The primary advantage of an electric induction furnace over a DC Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) during a cool start-up is its fundamentally superior heating mechanism. The induction furnace heats faster and with significantly higher thermal efficiency because it generates heat directly within the solid metal charge, whereas the EAF must first create a pool of molten metal and then transfer heat indirectly to the remaining solid scrap.
The core challenge of a cool start-up is efficiently converting electrical energy into heat within a solid mass. An induction furnace excels by turning the metal scrap itself into the heating element, bypassing the inefficient, localized, and indirect heating process inherent to an EAF in its initial phase.

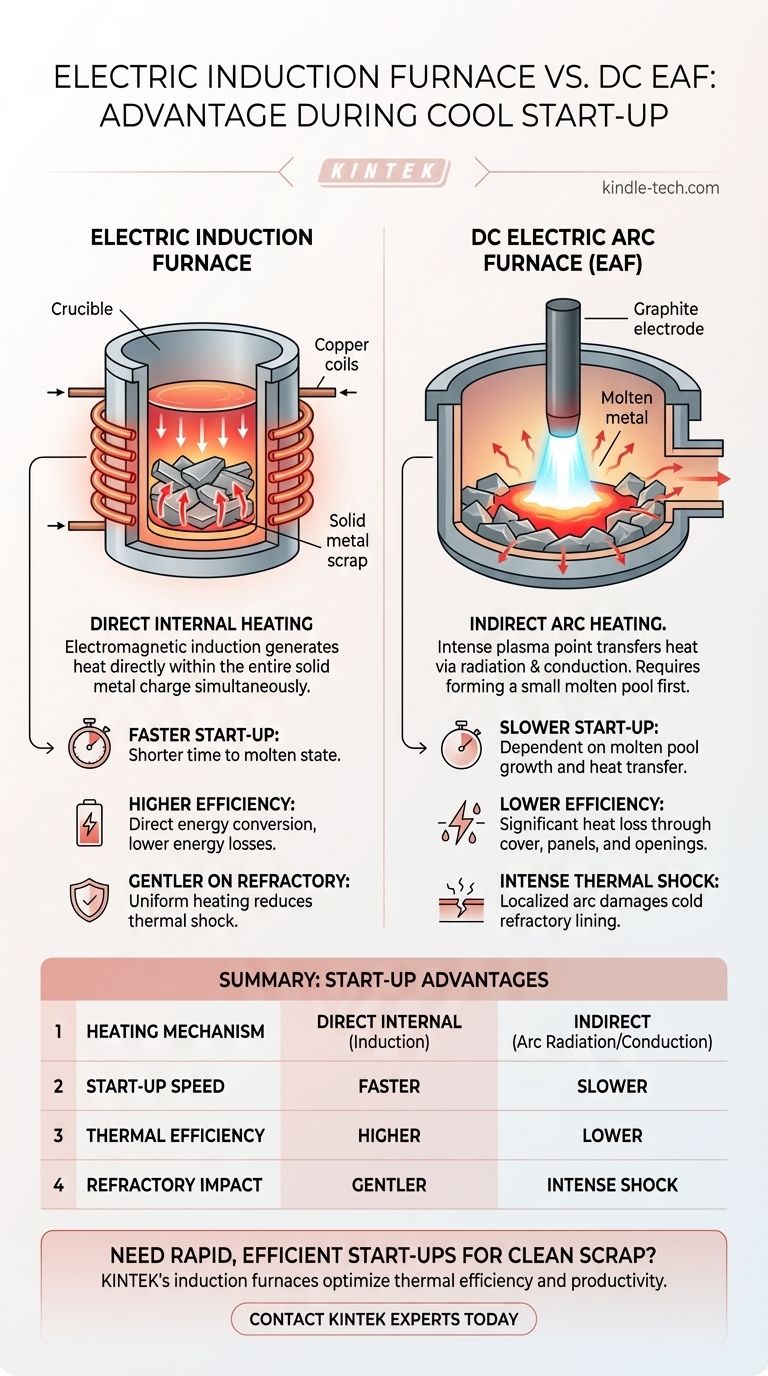
The Fundamental Difference in Heating Mechanisms
To understand the start-up advantage, we must first look at how each furnace generates and transfers heat. The two processes are fundamentally different, with profound implications for melting a cold, solid charge.
Induction Furnaces: Direct Internal Heating
An induction furnace operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. An alternating current flows through a copper coil, creating a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field.
This magnetic field penetrates the metal scrap placed inside the furnace, inducing strong electrical currents—known as eddy currents—directly within the metal pieces. The metal's own electrical resistance causes it to heat up rapidly and uniformly from the inside out.
DC EAF: Indirect Arc Heating
A DC Electric Arc Furnace operates by striking a massive electric arc between a single graphite electrode and the metallic charge. This creates an intensely hot plasma point, which is the primary source of heat.
Heat is transferred to the scrap through radiation and conduction from this extremely localized hot spot. The arc must first bore a hole through the top layer of scrap to create a small pool of molten metal.
The "Cold Start" Challenge for EAFs
During a cool start-up, the EAF's indirect heating mechanism is at its least efficient. The solid, irregularly shaped scrap provides poor electrical and thermal contact.
The arc's energy is concentrated in a very small area. The process of melting the entire charge relies on this small pool of liquid growing and transferring its heat to the surrounding solid metal, which is a slow and inefficient initial step.
Key Operational Advantages During Start-up
This difference in heating physics gives the induction furnace clear operational advantages when starting with a completely cold charge.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
Because the entire metallic charge in an induction furnace begins to heat internally and simultaneously, the time required to reach a molten state is much shorter.
This direct energy conversion results in significantly higher thermal efficiency and lower kilowatt-hour per ton (kWh/ton) consumption during the initial melt-down phase compared to an EAF.
Reduced Energy Losses
The EAF design inherently loses a significant amount of heat through its large furnace cover, water-cooled panels, and openings. These losses are particularly wasteful during the prolonged initial melting phase.
Induction furnaces are more compact and contained, minimizing radiant heat loss to the surrounding environment and directing more energy into the metal.
Gentler on Refractory Lining
The intense, localized heat of the electric arc can create severe thermal shock on the cold refractory lining of an EAF during start-up.
The more distributed and uniform heating of an induction furnace is far gentler on the refractory materials, potentially leading to longer lining life, especially in operations with frequent starts and stops.
Understanding the Broader Trade-offs
While the induction furnace has a clear advantage in cool start-ups, it is not universally superior. The choice of technology depends entirely on the operational scale and goals.
EAFs Excel in Scale and Scrap Versatility
EAFs can be built to much larger capacities, often exceeding 150 tons, making them the standard for high-volume steel production.
Their raw power and ability to form a refining slag layer allow them to process lower-quality, less-dense, and more contaminated scrap. The intense arc effectively melts and manages impurities that would be problematic for an induction furnace.
Induction Furnaces Require Cleaner Scrap
The performance of an induction furnace is highly dependent on the quality of the scrap. It requires a charge that is relatively clean, dense, and of a known chemical composition.
Non-metallic and non-conductive materials in the charge do not heat up and can interfere with the efficiency of the melting process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
The superiority of one furnace over the other is entirely context-dependent, hinging on the specific needs of the metal casting or steelmaking operation.
- If your primary focus is rapid melting, frequent cool start-ups, and processing clean scrap (e.g., in a foundry or specialty alloy plant): The induction furnace's speed and thermal efficiency make it the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is large-scale production using diverse or lower-grade scrap (e.g., in a mini-mill): The DC EAF's raw power, refining capability, and economies of scale are essential, despite its less efficient start-up phase.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace requires a clear understanding of how the physics of each heating method aligns with your specific production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electric Induction Furnace | DC Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | Direct internal heating via electromagnetic induction | Indirect heating via electric arc (radiation/conduction) |
| Start-up Speed | Faster (simultaneous heating of entire charge) | Slower (requires creating a molten metal pool first) |
| Thermal Efficiency (Start-up) | Higher (direct energy conversion) | Lower (significant heat losses) |
| Refractory Lining Impact | Gentler, more uniform heating | Intense thermal shock from localized arc |
| Ideal Scrap Type | Clean, dense, known composition | Diverse, lower-grade, contaminated |
Need a furnace for rapid, efficient start-ups?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including electric induction furnaces designed for superior thermal efficiency and faster melting times. If your operations demand frequent cool starts and you work with clean scrap or specialty alloys, our solutions can significantly reduce your energy consumption and increase productivity.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your specific needs and start optimizing your melting process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting



















