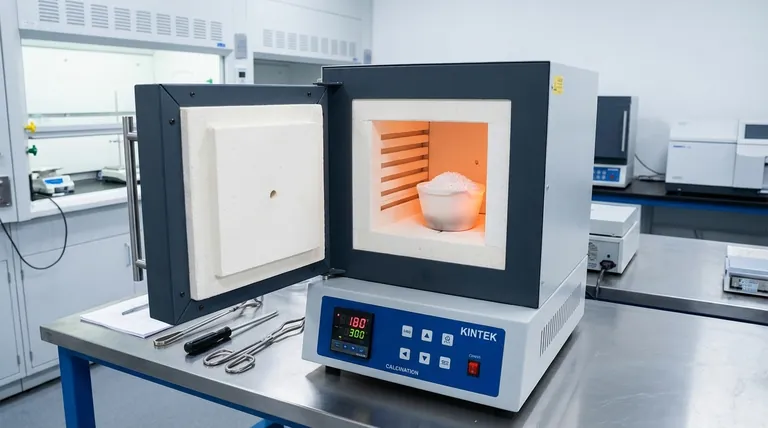
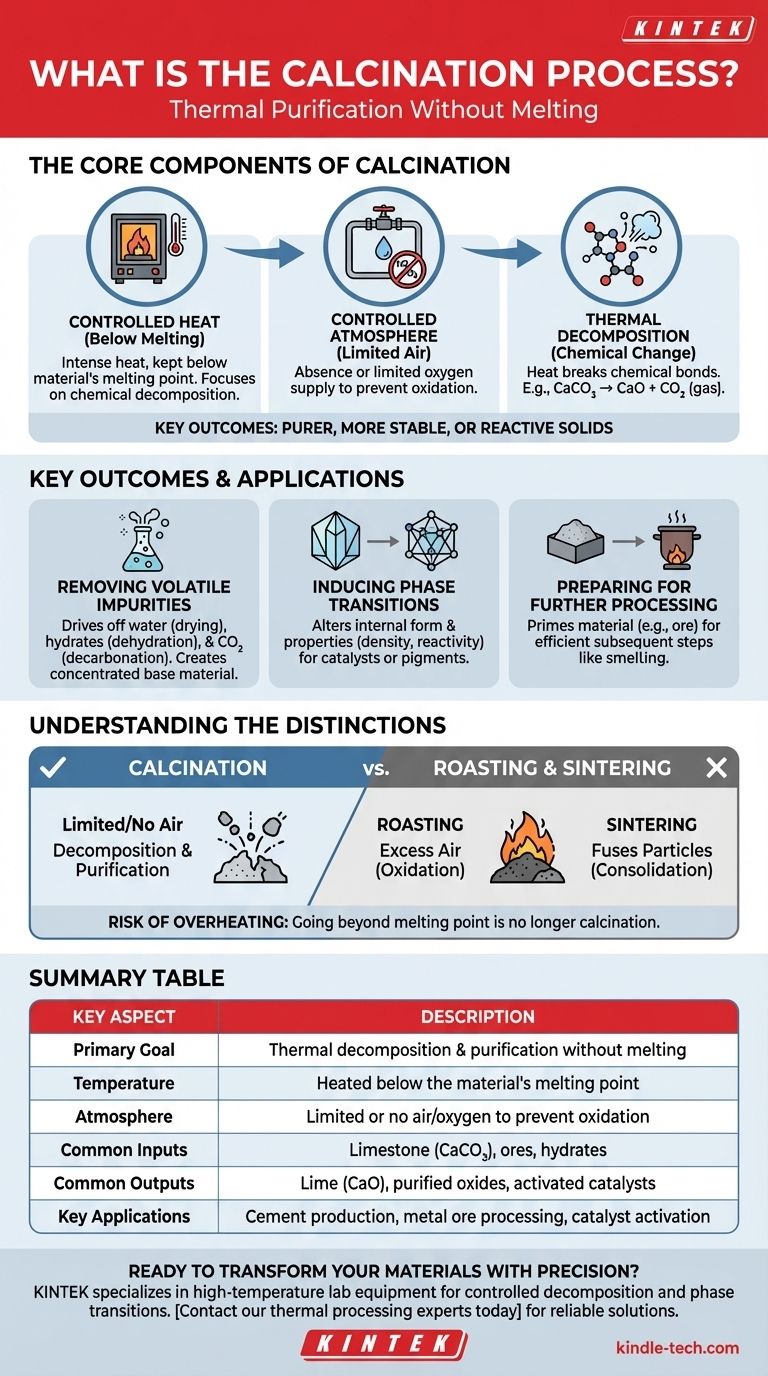
In essence, calcination is a thermal purification process. It involves heating a solid material to a high temperature, but below its melting point, in a controlled atmosphere with little to no air. This precise heating drives off volatile substances like water and carbon dioxide, triggers chemical decomposition, or changes the material's internal crystal structure, resulting in a purer, more stable, or more reactive solid.
The core purpose of calcination is not to melt a material, but to transform it. By carefully controlling heat and atmosphere, you can selectively remove unwanted components or change a material's properties without altering its solid state.

How Calcination Fundamentally Works
To grasp calcination, it's essential to understand its three core components: controlled heat, a specific atmosphere, and the resulting chemical changes.
The Role of Heat (Below Melting)
The most critical parameter in calcination is temperature. The material is heated intensely, but always kept below its melting point.
This ensures the process focuses on chemical decomposition rather than a change of state (from solid to liquid). It allows for the controlled breakdown of compounds within the solid structure.
The Controlled Atmosphere
Calcination is typically performed in the absence or with a limited supply of air (oxygen).
This is a crucial distinction. By limiting oxygen, you prevent oxidation or combustion. The goal is to break the material down with heat alone (thermal decomposition), not to react it with oxygen.
The Primary Goal: Decomposition
The heat applied during calcination provides the energy needed to break chemical bonds. This is known as thermal decomposition.
A classic example is the production of lime from limestone. When limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) is calcined, it decomposes into lime (calcium oxide, CaO) and releases carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas, a volatile component.
Key Outcomes of Calcination
Depending on the material and the goal, calcination achieves several specific outcomes.
Removing Volatile Impurities
The most common application is purification. The process drives off volatile substances, which are components that easily turn to gas when heated.
This includes physically bound water (drying), chemically bound water in hydrates (dehydration), and carbon dioxide from carbonate ores (decarbonation). The result is a more concentrated and purified version of the base material.
Inducing Phase Transitions
Sometimes, the goal isn't to remove anything but to change the material's internal form.
Calcination can induce a phase transition, which alters the crystalline structure of the material. This can change its properties, such as hardness, density, or reactivity, making it suitable for a specific application like a catalyst or pigment.
Preparing Materials for Further Processing
Often, calcination is a preparatory step. By removing impurities and creating a more reactive substance (like an oxide), the material is primed for a subsequent process.
For instance, calcining an ore can make the subsequent extraction of the final metal via smelting more efficient and less energy-intensive.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Distinctions
Calcination is often confused with other thermal processes. Understanding the differences is key to understanding its specific function.
Calcination vs. Roasting
Roasting is another thermal process, but it is performed with an excess of air. Its goal is to intentionally cause oxidation. For example, converting a metal sulfide ore into a metal oxide. Calcination, by contrast, actively avoids oxidation.
Calcination vs. Sintering
Sintering also uses heat below the melting point, but its goal is entirely different. Sintering aims to fuse small particles together to increase the material's density and strength. Calcination purifies and decomposes; sintering consolidates. In many industrial workflows, calcination is performed first, followed by sintering.
The Risk of Overheating
Controlling the temperature is paramount. If the material is heated beyond its melting point, the process is no longer calcination. It becomes melting or sintering, which may be undesirable and lead to a completely different, and often unusable, end product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Calcination is a precise tool used to achieve specific material transformations. Your goal dictates its application.
- If your primary focus is purifying an ore: Use calcination to drive off water and carbonates, creating a more concentrated oxide before smelting.
- If your primary focus is producing cement: Calcination of limestone to produce lime is the foundational, non-negotiable first step in the process.
- If your primary focus is activating a catalyst: Use calcination to achieve the ideal crystal structure and surface area needed for high chemical reactivity.
Ultimately, calcination is a foundational technique in materials science for deliberately modifying a solid's chemical makeup and structure through heat.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Thermal decomposition and purification without melting |
| Temperature | Heated below the material's melting point |
| Atmosphere | Limited or no air/oxygen to prevent oxidation |
| Common Inputs | Limestone (CaCO₃), ores, hydrates |
| Common Outputs | Lime (CaO), purified oxides, activated catalysts |
| Key Applications | Cement production, metal ore processing, catalyst activation |
Ready to transform your materials with precision?
The calcination process is critical for purifying ores, producing cement, and activating catalysts. KINTEK specializes in the high-temperature lab equipment needed to achieve these precise thermal transformations reliably and efficiently.
Whether you are processing minerals or developing advanced materials, our expertise in lab furnaces and consumables ensures you have the right tools for controlled decomposition and phase transitions.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss how KINTEK solutions can optimize your calcination workflow and enhance your material outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is a muffle furnace and how does it work? Achieve Clean, High-Temperature Heating for Your Lab
- What does a lab muffle furnace do? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Heating for Your Lab
- What is the point of a muffle? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processes
- How does a muffle work? Achieve Clean, Contamination-Free Heating for Your Lab
- How do you make biochar in a muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Controlled Pyrolysis



















