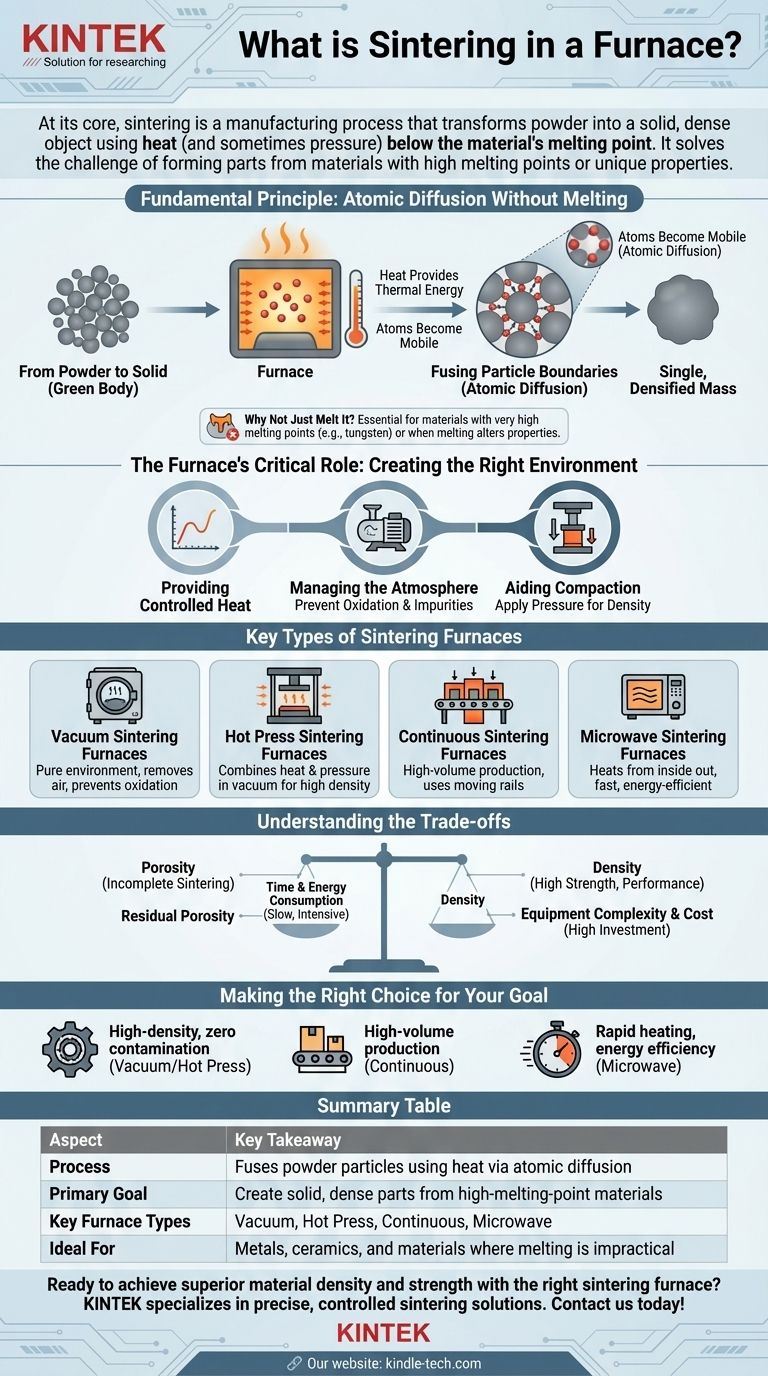
At its core, sintering is a manufacturing process that uses a furnace to transform a mass of powder into a solid, dense object. This is achieved by applying heat—and sometimes pressure—to a temperature below the material's actual melting point. Instead of liquefying, the individual particles of the material fuse together on an atomic level, creating a single, solid piece.
Sintering solves a fundamental manufacturing challenge: how to form solid parts from materials with extremely high melting points or unique properties. The process allows you to create dense, strong components from powders like ceramics and metals without having to reach the immense temperatures required to melt them.
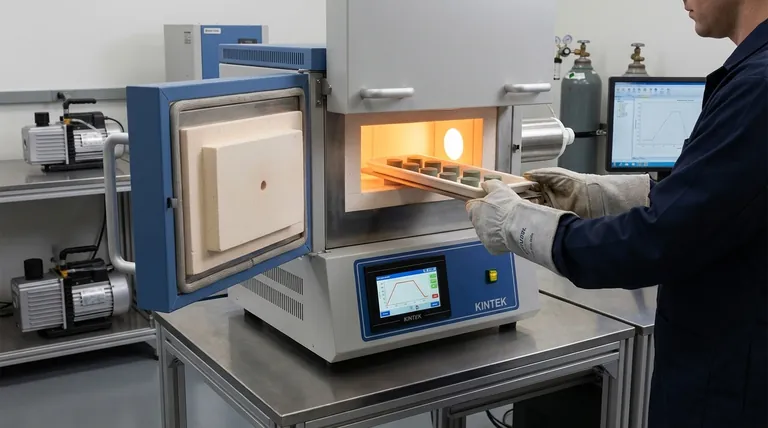

The Fundamental Principle: Atomic Diffusion Without Melting
From Powder to Solid
The process begins with a material in powder form, such as a metal or ceramic. This powder is typically compacted into a desired shape, often called a "green body," which is fragile but holds its form.
The Role of Heat
This green body is then placed in a furnace. The heat from the furnace provides the critical thermal energy that allows the atoms within the material's particles to become mobile and move around.
Fusing Particle Boundaries
As the atoms gain mobility, they migrate across the boundaries where individual particles touch. This process, known as atomic diffusion, effectively builds bridges between the particles, eliminating the gaps and pores between them. Over time, this fuses the countless individual particles into a single, densified mass.
Why Not Just Melt It?
Sintering is essential for materials with exceptionally high melting points, like tungsten and molybdenum, where reaching a liquid state is impractical or prohibitively expensive. It is also used when melting would alter or destroy the material's desired microstructure and final properties.
The Furnace's Critical Role: Creating the Right Environment
A furnace does more than just provide heat; it creates a highly controlled environment tailored to the specific material and desired outcome.
Providing Controlled Heat
The primary function is to apply a precise temperature profile. The material is heated, held at the sintering temperature for a specific duration, and then cooled in a controlled manner to ensure the final part has the correct properties and does not crack.
Managing the Atmosphere
Many materials will react with air at high temperatures. Sintering furnaces manage the internal atmosphere to prevent these unwanted reactions.
Preventing Oxidation
A vacuum atmosphere is one of the most common solutions. By removing air and oxygen, the furnace prevents the material from oxidizing, which would create impurities and weaken the final product. This is critical for reactive metals and advanced ceramics.
Aiding Compaction
Some advanced furnaces also apply immense pressure during the heating cycle. This pressure physically forces the particles closer together, which enhances the atomic diffusion process and results in a denser, stronger final component.
Key Types of Sintering Furnaces
Different furnaces are designed to meet specific production needs, from material type to production volume.
Vacuum Sintering Furnaces
These furnaces excel at creating a pure, contamination-free environment by removing nearly all of the air. They are the standard for processing materials that are highly sensitive to oxygen.
Hot Press Sintering Furnaces
This type combines high heat with direct, mechanical pressure in a vacuum. The dual action of heat and pressure is highly effective for producing extremely dense, high-performance ceramic components.
Continuous Sintering Furnaces
Designed for high-volume manufacturing, these furnaces continuously move parts through different zones. A walking-beam furnace, for example, uses moving rails to "walk" trays of parts through optimized heating, sintering, and cooling stages.
Microwave Sintering Furnaces
Rather than using conventional heating elements, these furnaces use microwave energy to heat the material from the inside out. This can lead to faster processing times and improved energy efficiency for certain compatible materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the sintering process involves balancing several competing factors.
Porosity vs. Density
The ultimate goal of sintering is typically to achieve the highest possible density by eliminating the pores between particles. Incomplete or improper sintering can leave residual porosity, which can compromise the material's mechanical strength and performance.
Time and Energy Consumption
Sintering can be a slow and energy-intensive process, as materials often need to be held at very high temperatures for extended periods. Optimizing the temperature and duration is key to balancing part quality with production cost.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
The technology required to achieve a high-vacuum, high-pressure, or controlled-atmosphere environment is complex and expensive. The choice of furnace is a direct trade-off between the performance requirements of the final part and the capital investment in equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of sintering furnace and process parameters should be driven by the end-use application of the component.
- If your primary focus is producing high-density ceramic or metal parts with zero contamination: A vacuum or hot press sintering furnace is the superior choice to prevent oxidation and achieve maximum compaction.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production of powder metallurgy parts: A continuous furnace, such as a walking-beam model, provides the efficiency and throughput needed for industrial scale.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and energy efficiency for specific ceramic materials: A microwave sintering furnace offers a modern alternative that heats the material directly and can significantly reduce cycle times.
Ultimately, selecting the right sintering approach requires balancing the final material properties you need against the realities of production cost, time, and scale.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Process | Fuses powder particles using heat (below melting point) via atomic diffusion. |
| Primary Goal | Create solid, dense parts from materials with high melting points. |
| Key Furnace Types | Vacuum, Hot Press, Continuous, Microwave. |
| Ideal For | Metals, ceramics, and materials where melting is impractical. |
Ready to achieve superior material density and strength with the right sintering furnace? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise, controlled sintering solutions your laboratory needs. Whether you're working with advanced ceramics or reactive metals, our expertise ensures you get the perfect furnace for your application. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can enhance your sintering process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is the physical description of a tube furnace? A Detailed Breakdown of its High-Temperature Design
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material



















