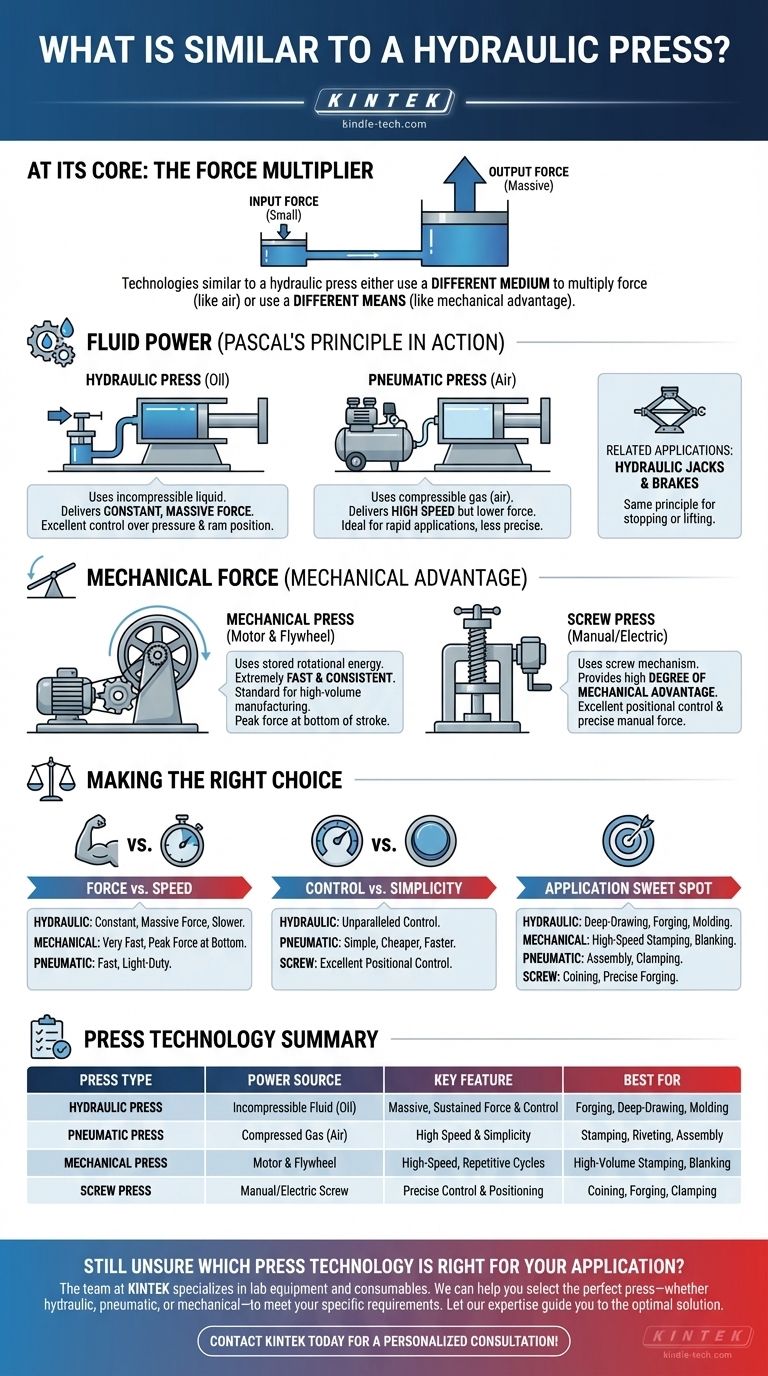
At its core, a hydraulic press is a force multiplier. Technologies that are most similar either use a different medium to multiply force, like a pneumatic press using air, or they achieve the same outcome through different means, such as the mechanical advantage of a screw press or a lever press.
The key to understanding what is similar to a hydraulic press is to recognize its function: converting a small input force into a massive output force. Similar machines achieve this same goal, but they replace the hydraulic fluid with either compressed gas or a purely mechanical system.

The Principle: How a Hydraulic Press Works
To find what's similar, we first must define the standard. A hydraulic press operates on a fundamental law of physics.
Pascal's Principle in Action
A hydraulic press uses Pascal's principle, which states that pressure applied to an enclosed, incompressible fluid is transmitted equally throughout that fluid.
The press consists of two interconnected cylinders of different sizes, each with a piston. A small force applied to the smaller piston (the plunger) creates pressure in the hydraulic fluid.
The Source of Its Power
This pressure acts on the entire system, including the much larger surface area of the second piston (the ram). Because the ram's area is so much larger, the resulting output force is magnified enormously. This is how a small effort can generate enough force to shape metal.
Machines with a Similar Principle: Fluid Power
The most direct relatives to a hydraulic press are those that also use fluid power, simply swapping the type of fluid.
Pneumatic Presses
A pneumatic press is the closest cousin to a hydraulic press. Instead of an incompressible liquid like oil, it uses a compressible gas, usually air.
Because air is compressible, pneumatic presses deliver force very quickly, making them ideal for rapid, lower-force applications like stamping, riveting, and assembly. However, they lack the immense force and precision of a hydraulic system.
Hydraulic Jacks and Brakes
While not "presses," hydraulic car jacks and braking systems use the exact same principle for a different purpose. They multiply a small force (from your foot on the brake pedal or hand on the jack handle) into a powerful force capable of stopping a vehicle or lifting it off the ground.
Machines with a Similar Function: Mechanical Force
Other machines achieve the same goal of pressing and forming materials but use mechanical advantage instead of fluid pressure.
Mechanical Presses
A mechanical press uses a motor to spin a flywheel, which stores rotational energy. This energy is then transferred through a system of cranks, gears, and levers to drive the ram down with significant force.
These presses are extremely fast and consistent, making them the standard for high-volume manufacturing like automotive body panel stamping. Their force, however, varies depending on the ram's position in its stroke.
Screw Presses
A screw press uses a simple but powerful machine: the screw. Turning the screw converts rotational motion into linear motion, creating compressive force with a high degree of mechanical advantage.
A simple bench vise is a form of screw press. Larger, powered versions are used in forging and coining, where precise control over the applied force and position is critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these technologies depends entirely on the specific requirements of the task. There is no single "best" option.
Force vs. Speed
A hydraulic press delivers constant, massive force throughout its entire stroke but is generally slower. A mechanical press is very fast but only delivers its peak force at the very bottom of the stroke.
Control vs. Simplicity
Hydraulic systems offer unparalleled control over pressure and ram position. Pneumatic systems are simpler, cheaper, and faster for light-duty tasks but offer less control. Screw presses provide excellent positional control.
Application Sweet Spot
Hydraulics excel at deep-drawing, forging, and molding where sustained pressure is key. Mechanical presses dominate high-speed stamping and blanking. Pneumatics are perfect for quick assembly and clamping operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's needs dictate the best technology.
- If your primary focus is maximum force and control: A hydraulic press is the clear choice for its ability to deliver immense, sustained pressure.
- If your primary focus is high-speed production: A mechanical press is ideal for its rapid and highly repeatable cycles.
- If your primary focus is quick action on lighter tasks: A pneumatic press offers speed and simplicity at a lower cost.
- If your primary focus is precise manual force: A screw press provides a direct and controllable way to apply significant pressure.
Ultimately, understanding the core principle of force multiplication allows you to see how different tools solve the same fundamental problem.
Summary Table:
| Press Type | Power Source | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Press | Incompressible Fluid (Oil) | Massive, Sustained Force & Control | Forging, Deep-Drawing, Molding |
| Pneumatic Press | Compressed Gas (Air) | High Speed & Simplicity | Stamping, Riveting, Assembly |
| Mechanical Press | Motor & Flywheel | High-Speed, Repetitive Cycles | High-Volume Stamping, Blanking |
| Screw Press | Manual/Electric Screw | Precise Control & Positioning | Coining, Forging, Clamping |
Still unsure which press technology is right for your application?
The team at KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables. We can help you select the perfect press—whether hydraulic, pneumatic, or mechanical—to meet your specific force, speed, and control requirements. Let our expertise guide you to the optimal solution for your laboratory or workshop needs.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual Lab Heat Press
People Also Ask
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.



















