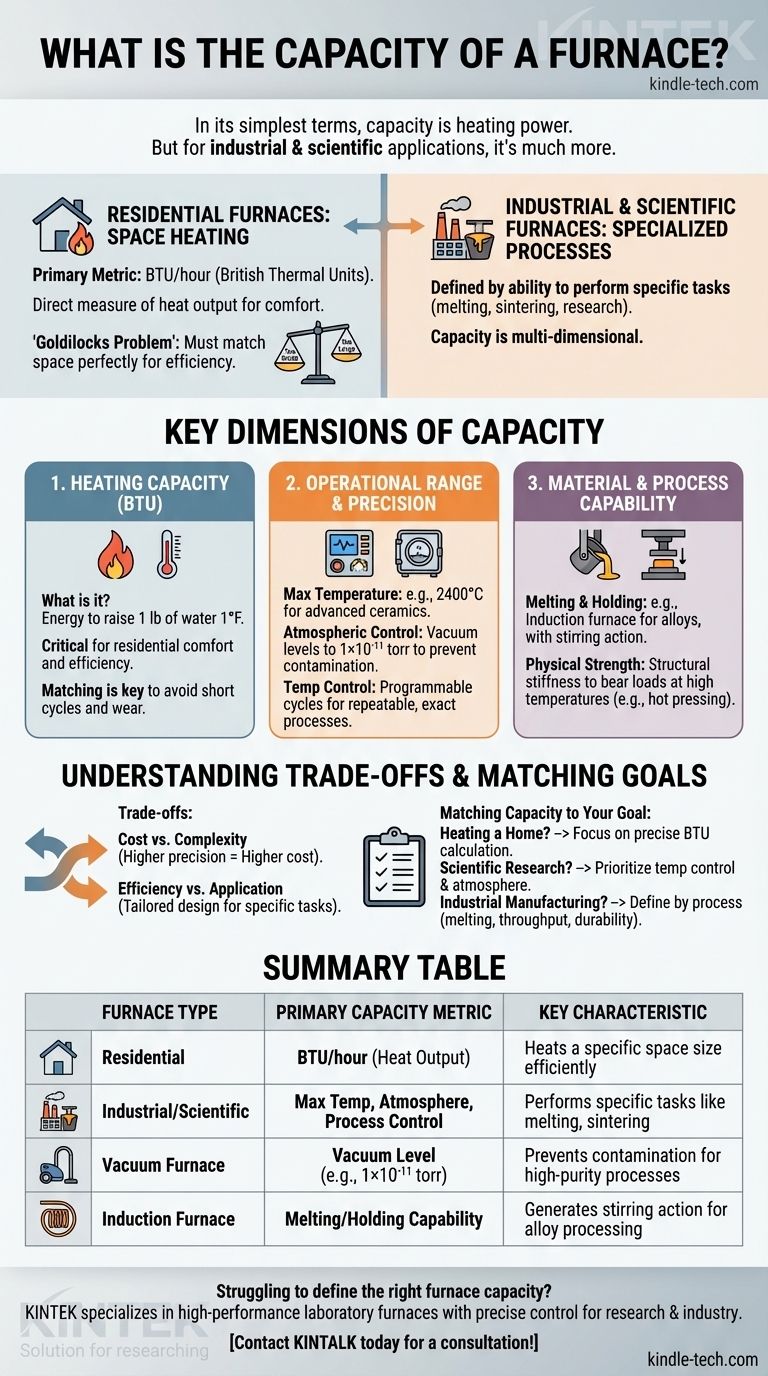
In its simplest terms, a furnace's capacity is its heating power. For residential heating, this is measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs) per hour, which quantifies the amount of heat the unit can produce to warm a given space.
The concept of "furnace capacity" extends far beyond a single measurement. While BTUs define the heating power for a home, industrial and scientific furnaces define their capacity by a range of factors including maximum temperature, atmospheric control, material throughput, and process precision.

The Two Worlds of Furnaces: Residential vs. Industrial
The term "furnace" applies to vastly different equipment, and understanding its capacity begins with identifying its application. There are two primary categories.
Residential Furnaces
These units are designed for one purpose: space heating. Their capacity is a direct measure of heat output, ensuring comfort within a home. The primary metric is BTUs.
Industrial and Scientific Furnaces
These are highly specialized tools used for manufacturing, metallurgy, and research. Their capacity is defined by their ability to perform specific processes like melting metal, sintering ceramics, or creating materials in a vacuum.
Dimension 1: Heating Capacity (BTU)
For most people, furnace capacity is synonymous with British Thermal Units. This is the correct metric for heating a building.
What is a BTU?
A British Thermal Unit (BTU) is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. A furnace's BTU rating indicates its heat output per hour.
Why Matching BTUs is Critical
Choosing the right BTU capacity is a "Goldilocks" problem. A furnace that is too small will run constantly without ever adequately heating the space. A furnace that is too large will heat the space too quickly, leading to inefficient short cycles, uneven temperatures, and unnecessary wear.
Dimension 2: Operational Range and Precision
In technical applications, capacity is less about raw heat and more about control and environment.
Maximum Temperature
Industrial furnace capacity is often defined by its peak operational temperature. A vacuum sintering furnace might be rated for 2400°C (4352°F), making it capable of processing advanced ceramics, while another furnace might be designed for lower-temperature metal alloys.
Atmospheric Control
Many advanced processes require a controlled atmosphere. A vacuum furnace's capacity is measured by the purity of its environment, with vacuum levels reaching as low as 1×10−11 torrs. This prevents contamination from oxygen and other gases.
Temperature Control and Programming
The ability to precisely control the heating process is a key capacity metric. Scientific furnaces feature multi-stage programmable controllers that can execute complex heating, soaking, and cooling cycles automatically, ensuring the process is repeatable and exact.
Dimension 3: Material and Process Capability
The ultimate measure of an industrial furnace's capacity is what it can do to a material.
Melting and Holding
A channel induction furnace, for example, has the capacity to melt low-temperature alloys or act as a holding unit for high-temperature metals like cast iron. Its design generates a stirring action, which is a crucial part of its processing capability.
Physical Strength and Durability
Some furnaces must withstand immense physical force. A hot pressing furnace's capacity includes its structural stiffness—the ability to bear heavy loads at high temperatures without deforming. This is a measure of its mechanical, not just thermal, capability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
It is crucial to recognize that no single furnace excels in all areas. The design choices that optimize a furnace for one task make it unsuitable for another.
Cost vs. Complexity
A simple, high-BTU residential furnace is relatively inexpensive. A high-temperature vacuum furnace with precise PLC controls is a complex, costly piece of scientific equipment. Higher capacity in precision and control comes at a significant financial cost.
Efficiency vs. Application
The efficiency of a furnace is tied directly to its intended use. Using an industrial induction furnace to heat a room would be extraordinarily inefficient and impractical, just as a home furnace is incapable of melting steel. The "best" capacity is always the one that is correctly matched to the job.
Matching Furnace Capacity to Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace requires a clear understanding of your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is heating a home: Work with a professional to calculate the precise BTU requirement based on your home's size, insulation, and local climate.
- If your primary focus is scientific research or lab work: Prioritize furnaces with precise temperature controls, programmable cycles, and the specific atmospheric capabilities (e.g., vacuum) your experiments demand.
- If your primary focus is industrial manufacturing: Define capacity by the required process (melting, sintering, holding), material throughput, and the physical durability needed for your production environment.
Ultimately, defining "capacity" correctly is the first step in selecting a tool that is perfectly suited to the task at hand.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Capacity Metric | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Residential | BTU/hour (Heat Output) | Heats a specific space size efficiently |
| Industrial/Scientific | Max Temperature, Atmosphere, Process Control | Performs specific tasks like melting, sintering |
| Vacuum Furnace | Vacuum Level (e.g., 1×10⁻¹¹ torr) | Prevents contamination for high-purity processes |
| Induction Furnace | Melting/Holding Capability | Generates stirring action for alloy processing |
Struggling to define the right furnace capacity for your lab or production needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory furnaces, offering solutions with precise temperature control, programmable cycles, and advanced atmospheric capabilities (like vacuum) for research and industrial applications. Our expertise ensures you get a furnace perfectly matched to your process requirements, enhancing your efficiency and results.
Contact KINTALK today for a personalized consultation and discover the ideal furnace for your specific capacity needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature of a muffle furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Application
- What are the uses of muffle furnaces? Achieve Precise, Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is a muffle furnace used for? Achieve High-Temperature Processing with Purity
- What is the difference between oven incubator and muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lab Heating Tool
- What is the use of muffle furnace in chemistry? Achieve Contaminant-Free Heating for Accurate Analysis



















