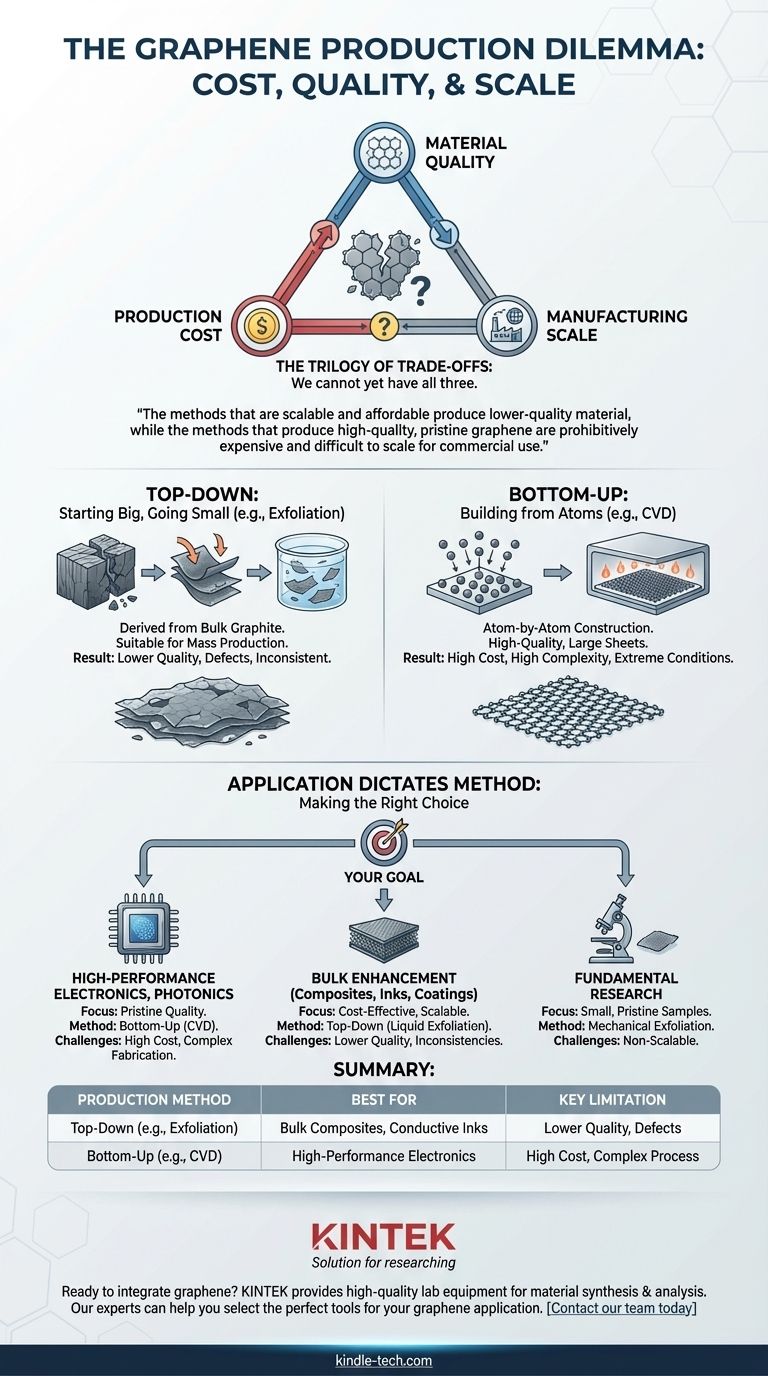
The biggest obstacle to producing graphene is not a single issue, but a fundamental conflict between three competing goals: production cost, material quality, and manufacturing scale. Current methods force a trade-off, meaning we cannot yet produce high-quality graphene cheaply and at a massive scale.
The core challenge in graphene production is a persistent dilemma: the methods that are scalable and affordable produce lower-quality material, while the methods that produce high-quality, pristine graphene are prohibitively expensive and difficult to scale for commercial use.

The Two Paths of Graphene Production
To understand the production obstacle, you must first understand the two fundamentally different approaches to making graphene: starting big and going small ("top-down"), or starting small and building up ("bottom-up").
Top-Down: Deriving Graphene from Graphite
This approach begins with bulk graphite—the same material found in pencils—and separates it into individual layers of graphene.
The most famous example is mechanical exfoliation, the "Scotch tape method," which peels layers apart. While it produces exceptionally high-quality graphene for lab research, it is completely unscalable.
A more commercially viable top-down method is liquid-phase exfoliation. This process uses chemical or mechanical force in a liquid to break graphite apart into graphene flakes. It's suitable for mass production but results in a product with significant defects and inconsistent quality, limiting its electrical performance.
Bottom-Up: Building Graphene from Atoms
This approach constructs a graphene sheet atom by atom on a substrate material.
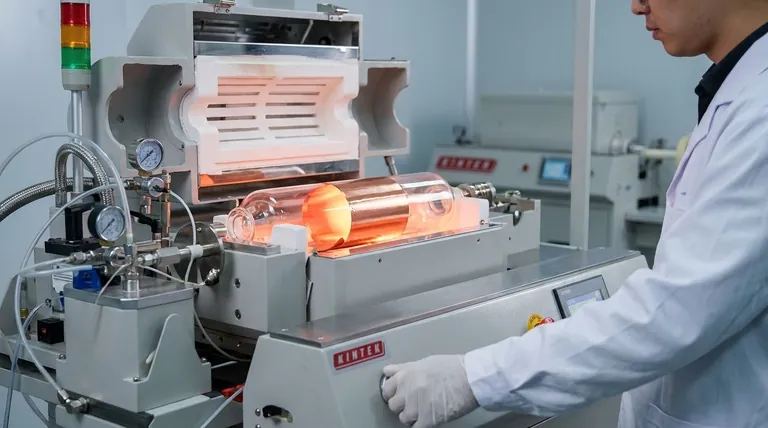
The most promising bottom-up technique is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). In this process, a carbon-containing gas is introduced into a high-temperature chamber, where it decomposes on a metal substrate (like copper foil), forming a continuous, high-quality layer of graphene.
The Core Challenge: The Quality vs. Scale Dilemma
Each production path presents its own significant, and currently unavoidable, set of obstacles that create the central conflict.
The Problem with Scale (Top-Down)
The primary issue with scalable top-down methods like liquid exfoliation is quality control. The resulting material is often a mix of single-layer, few-layer, and multi-layer graphene flakes with structural defects.
This inconsistent quality makes the material unsuitable for high-performance applications like advanced electronics, which demand the pristine, flawless structure of a single atomic layer.
The Problem with Cost and Complexity (Bottom-Up)
While CVD can produce large sheets of high-quality graphene, it faces immense hurdles in cost and complexity.
The process requires extreme physical conditions, including high temperatures (800–1050 °C) and low-pressure vacuum environments. This necessitates specialized, expensive equipment and consumes a significant amount of energy, driving up costs.
Furthermore, the graphene grown via CVD must be carefully transferred from its growth substrate to a final, usable substrate. This delicate transfer process is a major source of defects, wrinkles, and contamination that can degrade the material's exceptional properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Navigating the world of graphene requires a pragmatic understanding of its limitations and the nuances of what is being offered.
"Graphene" Isn't Always Graphene
A critical point to understand is that much of the bulk material marketed as "graphene" is actually graphene oxide or graphene nanoplatelets derived from top-down methods.
While useful for applications like strengthening composites or creating conductive inks, these materials do not possess the revolutionary electronic and mechanical properties of the pristine, single-layer graphene sheets produced in labs.
Application Dictates Method
There is no single "best" method for producing graphene; there is only the best method for a specific application.
The low-cost, lower-quality material from exfoliation is perfectly adequate—and economically sensible—for enhancing polymers or concrete. Conversely, attempting to build a high-speed transistor with this material would be impossible.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's requirements will determine which production trade-offs are acceptable.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or photonics: You must use high-quality material from a bottom-up method like CVD and be prepared for high costs and complex fabrication challenges.
- If your primary focus is bulk material enhancement (e.g., composites, coatings, inks): Top-down liquid-phase exfoliation offers the most cost-effective and scalable pathway, provided you can tolerate inconsistencies in quality.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Mechanical exfoliation remains a simple and effective way to obtain small quantities of pristine graphene for study.
Successfully leveraging graphene depends less on waiting for a single perfect production method and more on understanding which current method best aligns with your technical and commercial goals.
Summary Table:
| Production Method | Best For | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Top-Down (e.g., Exfoliation) | Bulk Composites, Conductive Inks | Lower Quality, Defects |
| Bottom-Up (e.g., CVD) | High-Performance Electronics | High Cost, Complex Process |
Ready to integrate graphene into your research or product development? The right equipment is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including systems for material synthesis and analysis. Our experts can help you select the perfect tools for your graphene application, whether you're focused on research-scale quality or production-scale efficiency. Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and how we can support your innovation goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different techniques for carbon nanotube synthesis? From Research to Industrial Scale
- What is the sputtering process in nanotechnology? A Guide to Atomic-Level Thin Film Deposition
- Are carbon nanotubes safe for the environment? Weighing Performance Benefits Against Ecological Risks
- What are the best sources of graphene? Choose the Right Carbon Source for Your Application
- What is the chirality diameter of a carbon nanotube? How Chirality Determines CNT Properties
- What does the deposition rate depend on? Key Factors for Thin-Film Process Control
- Can carbon nanotubes be used for semiconductors? Unlock Next-Gen Electronics with CNTs
- What are the applications of thin-film in renewable energy? Beyond Solar Panels to Energy Storage & Hydrogen



















