In essence, the atmosphere of a heat treatment furnace is a carefully engineered and controlled gaseous environment introduced during the heating process. Its purpose is to actively protect the surface of the workpiece from undesirable reactions, such as oxidation, and to facilitate specific chemical changes like adding carbon or nitrogen to the surface layer.
Thinking of a furnace atmosphere as just "background gas" is a critical mistake. It is an active and essential component of the heat treatment process, directly controlling the final chemical and physical properties of the material's surface.

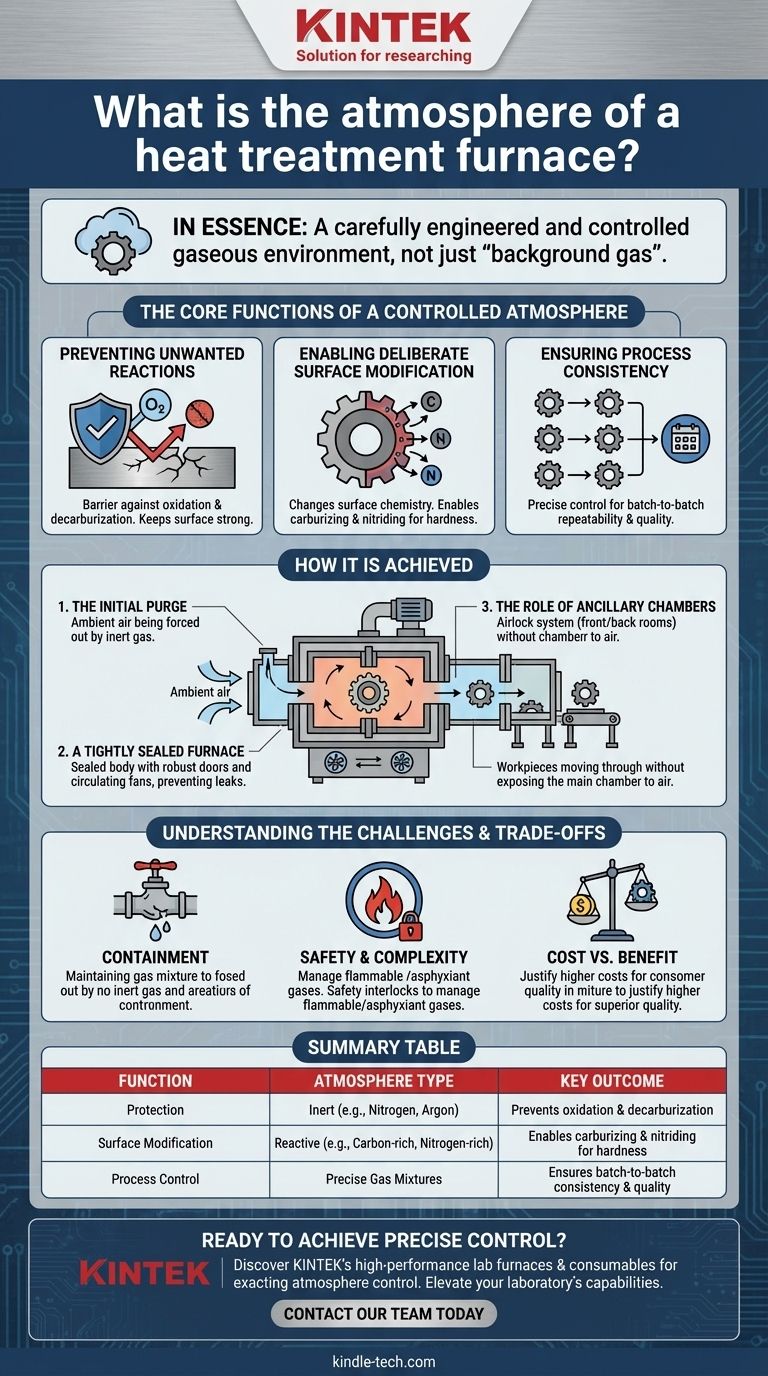
The Core Functions of a Controlled Atmosphere
The primary reason for controlling a furnace's atmosphere is that at high temperatures, metal surfaces become highly reactive. The gas surrounding the part dictates the outcome of these reactions, for better or worse.
Preventing Unwanted Reactions
The most basic function of a controlled atmosphere is protective. It creates a barrier between the hot metal surface and reactive elements like oxygen.
This prevents common defects like oxidation (scaling) and decarburization, which is the loss of carbon content from the surface of steel, making it softer and weaker.
Enabling Deliberate Surface Modification
Beyond simple protection, a controlled atmosphere can be used to intentionally alter the workpiece's surface chemistry. This is a foundational concept in metallurgy.
Processes like carburizing use a carbon-rich atmosphere to diffuse carbon into the surface of steel, creating a hard, wear-resistant outer layer while maintaining a tougher core.
Similarly, nitriding uses a nitrogen-rich atmosphere to achieve a very hard surface case, enhancing wear and fatigue resistance.
Ensuring Process Consistency
By precisely managing the gas composition, temperature, and pressure, a controlled atmosphere ensures that every part in a batch—and every subsequent batch—receives the exact same treatment. This repeatability is critical for quality control in manufacturing.
How a Controlled Atmosphere is Achieved
Creating and maintaining this precise gaseous environment requires specialized furnace construction and careful operational procedures.
The Initial Purge
Before the heating cycle begins, the furnace must be purged of ambient air. This is done by flooding the chamber with the desired process gas, such as nitrogen, argon, or the specific reactive gas mixture.
A Tightly Sealed Furnace
The furnace body must be exceptionally well-sealed to prevent the controlled atmosphere from leaking out and, more importantly, to prevent air from leaking in.
Key components include a sealed furnace body, water-cooled fans to circulate the atmosphere without compromising the seal, and robust door mechanisms.
The Role of Ancillary Chambers
Many atmosphere furnaces include front and back rooms or vestibules. These act as airlocks, allowing workpieces to be loaded or moved to a quench tank without exposing the main heating chamber to outside air, thus preserving the integrity of the atmosphere.
Understanding the Challenges and Trade-offs
While essential for high-quality results, implementing a controlled atmosphere introduces complexity and potential issues that must be managed.
The Challenge of Containment
Maintaining the precise gas mixture is the primary challenge. Even small leaks can contaminate the atmosphere with oxygen or moisture, compromising the entire process and potentially ruining the parts.
Safety and Operational Complexity
Many gases used in heat treatment atmospheres are flammable (like hydrogen or endothermic gas) or asphyxiants (like nitrogen). This necessitates sophisticated safety interlocks, ventilation, and explosion-proof devices, adding to the furnace's cost and operational complexity.
Cost vs. Benefit
A controlled atmosphere furnace is significantly more expensive to build, operate, and maintain than a simple air furnace. The cost of the gases themselves, along with the monitoring equipment, must be justified by the superior quality, properties, and value of the finished components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The type of atmosphere you need is dictated entirely by the desired outcome for your material.
- If your primary focus is simple heating or annealing where surface finish is not critical: An uncontrolled air atmosphere may be sufficient, but you must account for surface oxidation and scale.
- If your primary focus is preventing decarburization and maintaining a clean surface on a finished part: A neutral or inert protective atmosphere is essential.
- If your primary focus is case hardening or altering surface chemistry (e.g., carburizing): A highly specific, reactive atmosphere is non-negotiable and is the core of the process.
Ultimately, mastering the furnace atmosphere transforms heat treatment from a simple heating process into a precise material engineering discipline.
Summary Table:
| Function | Atmosphere Type | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Protection | Inert (e.g., Nitrogen, Argon) | Prevents oxidation & decarburization |
| Surface Modification | Reactive (e.g., Carbon-rich, Nitrogen-rich) | Enables carburizing & nitriding for hardness |
| Process Control | Precise Gas Mixtures | Ensures batch-to-batch consistency & quality |
Ready to achieve precise control over your heat treatment processes? The right furnace atmosphere is critical for preventing defects and enhancing material properties. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab furnaces and consumables designed for exacting atmosphere control. Our experts can help you select the ideal equipment to meet your specific metallurgical goals, ensuring superior surface quality and consistent results.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK's solutions can elevate your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab



















