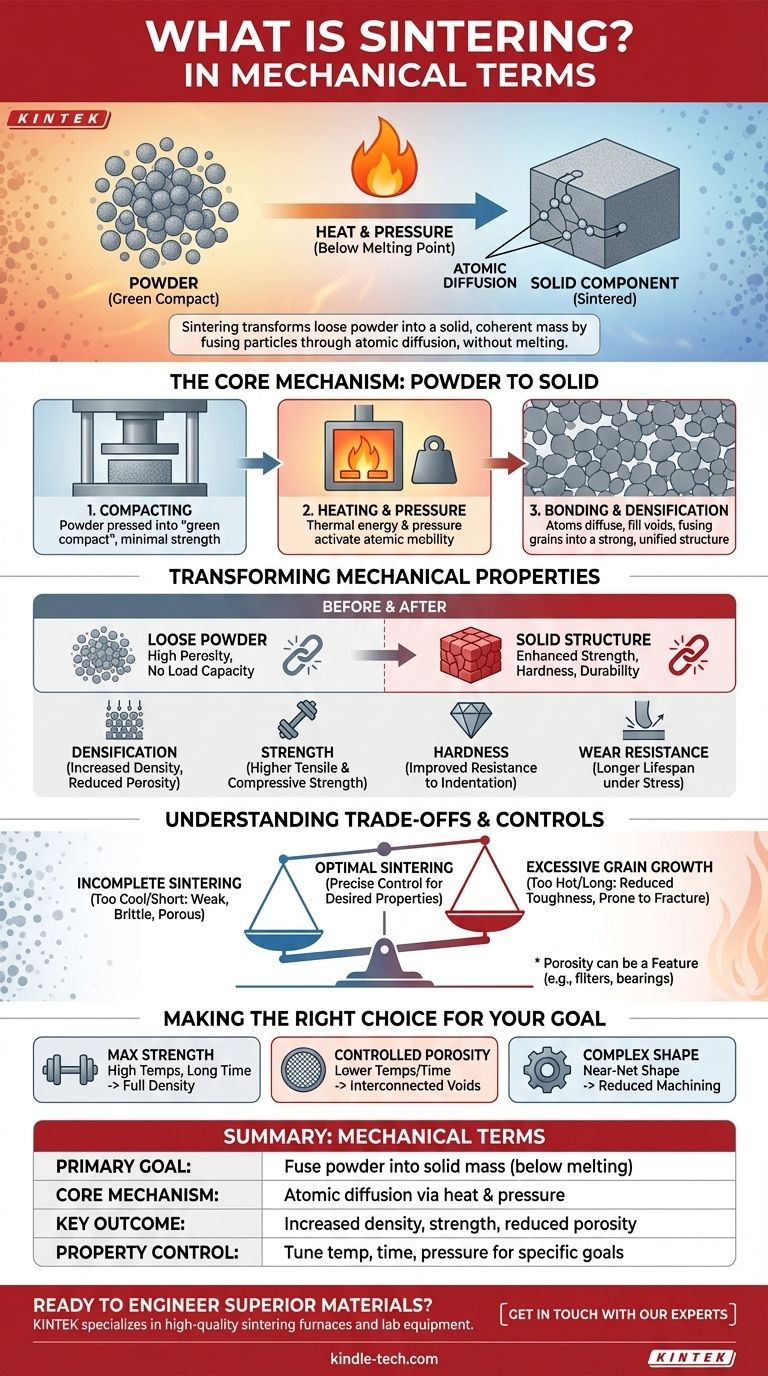
In mechanical terms, sintering is a transformative process that fuses individual particles of a material, typically a powder, into a solid, coherent mass. This is achieved by applying heat and pressure at levels below the material's melting point, causing atoms to diffuse across particle boundaries and create strong, permanent bonds where there were once only voids.
The core purpose of sintering is not simply to stick particles together, but to fundamentally re-engineer a material at the atomic level. It transforms a loose powder with no mechanical integrity into a dense, solid component with significantly enhanced strength, hardness, and durability.

The Core Mechanism: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is best understood as a multi-stage thermal process that creates a solid structure from a collection of individual grains.
The Starting Point: A Mass of Particles
The process begins with a material in powder form, such as a metal, ceramic, or plastic. This powder is often compacted into a desired shape, known as a "green compact," which has minimal strength and high porosity.
The Role of Heat and Pressure
The green compact is then heated in a controlled furnace. The heat provides the thermal energy necessary to make the atoms within the particles highly mobile. Pressure is often applied simultaneously to force the particles into intimate contact, reducing the distance atoms need to travel.
Atomic Diffusion: The Key to Bonding
With sufficient energy and proximity, atoms begin to migrate across the boundaries of adjacent particles. This atomic diffusion fills the voids (pores) between particles, reduces the overall surface area, and ultimately fuses the separate grains into a single, unified polycrystalline structure.
How Sintering Transforms Mechanical Properties
The atomic-level changes during sintering have a direct and profound impact on the material's bulk mechanical performance.
From Loose Powder to Structural Integrity
A powder compact has virtually no load-bearing capacity. Sintering creates a continuous, solid network that can withstand significant mechanical stress, transforming the material into a functional structural component.
Enhancing Density and Reducing Porosity
The primary mechanical benefit of sintering is densification. As atoms diffuse and fill the voids, the material's density increases dramatically. This reduction in porosity is directly responsible for most of the improvements in mechanical properties.
Boosting Strength, Hardness, and Wear Resistance
A denser, less porous material is inherently stronger and harder. The elimination of internal voids removes potential failure points (stress concentrators), leading to a significant increase in tensile strength, compressive strength, and resistance to wear and abrasion.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Controls
While powerful, sintering is a precise process where temperature, time, and pressure must be carefully managed to achieve the desired outcome.
The Risk of Incomplete Sintering
If the temperature is too low or the time is too short, atomic diffusion will be insufficient. This results in a component with high residual porosity, leaving it mechanically weak and brittle.
The Danger of Grain Growth
Conversely, excessive heat or time can cause a phenomenon called grain growth, where smaller grains merge into larger ones. While this increases density, overly large grains can sometimes reduce toughness, making the material more prone to fracture.
Porosity as a Feature, Not a Bug
In some applications, complete densification is not the goal. Sintering allows for precise control over the final porosity, which is essential for manufacturing products like porous metal filters or self-lubricating bearings that hold oil in their pores.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The parameters of the sintering process are tuned based on the intended mechanical properties of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: You will use higher temperatures and longer sintering times to minimize porosity and create a fully dense, robust part.
- If your primary focus is controlled porosity for filtration: You will use lower temperatures or shorter times to fuse the particles just enough to create a strong network while preserving a specific volume of interconnected voids.
- If your primary focus is creating a complex shape: You will leverage sintering's ability to form a "near-net shape" from powder, drastically reducing the need for post-process machining.
Sintering empowers you to engineer a material's final mechanical properties directly from its foundational particles.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description in Mechanical Terms |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Fuse powder particles into a solid mass below the melting point. |
| Core Mechanism | Atomic diffusion across particle boundaries, driven by heat and pressure. |
| Key Outcome | Increased density, reduced porosity, and enhanced mechanical properties. |
| Property Control | Tune temperature, time, and pressure to achieve desired strength or porosity. |
Ready to engineer superior materials with precise sintering? The right lab equipment is critical for achieving the perfect balance of strength, density, and porosity in your sintered components. KINTEK specializes in high-quality sintering furnaces and lab equipment, serving the exact needs of research and production laboratories. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your sintering process and help you achieve your material goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum environment system contribute to the hot pressing sintering of B4C-CeB6? Unlock Peak Ceramic Density
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution
- What are the main advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity and Performance
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics



















