating the need for post-process cleaning.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the retort furnace design is not the universal solution for all heat treatment needs. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Initial and Maintenance Costs
The need for a sealed retort, gas handling systems, and vacuum pumps makes these furnaces more complex and expensive than simple air furnaces. The retort itself is often a consumable item that requires periodic replacement.
Thermal Cycling and Retort Lifespan
The retort is repeatedly heated and cooled, which causes significant thermal stress. This cycling can lead to material fatigue and eventual failure, making retort lifespan a primary operational consideration.
Potentially Longer Cycle Times
The process of sealing the chamber, purging the existing air, introducing the process atmosphere, and cooling can add time to the overall treatment cycle compared to simpler, open-air processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace is critical because the equipment directly dictates the results you can achieve. Your process requirements should guide your choice.
- If your primary focus is surface purity and a "bright" finish: A retort furnace is essential to prevent the oxidation and discoloration that occurs in open-air heating.
- If your primary focus is altering surface chemistry (like carburizing or nitriding): The sealed environment of a retort furnace is non-negotiable for containing and controlling the necessary reactive atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is simple tempering or stress relief where slight oxidation is acceptable: A less complex and more cost-effective direct-fired or air convection furnace is likely the more suitable choice.
Ultimately, choosing a retort furnace is a decision to prioritize precise atmospheric control to achieve superior and highly repeatable material properties.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Sealed Retort Chamber | Isolates the workpiece from the heating elements and outside air. |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Enables vacuum or specific gas environments for precise treatment. |
| Prevents Oxidation | Ensures clean, "bright" finishes without surface scale. |
| Enables Surface Hardening | Essential for processes like carburizing and nitriding. |
Ready to achieve superior, repeatable results in your heat treatment processes?
A retort furnace is the key to preventing oxidation, enabling surface hardening, and ensuring bright, clean finishes. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including retort furnaces, designed to meet the precise needs of laboratories and research facilities.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK retort furnace can enhance your material processing capabilities and deliver the quality you demand.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main types of biomass conversion processes? Unlock the Best Pathway for Your Energy Needs
- What is the range of pyrolysis? Master Temperature Control for Optimal Bio-Product Yields
- What is the temperature range for pyrolysis? Optimize for Biochar, Bio-oil, or Syngas
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity



















