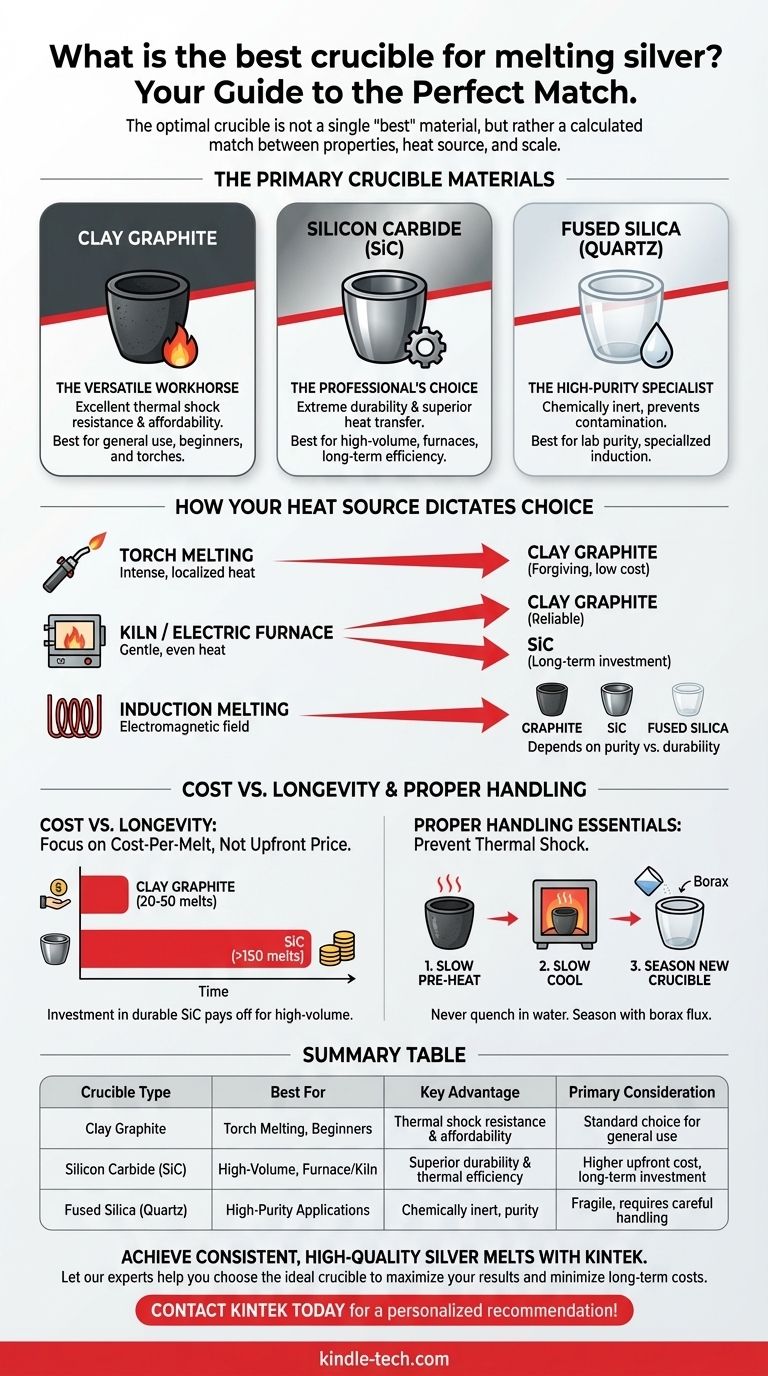
For most applications, the best and most versatile crucible for melting silver is a clay graphite crucible. It offers an excellent balance of thermal shock resistance, durability, and affordability, making it the standard choice for everyone from hobbyists using a torch to small-scale professional foundries. While it is the best general-purpose option, the truly "best" crucible depends on your heat source and the scale of your work.
The optimal crucible is not a single "best" material, but rather a calculated match between the crucible's properties and your specific melting process. The key is to balance upfront cost against long-term durability and efficiency, all while considering your heat source.

The Primary Crucible Materials for Silver
Choosing the right crucible begins with understanding the core materials and their distinct advantages. Silver melts at 961.8°C (1763.2°F), a temperature easily handled by several types of crucibles, but each behaves differently.
Clay Graphite: The Versatile Workhorse
A clay graphite crucible is a composite material. The graphite provides excellent thermal conductivity for efficient heat transfer, while the clay and other binders provide structural integrity and resistance to thermal shock.
This is the most common and recommended type for general silver melting. It performs well with torches, in kilns, and in electric furnaces.
Silicon Carbide (SiC): The Professional's Choice
Silicon Carbide is a synthetic compound known for its extreme hardness and durability. SiC crucibles have superior thermal conductivity compared to clay graphite, meaning they heat up faster and more evenly, potentially saving fuel and time.
While their initial cost is significantly higher, they can last many times longer than a clay graphite crucible, making them a cost-effective investment for high-volume operations.
Fused Silica (Quartz): The High-Purity Specialist
Fused silica, or quartz, crucibles are used when melt purity is the absolute highest priority. They are chemically inert and will not contaminate the silver.
However, they are more fragile and susceptible to cracking from thermal shock if not handled with extreme care. They are most often used in laboratory settings or with induction heating for specialized applications.
How Your Heat Source Dictates Your Choice
The single biggest factor in choosing a crucible is the method you use to heat it. An inappropriate match between heat source and crucible is the most common cause of failure.
For Torch Melting
A direct flame from a propane or MAPP gas torch creates intense, localized hot spots. This environment is extremely harsh and puts immense stress on the crucible, making thermal shock a primary concern.
A clay graphite crucible is the ideal choice here. Its superior thermal shock resistance and lower cost make it more forgiving. If it cracks from improper heating, the financial loss is minimal.
For Kiln or Electric Furnace Melting
These methods provide gentle, even, and highly controlled heat. This is the ideal environment for any crucible, as it dramatically reduces the risk of thermal shock.
In a furnace, both clay graphite and Silicon Carbide (SiC) are excellent choices. The decision comes down to budget and frequency. Clay graphite is a reliable, low-cost option, while SiC is a long-term investment that offers better performance.
For Induction Melting
Induction systems heat the metal directly via an electromagnetic field. The crucible's role is primarily to contain the molten metal.
Graphite, SiC, and Fused Silica are all commonly used. SiC's excellent thermal properties help maintain temperature, while Fused Silica is chosen for its purity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Longevity
Beginners often choose a crucible based on the lowest upfront price. This can be a false economy, as a cheap crucible that fails quickly can be more expensive in the long run.
The Upfront Cost Fallacy
A low-quality crucible may only last a few melts before cracking. A high-quality clay graphite crucible might last for 20-50 melts if cared for, while a SiC crucible can last for over 150 melts.
Focus on the cost-per-melt, not the initial purchase price. For anyone melting silver more than a few times a month, the investment in a more durable crucible quickly pays for itself.
The Importance of Proper Handling
No crucible, regardless of price, will survive improper use. The number one cause of crucible failure is thermal shock, which is cracking caused by rapid changes in temperature.
Always pre-heat your crucible slowly and gently before introducing intense heat. Likewise, allow it to cool slowly inside the furnace or on a heat-proof surface. Never quench a hot crucible in water or place it on a cold, conductive surface.
Finally, you must season a new crucible by melting a small amount of borax flux inside it. This creates a thin, glassy layer that seals the crucible's pores, preventing molten silver from sticking and protecting the crucible material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your crucible based on a clear understanding of your goals, frequency, and equipment.
- If you are a beginner or melt infrequently with a torch: Start with a quality clay graphite crucible to learn the process without a large financial risk.
- If you operate a small studio with an electric furnace: A premium clay graphite crucible offers great value, but consider upgrading to Silicon Carbide for better efficiency and a much longer service life.
- If you are running a high-volume operation: Invest in Silicon Carbide (SiC) crucibles. Their durability and thermal efficiency provide the lowest long-term cost and the most reliable performance.
Choosing the right tool is the first step toward achieving consistent, high-quality results in your work.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Type | Best For | Key Advantage | Primary Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clay Graphite | Torch Melting, Beginners | Excellent thermal shock resistance & affordability | Standard choice for general use |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | High-Volume, Furnace/Kiln | Superior durability & thermal efficiency | Higher upfront cost, long-term investment |
| Fused Silica (Quartz) | High-Purity Applications | Chemically inert, prevents contamination | Fragile, requires careful handling |
Achieve consistent, high-quality silver melts with the right crucible from KINTEK.
Whether you're a hobbyist starting with a torch or a professional running a high-volume foundry, selecting the correct crucible is critical for efficiency, safety, and melt purity. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering a range of crucibles—including durable clay graphite and long-lasting silicon carbide—perfectly suited to your specific laboratory or studio needs.
Let our experts help you choose the ideal crucible to maximize your results and minimize long-term costs. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
People Also Ask
- What protective roles do ceramic crucibles and active carbon particles serve? Optimize WC/Cu Sintering Success
- What influence can a graphite crucible have on low-temperature ceramization? Ensure Material Stability and Purity
- Why is porcelain used for crucible? Discover the Ideal Balance of Heat Resistance and Affordability
- What is the function of a crucible? A Guide to High-Temperature Material Containment
- Why is a high-temperature crucible essential for Li13In3 alloy electrodes? Ensure Purity & Precise Thermal Control
- What crucibles are used in muffle furnace? Choose the Right Material for Your High-Temp Application
- Why is a ceramic crucible essential for ZrCu-based master alloys? Ensuring Purity and Thermal Stability
- How much heat can a crucible take? Choosing the Right Material for Your Melting Application



















