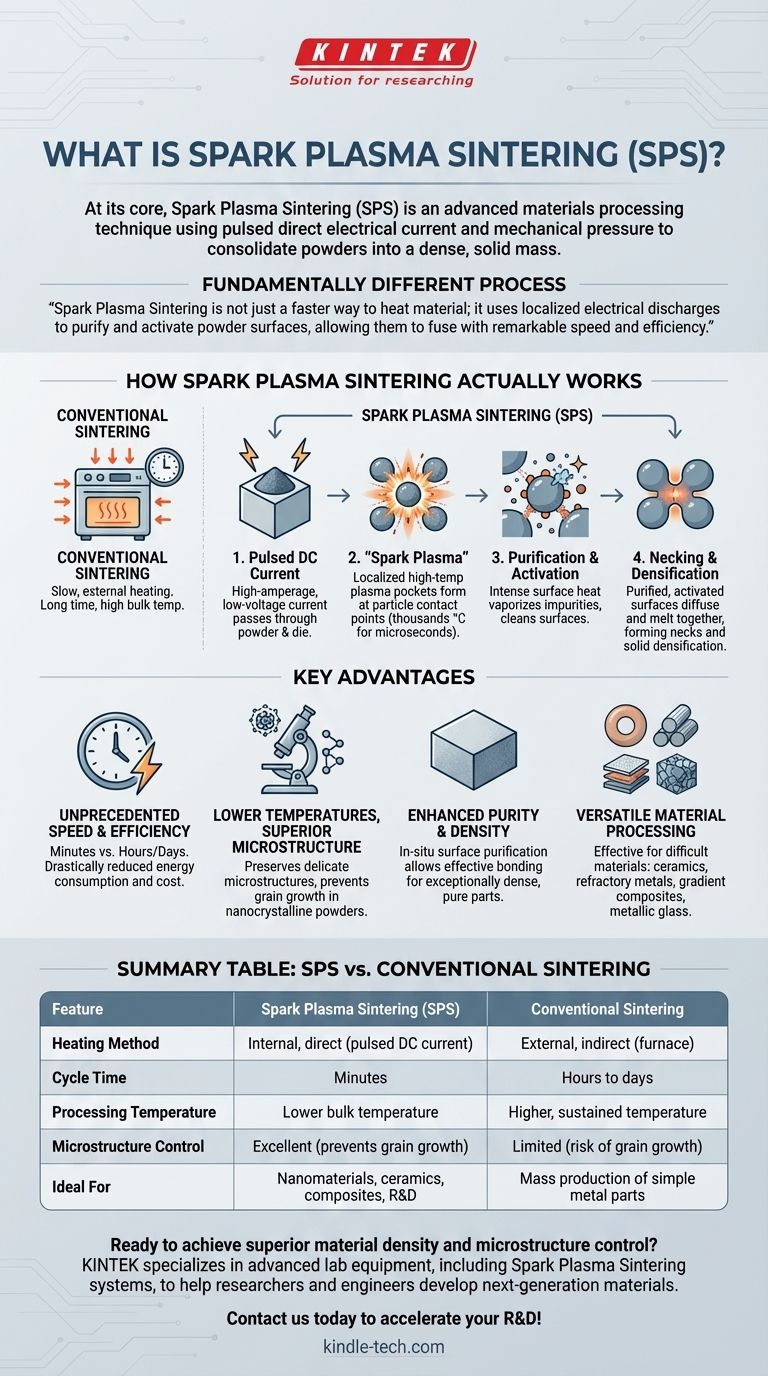
At its core, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is an advanced materials processing technique that uses a pulsed direct electrical current and mechanical pressure to consolidate powders into a dense, solid mass. Unlike conventional sintering which relies on slow, external heating in a furnace, SPS heats the material internally and directly, enabling dramatically faster processing at lower overall temperatures.
Spark Plasma Sintering is not just a faster way to heat material; it is a fundamentally different process. It uses localized electrical discharges between powder particles to purify and activate their surfaces, allowing them to fuse together with remarkable speed and efficiency.

How Spark Plasma Sintering Actually Works
Conventional sintering is like a slow oven, gradually heating an entire volume of material until particles begin to fuse. SPS is more like a series of microscopic, precision welding events happening simultaneously throughout the powder.
The Role of Pulsed DC Current
The process begins by placing a powder material into a conductive die, typically made of graphite. A high-amperage, low-voltage pulsed DC current is then passed through the die and, crucially, through the powder particles themselves.
Creating the "Spark Plasma"
At the contact points between individual powder particles, the electrical resistance is high. The pulsed current generates sparks or electrical discharges in the gaps, creating momentary, localized pockets of high-temperature plasma.
These plasma zones can reach thousands of degrees Celsius, but only for microseconds and only on the surface of the particles. The bulk of the material remains at a much lower temperature.
Purification and Necking
This intense, localized surface heat has two effects. First, it vaporizes and cleans away surface contaminants and oxides, which is why a significant reduction in elements like hydrogen is observed.
Second, the purified, super-activated surfaces of adjacent particles begin to diffuse and melt into each other, forming solid bridges called necks. As this happens across millions of particles, the entire powder compact rapidly densifies into a solid piece.
The Key Advantages Over Traditional Methods
The unique mechanism of SPS provides several significant advantages that make it a powerful tool for advanced materials science and manufacturing.
Unprecedented Speed and Efficiency
By heating the material directly and rapidly, SPS can complete a sintering cycle in minutes, compared to the many hours or even days required for conventional furnace sintering. This drastically reduces energy consumption and cost.
Lower Temperatures, Superior Microstructure
Because the bulk temperature of the material stays relatively low, SPS is exceptional at preserving delicate or engineered microstructures. It can consolidate nanocrystalline powders without causing the grain growth that would occur during prolonged high-temperature heating.
Enhanced Purity and Density
The in-situ surface purification process removes barriers to diffusion, allowing the particles to bond more effectively. This results in final parts that are exceptionally dense and free from the impurities that can compromise material properties.
Versatile Material Processing
SPS is effective for a vast range of materials that are difficult or impossible to process with conventional methods. This includes high-performance ceramics, refractory metals like tungsten, gradient composites, and even amorphous materials like metallic glass. It can also be used to join dissimilar materials, such as a ceramic to a metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, SPS is not a universal solution. Its application involves specific considerations that make it unsuitable for certain manufacturing scenarios.
Equipment and Tooling Costs
SPS systems are complex and represent a significant capital investment compared to traditional furnaces. The conductive graphite dies are also consumable items that have a limited lifespan and add to the operational cost.
Sample Geometry Limitations
The need to pass a uniform current and apply uniaxial pressure means that SPS is typically limited to producing simple shapes, such as discs, cylinders, and rectangular blocks. Complex, three-dimensional parts are not feasible.
Material Conductivity
The process works best when the current can pass through the powder itself. While techniques exist for sintering non-conductive powders (the graphite die heats up instead), the primary benefits of SPS are most pronounced with conductive or semi-conductive materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right sintering method depends entirely on your material, your desired properties, and your production goals.
- If your primary focus is preserving nanostructures or fine grains: SPS is the superior choice due to its low bulk temperatures and rapid processing times.
- If your primary focus is rapid development of novel alloys or composites: The extremely short cycle times of SPS make it an ideal tool for research and development.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density in difficult-to-sinter materials: SPS excels at densifying technical ceramics, refractory metals, and composites that resist conventional methods.
- If your primary focus is mass production of simple, low-cost metal parts: Traditional press-and-sinter powder metallurgy is likely the more economical and scalable solution.
By understanding its unique mechanism, you can leverage Spark Plasma Sintering to create next-generation materials with properties that were previously unattainable.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Internal, direct (pulsed DC current) | External, indirect (furnace) |
| Cycle Time | Minutes | Hours to days |
| Processing Temperature | Lower bulk temperature | Higher, sustained temperature |
| Microstructure Control | Excellent (prevents grain growth) | Limited (risk of grain growth) |
| Ideal For | Nanomaterials, ceramics, composites, R&D | Mass production of simple metal parts |
Ready to achieve superior material density and microstructure control?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including Spark Plasma Sintering systems, to help researchers and engineers develop next-generation materials. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution for consolidating nanocrystalline powders, technical ceramics, or complex composites.
Contact us today to discuss how SPS can accelerate your R&D and enhance your material properties!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification


















